4 pts. Due April 26.
Shoot a total of 30 environmental portraits of three different subjects- 10 each.
Environmental Portrait-a portrait executed in the subject’s usual environment, such as in their home or workplace, and so that the surroundings illuminate something about the subject’s life.
When shooting indoors, remember keep the shutter speed faster than 1/60. Better the raise the ISO. It may be too dark. If so change the location!
When shooting outdoor, shoot in diffused light: either shade or cloudy weather.
Make sure that there is light on your subject’s face.
Environmental portrait examples: https://www.popphoto.com/how-to/2013/10/tips-pro-brian-harkin-environmental-portrait-photography
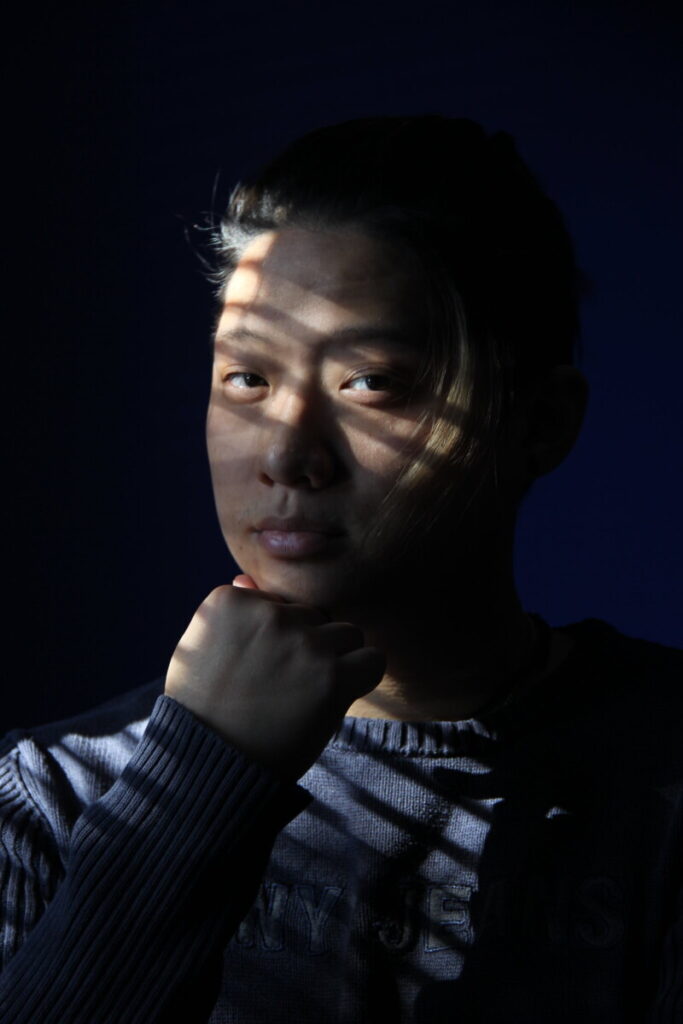
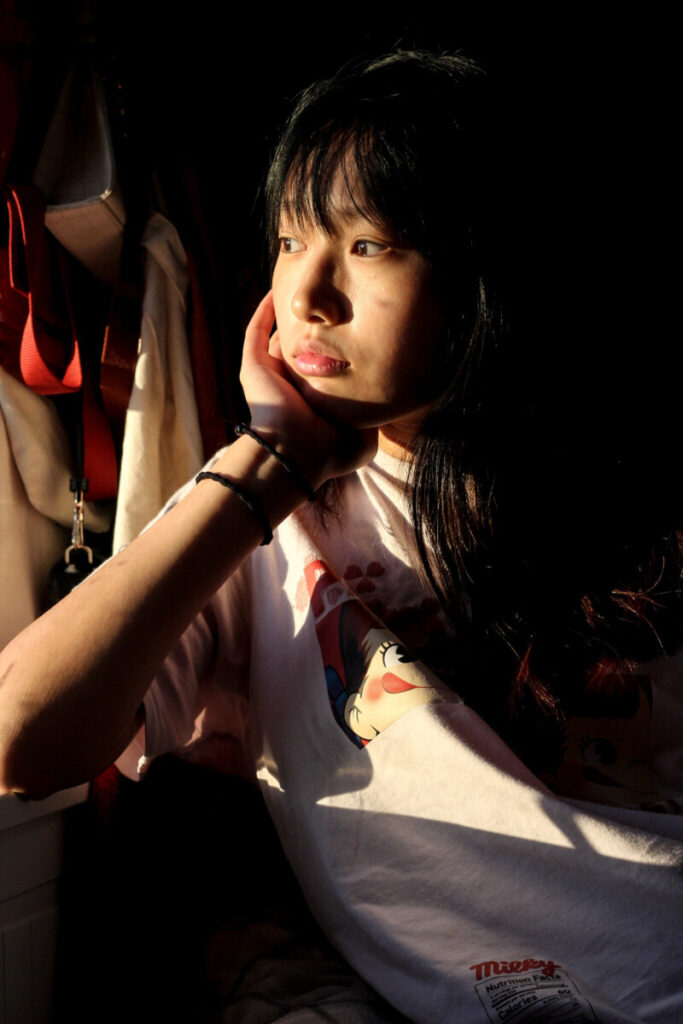
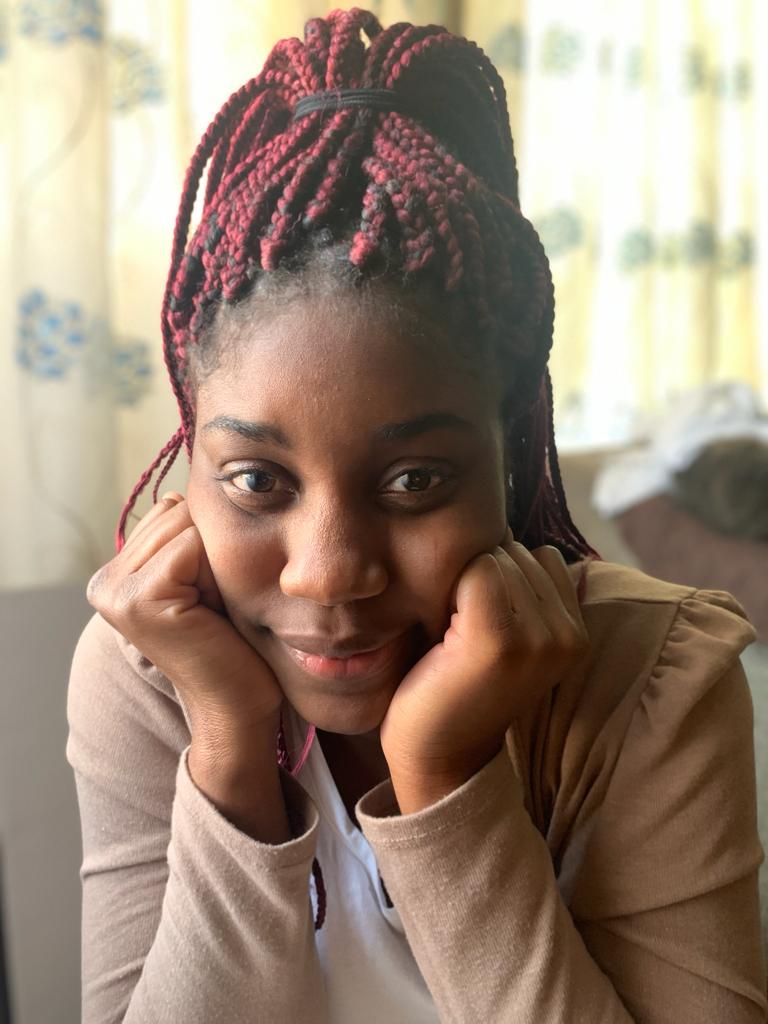
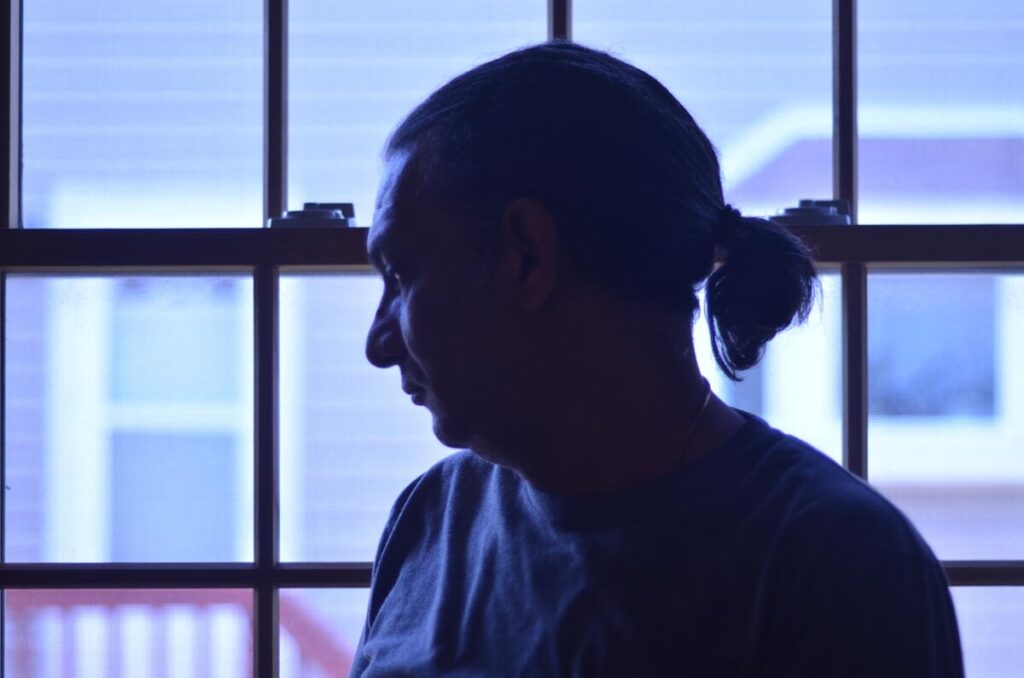
