Contents
Prelab Questions
- What are fruits?
- Where do they come from?
- What are they made of?
- Use phylogeny to classify plants (DKPCOFGS)
- Where is DNA located within the fruits? Where is it located in you?
- Why would you want to extract DNA from an organism?
- What class of molecule is DNA?
Extraction of DNA from fruit
single panel instructions can be found at https://github.com/jeremyseto/bio-oer/blob/master/figures/chemistry/DNA/fruitdnaisolation.svg
- Mash about 10g or 3cm of over-ripe banana OR 3 grapes OR 1 strawberry in zip-top bag

- over-ripe banana is best since the cell walls are already decomposing
- physical mashing continues to break up the cell walls
- Add 7ml of salt solution

- The salt solution helps the DNA to aggregate (clump together).
- Add 7 ml of liquid detergent and mix

- dissolves the lipids in the cell and nuclear membranes
- releases DNA into the salt solution
- Place a coffee filter over a cup or beaker and fasten with an elastic band
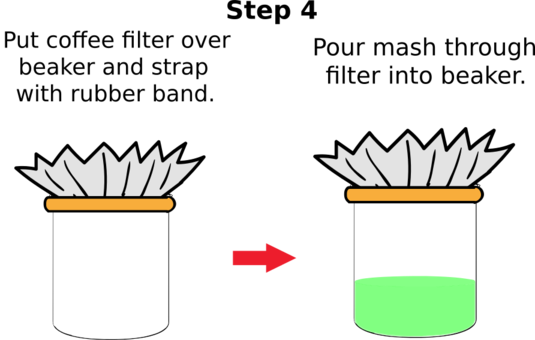
- Pour mash through filter into a beaker
- Pour about 5 ml of filtrate into a test tube

- Slowly pour an EQUAL volume of cold ethanol down the side of tube to form a layer on top of the fruit fluid.
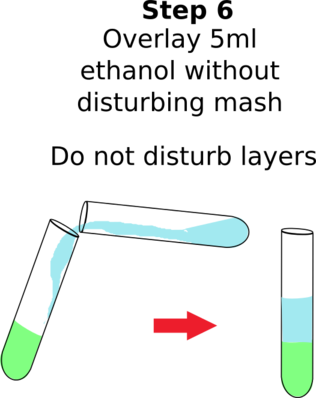
- carefully run the alcohol down the side to form a separate layer on top of the fruit solution
- Do not mix the alcohol and banana solution.
- Ice-cold 100% ethanol works best
- Spool the DNA: use a plastic loop or glass rod to gently swirl at the interface of the two solutions

- the interface is where the two solutions meet
- DNA is not soluble in alcohol
- bubbles may form around a wooly substance (this is the DNA)
- Transfer the DNA

Dische Diphenylamine Test For DNA
DNA can be identified chemically with the Dische diphenylamine test. Acidic conditions convert deoxyribose to a molecule that binds with diphenylamine to form a blue complex. The intensity of the blue color is proportional to the concentration of DNA. The Dische’s Test will detect the deoxyribose of DNA and will not interact with the ribose in RNA. The amount of blue corresponds to the amount of DNA in solution.

- Obtain 3 test tubes and number them 1-3.
- Suspend the spooled DNA in 3 ml of distilled water. MIX.
- Add to tubes:
- 2 ml of DNA solution
- 1 ml of DNA solution with 1 ml H2O
- 2 ml of H2O
- Add 2 ml of the Dische’s diphenylamine reagent to each tube and mix thoroughly.
- Place in a boiling water bath for 10 minutes.
- Evaluate your results. A clear tube indicates no nucleic acids. A blue color indicates the presence of DNA. A greenish color indicates the presence of RNA.


