Review Global Corrections
Global corrections adjust the entire file. In the Lightroom, it includes the controls under Light, Color and Effects. In Lightroom Classic, this includes everything in the basic panel: White balance, Exposure, Tone and Presence.
Local Corrections
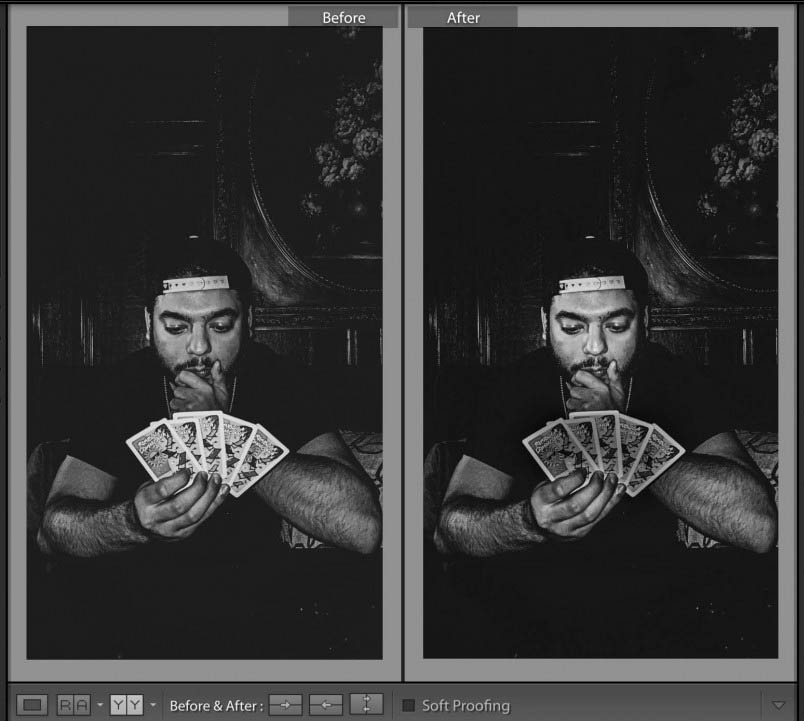
After you make global corrections, sometimes you will want to make corrections to part of your image. Generally, the brightest part of the image commands the most attention. Sometimes that is not where you want your viewer to look first so shifting the exposure of parts of your image can create the image you want.
The important thing in this photo by Bryan Rodriguez is the face of the card player. However the cards are brighter and demanded too much attention. Using the adjustment brush, I darkened the cards. Creating a second adjustment, I lightened the face of the card player a little more. The goal was to bring more attention to the person’s face and less to the overly bright cards.
The main tools for local adjustments are the adjustment brush, the radial filter and the graduated filter.
Lab exercises
Homework
This is the rubric.
Deliverables, due next week, Dec. 14th:
- Final project statement and mood board
2. 3 albums each of a minimum of 30 photos
3. 1 album of the 10 best photos of the 90 total, adjusted in Lightroom
4. a 3-5 min presentation of the final project – projected from the album on Flickr.
Presentation Guidelines
- Start by introducing yourself and your project. Give us the big picture in a few short sentences such as, ” I photographed variations on the theme of windows. most of the photos were taken in downtown Brooklyn.
- If you are showing 10 images, you have about 30 seconds to describe each photo. Tell us what your intention was, what interested you about the photo we are looking at, and give us information we may need to know to understand the photo. Tell us what makes it visually interesting ie the use of shallow depth of field or some other feature.
- Practice your presentation.
- Try making a simple notecard for each image that lists the one or two points you want to make about that image.
- Do not tell us about what you did to the photo in Lightroom or what would have made the photo better..



































Recent Comments