Tasks from last week
- Review Signs and Meaning in Communication Design
- Complete Reading Response 7
- Complete Midterm Assessment Post
- Submit Week 8 Agenda Checklist
This Week’s Topics
- Check-in
- Models of Communication
- The Medium is the Message
- Reading Response 8
- Week 9 Agenda Checklist
Check-In & Share
Do you have anything to share from your Research Journal? Add a comment to this post with something you’ve added to your Research Journal recently.
Or suggest a track for the playlist on the COMD3504 playlist post.
Midterm Assessment Post
If you haven’t posted your Midterm Assessment, please do it before the end of class.
Activities
Below find the information covered in this session. Complete all of the following activities, videos, and assignments.
1. Research Project Outline Presentations (30 min)
Please present your Research Project Outline post to the class. Give a brief “elevator pitch,” explaining your research question.
2. Models of Communication (20 min)
Last class, we looked at semiotics theory or the theory of signs and meaning in communication. We started with French philosopher Ferdinand de Saussure, who identified a sign as composed of a signifier and a signified. The signifier is that part of the communication process that carries the message (sound, image, text), and the signified is the concept delivered to the receiver. We will expand on this in the reading this week.
Careful analysis of the message cycle can help us to understand when our communication works and when it doesn’t – and why. If we are aware of these concepts and the communication models, we can be more effective communication designers!
- Messages take different paths between the sender and receiver and back again via different mediums.
- Noise is the distortion in the meaning of a message, whether intended or not. It affects whether or not the message has successfully reached its destination.
- Truth in communication. Where a message says it is from may be very different from where it is really from. It can sometimes be hard to determine the intention of the sender, and that can affect how we understand the message.
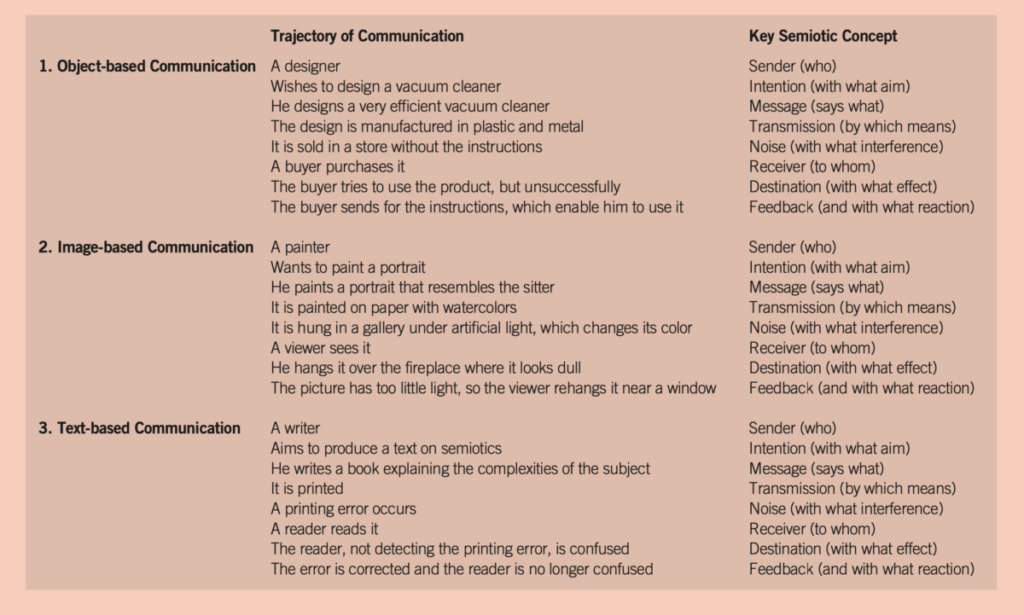
Check out the following videos to reinforce the following concepts: sender, intention, transmission, noise, receiver, destination, feedback.
Let’s overlay these concepts of Communication Models on mass media communication in the mid/late 20th Century and contemporary digital communications, specifically social media.
3. The Medium is the Message (1+ hours)
This week we will examine Marshall McLuhan’s theories about media as television became the dominant medium. His theories were radical at the time and have been influential in the study and practice of design and media theory. They are relevant now with the persuasive advertising model used by social media.
Marshall McLuhan was a Canadian professor and philosopher. He is known for coining the phrase, “The medium is the message.” This statement first appeared in his book “Understanding Media: The Extensions of Man – The Medium is the Message, published in 1964.
And in his more experimental text, “The Medium is the Massage: An Inventory of Effect, “co-created by McLuhan and Quentin Fiore in 1967. Note that the cover design was created by David Carlson aka the ‘Godfather of grunge’. Grunge was inspired by underground rock culture, and was all about breaking the rules of traditional graphic design (more on that after Spring Break).
