Contents
Managing Reflection
The subject’s material can transmit, absorb or reflect the light that hits it.
Types of reflections:
- Diffuse reflections-the material reflects the light equally in all directions. Neither the angle nor the size of the light source changes the appearance of a diffuse reflection. The distance of the light to the subject will make the subject look brighter. An example of a material that creates diffuse reflection is paper.
- Direct reflections are a mirror image of the light that produces them. If a direct reflection is seen is determined by the angles between the light source, the subject, and the camera. Brightly polished metal or glass are both examples of materials that create direct reflection.
Metal
To manage reflections on metal, either light it and let it go dark or fill the surface with light so the whole thing is reflecting the light.

Rany Selem 
Jonathan Baez
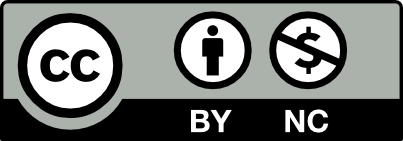
Glass
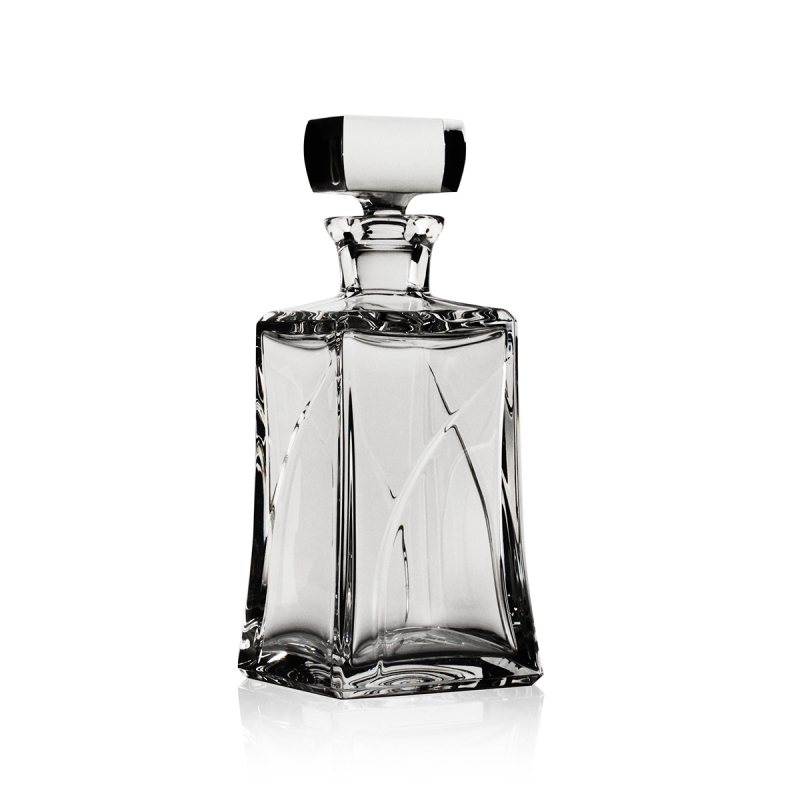

Glass produces direct reflection but it is also transparent. One needs to bring out the edges to see the shape of the glass. So there are two problems when photographing glass:
Controlling the direct reflection
Bringing out the edges by reflecting onto them so they are visible.
Labs
Homework
Next week
Class is online. Everyone is welcome to come in to the classroom as I will be there.



Leave a Reply