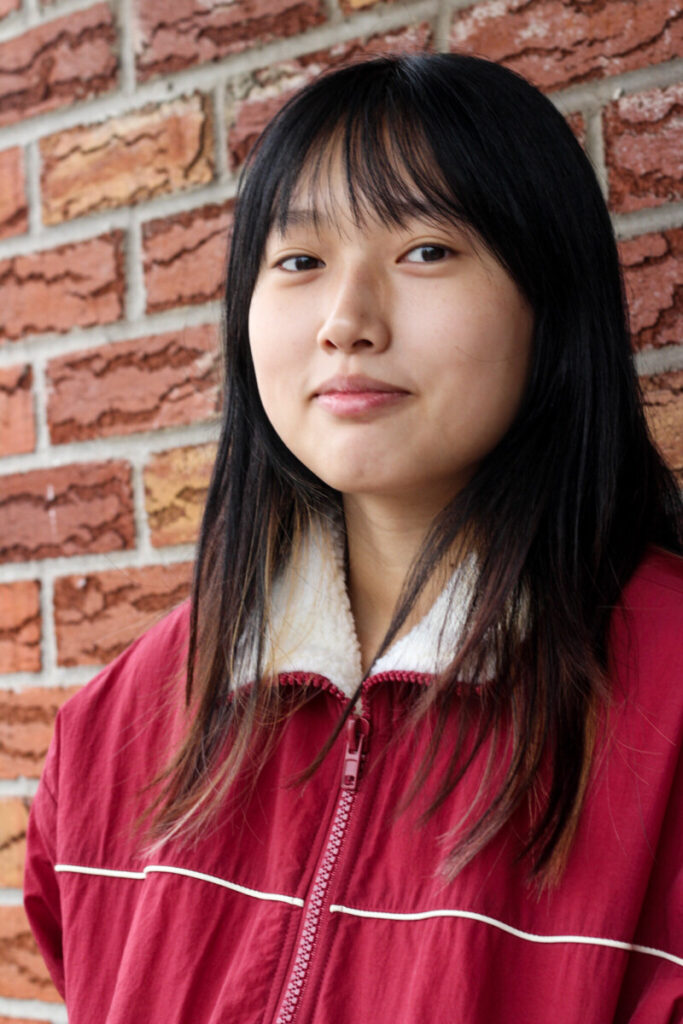
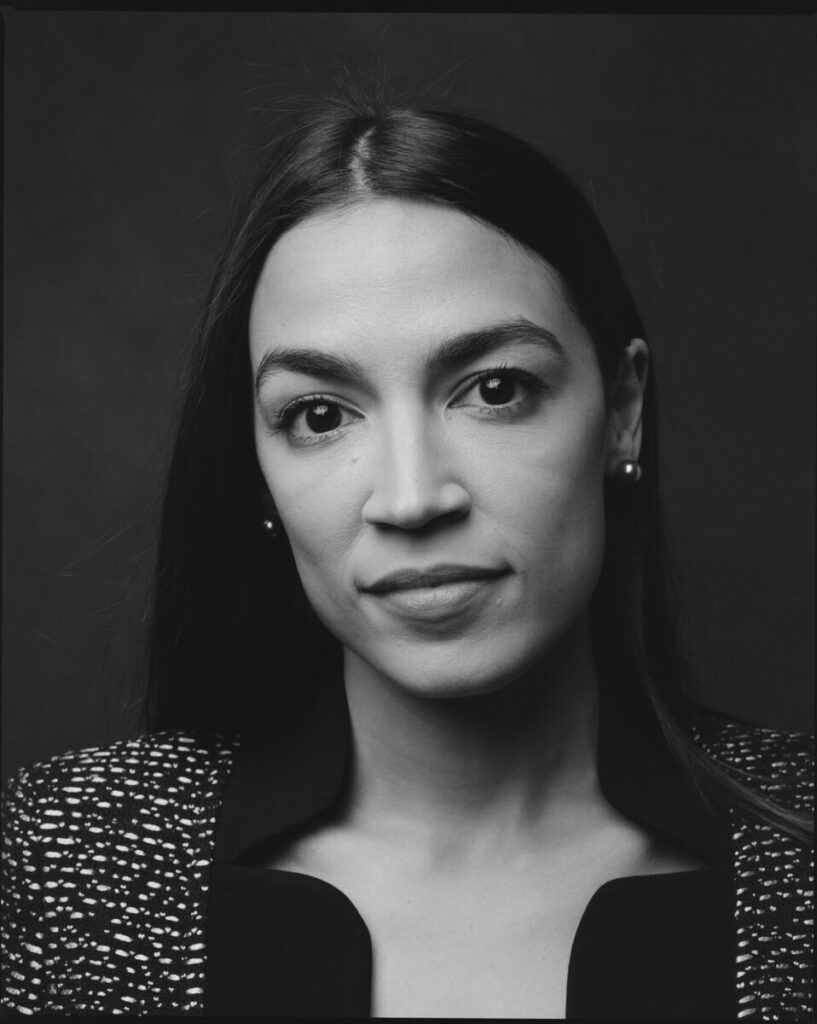
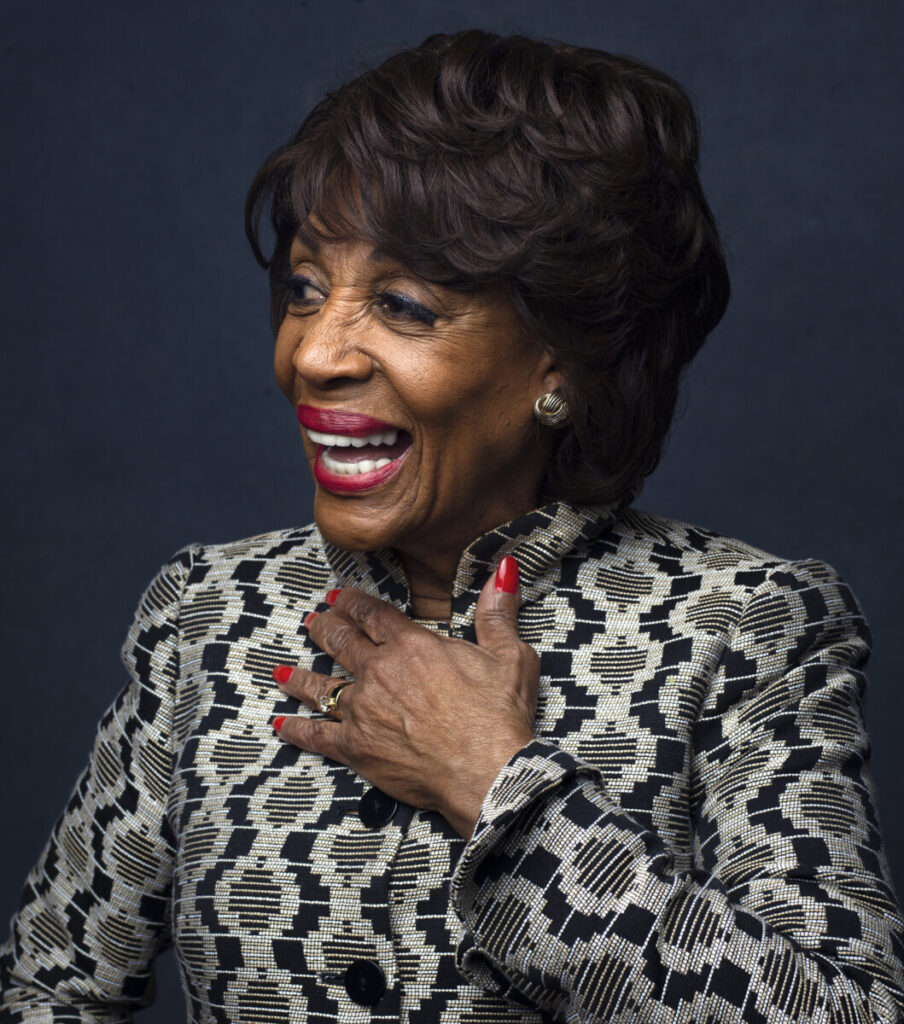
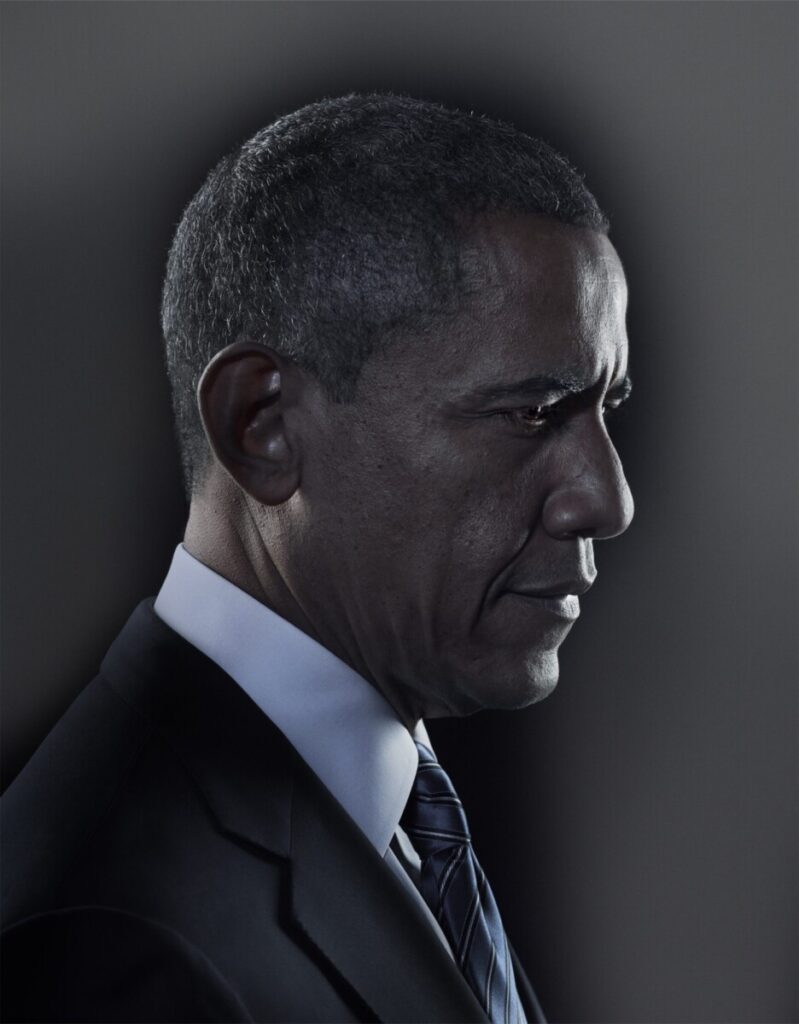