McLuhan died before the birth of the internet, but many believe that his theories about electronic media were prophetic, that he envisioned the internet decades before its arrival. He spoke about communication technologies as having the ability to create a “global village” and the increasing loss of privacy as a result.
McLuhan argued that we should focus on the medium of communication itself and he defined media as a technological extension of the body. He used the term “media” in a very broad sense, including the spoken word, the written word, the printed word, telephone, films, radio, television, etc.
There are many excellent interpretations and critiques of McLuhan’s ideas. Let’s watch a few videos to help us to understand his ideas in the context of today’s contemporary media.
Marshall McLuhan – A film by Daniel Savage
The media has the power to transform human nature and furthermore, no matter how powerful or persuasive the message, it’s the media that has changed our thought patterns and behavior. What does this mean for the “electronic environment” we inhabit? How do we decipher what media is fact and which is fiction? Discerning the difference is crucial now, more than ever.
Daniel Savage: The Medium of the Message – ADC LAUREN FESTA
What does “The Medium is the Message” really mean?
“The idea is that the mediums have a far greater impact on the fundamental shape and nature of society than any message that is delivered through that medium. What has had a greater impact on society and the way that we interact with one another, all the content of every Youtube video ever made or the existence of Youtube itself? All the conversations that you’ve ever had, the existence of your cell phone?… How do the mediums that you use help shape the world?”
The Medium is the Message explained by Dan Olson
This Is Marshall McLuhan – The Medium Is The Massage (1967)
“The electric age is changing you, it’s changing your family, it’s changing your neighborhood, it’s changing your education, your job, it’s changing your government, it’s changing your relationship to others. These little circuits are making our world go. The electric age is having a profound effect on us. We are in a period of fantastic change that’s coming about at fantastic speed. Your life is changing dramatically, and you are numb to it.”
This Is Marshall McLuhan – The Medium Is The Massage (1967)
Created in 1967, this strange documentary predicts a world that is eerily familiar. Watch from 13:19-20:00 (or longer if you have time.)
Social Media is the Message
McLuhan believed that media (in the broadest sense) is an extension of humanity, of the human body, and mind. How does media affect us? Our bodies? Our relationships? Our understanding of the world? Are we being changed right now?
If the camera is an extension of the eyes, what is the internet an extension of?
Tristan Harris, the founder of the Center for Humane Technology, believes social media as it exists now “is a simultaneous utopia and dystopia.” The utopia the user experiences is the dopamine hits and efficiency of on-demand everything, and the dystopia of the giant manipulative matrix that we are living in. How do we recognize the Matrix if we don’t know that we’re in the Matrix?
The Social Dilemma – Persuasive Media
In the documentary, The Social Dilemma, early leaders in social media, like Tristan Harris, have revealed that the medium of the internet, specifically social media, is becoming an existential threat to human society.
While he didn’t foresee the negative effect on society, consider Marshall McLuhan’s prophetic theories about electronic media in the late 1960’s, specifically how technology is an extension of humanity. Think about the current design of social media and the consequences of our growing dependence on it.
Clips from The Social Dilemma
Tristan Harris – A New Agenda For Tech Presentation (54 mins)
What will become of society if the persuasive technology used for for-profit social media advertising is allowed to continue as it is now?
2. Assignment: Reading Response 8 (2+ Hours)
Follow the assignment guidelines and prompts for Reading Response 8 – Wednesday before next class.
In our reading this week, we will look at an excerpt from Roland Barthes’ 1977 essay, “Rhetoric of the Image.” close-reading of an image, a French Panzani advertisement.
Let’s review the Reading Response Guidelines, read part of the essay together, and then take a look at this breakdown of “Rhetoric of the Image” by Lesley Lanir where she covers some of the following terms.
- Encoding: creating a message for transmission (i.e., creation and distribution of an advertisement)
- Decoding: the process of interpreting a message (i.e., watching and interpreting an advertisement)
- Denotation: Literal meaning (a message without code)
- Connotation: symbolic or cultural meaning (a coded message)
- Linguistic message: words used to convey meaning
- Non-coded iconic message: an image with literal meaning
- Coded iconic message: an image with a coded message
Refer to Assignment: Reading Response 8 for prompts.
Resources
- Assignment: Reading Response 8
- Using Hypothesis
- Research Journal
- Grammarly
- Reading Response (Example) post
Week 9 Agenda Checklist
Below are all of the tasks, big and small, for this week. he due date is Wednesday, 11:59 pm before our next Thursday class. Timely completion of these tasks will contribute to your success in this course.
If you have any questions, don’t hesitate to reach out.



Leave a Reply