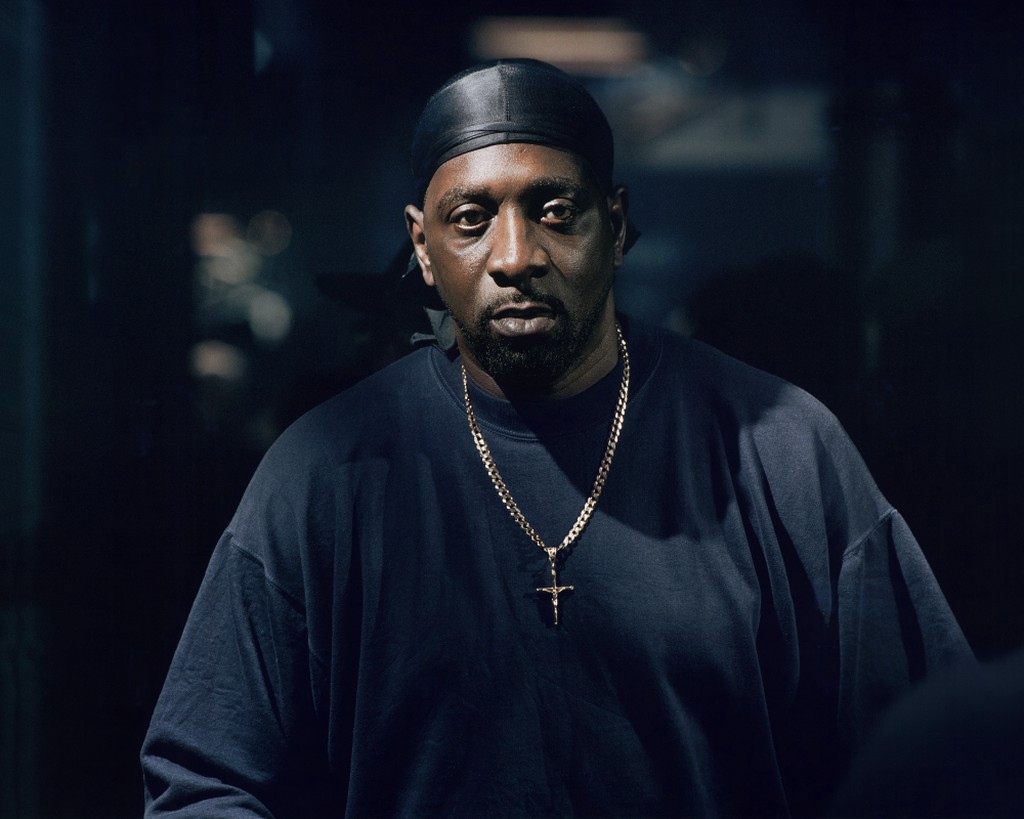
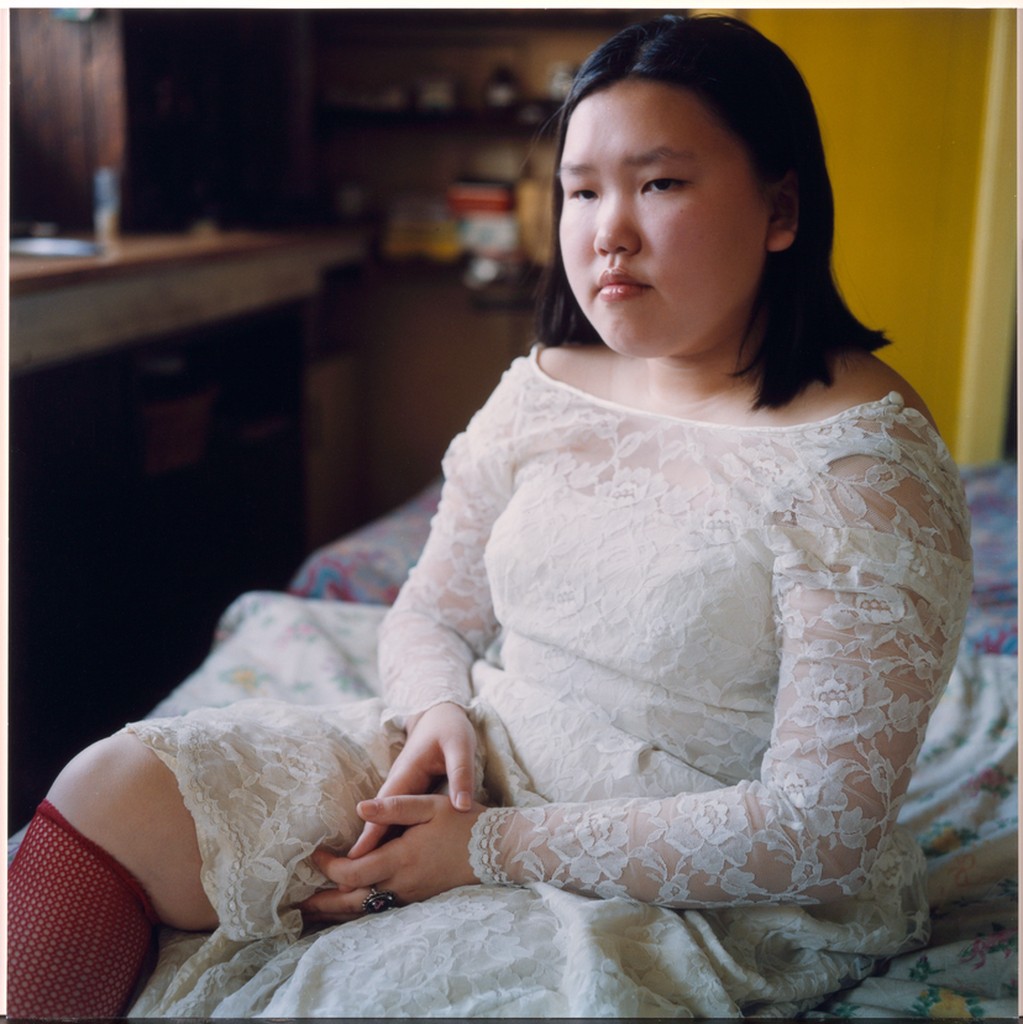
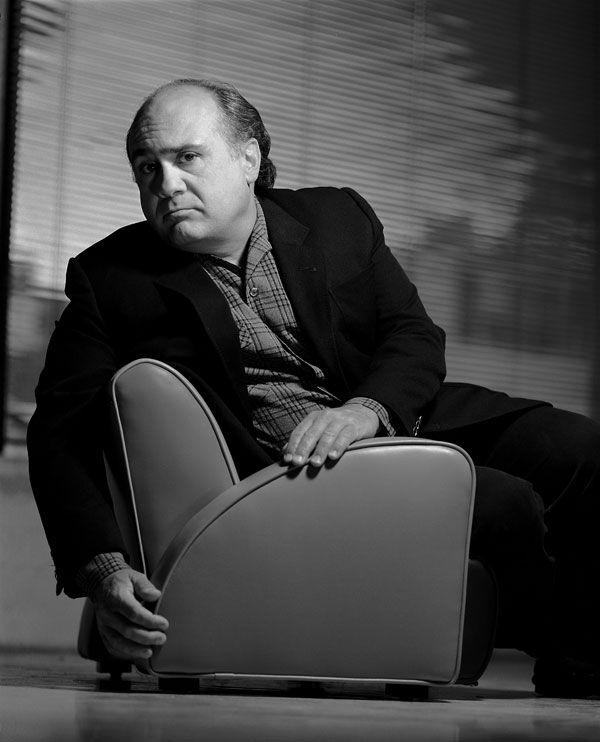
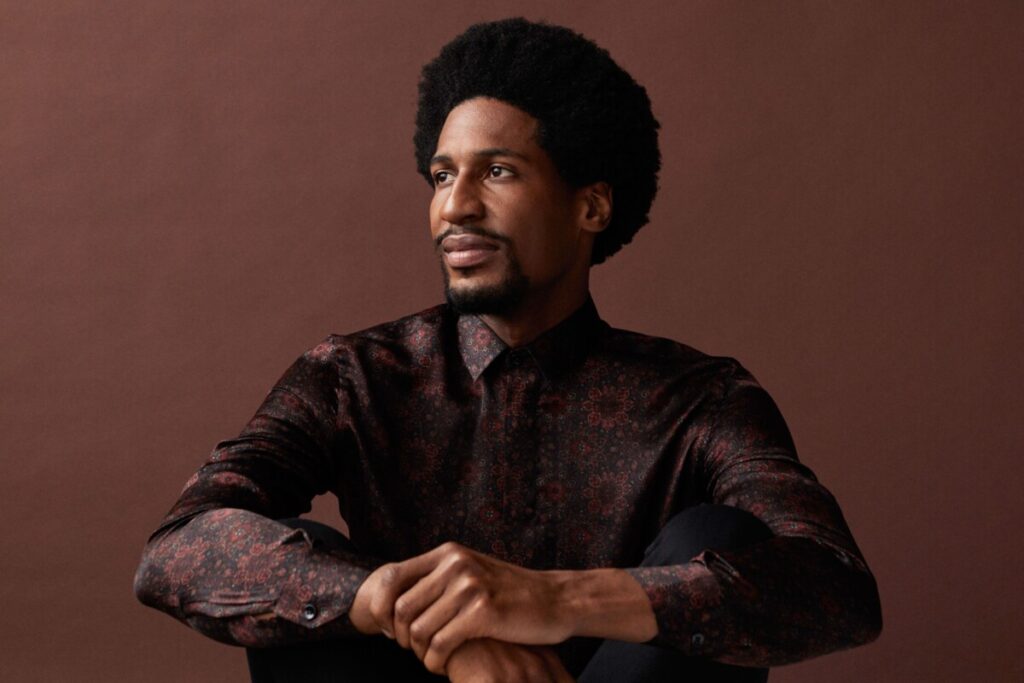
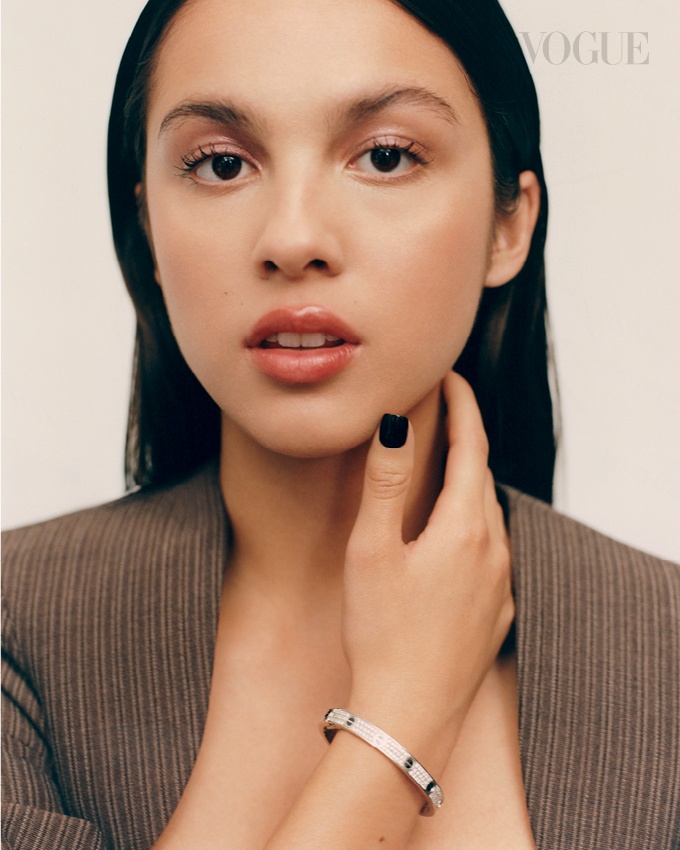
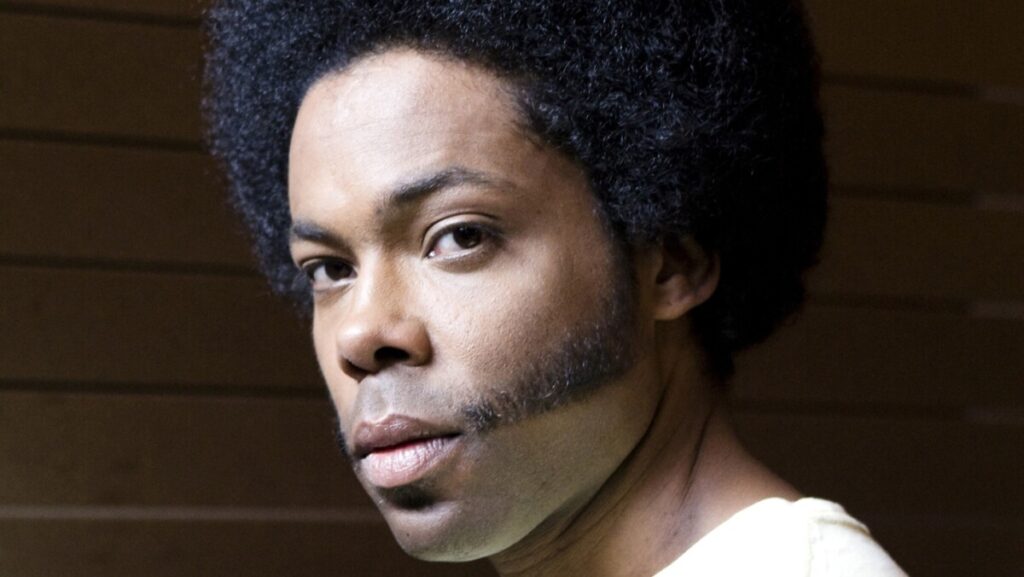
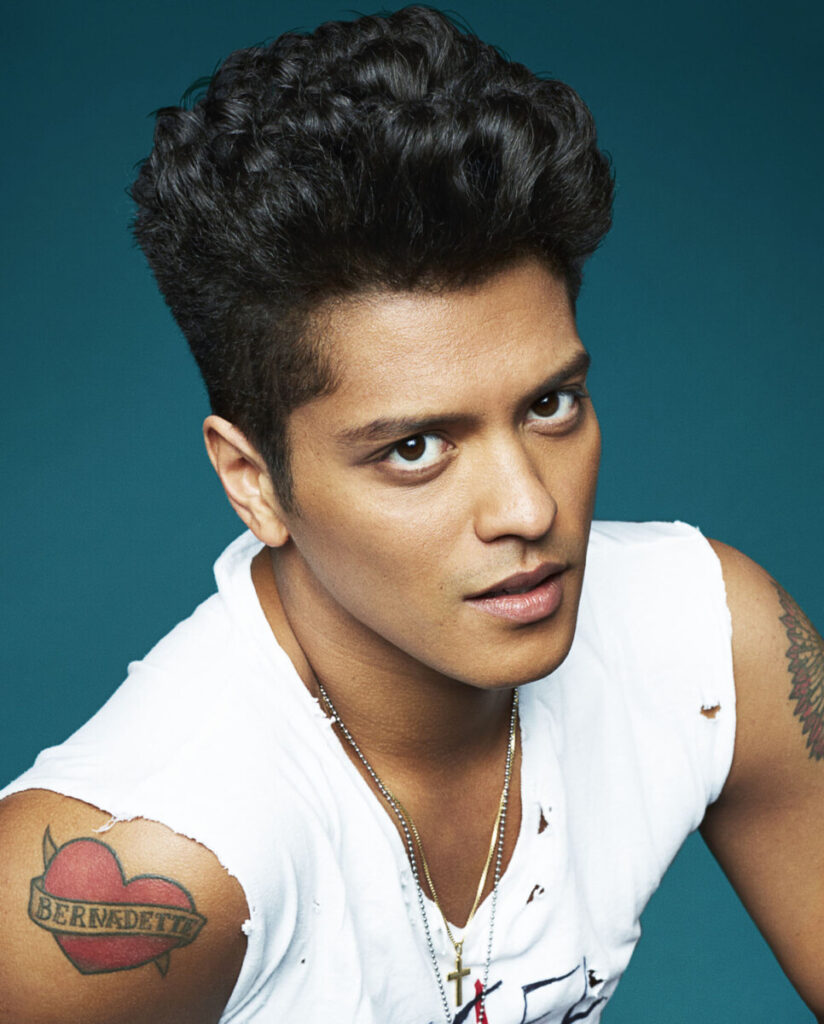







































Recent Comments