Light Quality
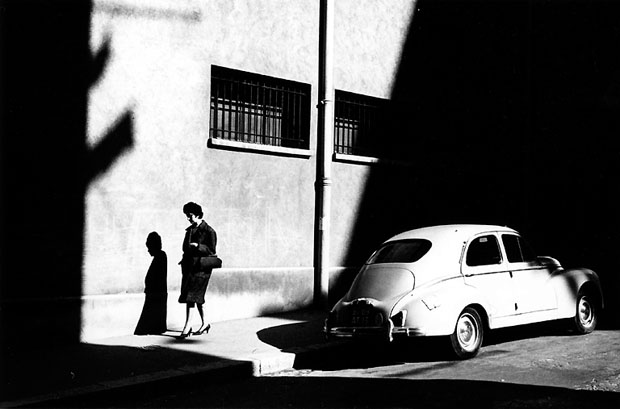
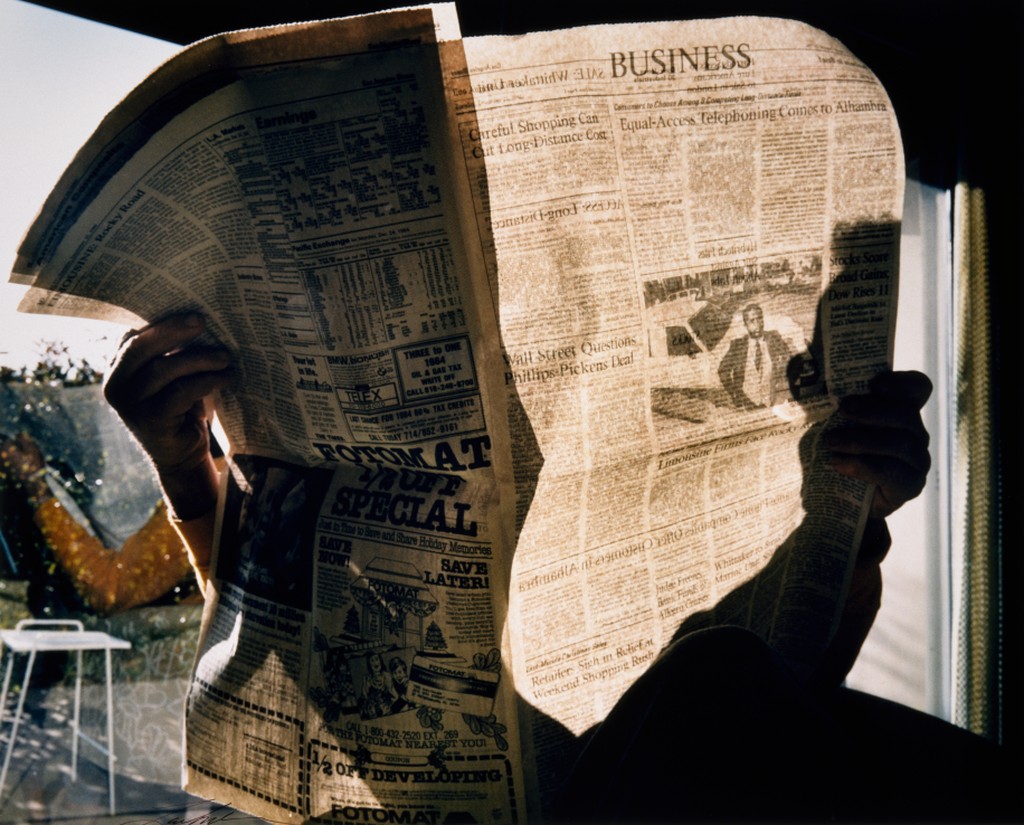
Direct light or hard light – the rays of light are nearly parallel and strike the subject from one direction creating hard edged dark shadows with little detail.
Examples: a spotlight, sun on a clear day, or a bare flash
Diffused light or soft light– the rays of light are scattered and coming from many directions. It appears even and produces indistinct shadows. Examples: overcast daylight, a light covered with tracing paper or other translucent material.
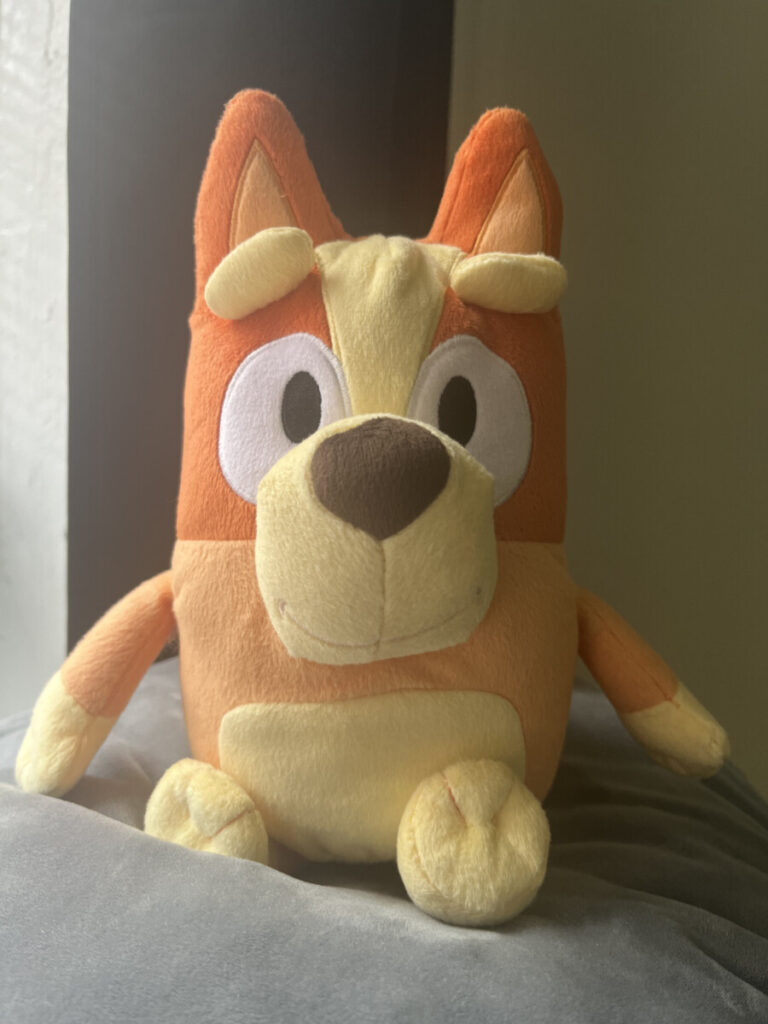
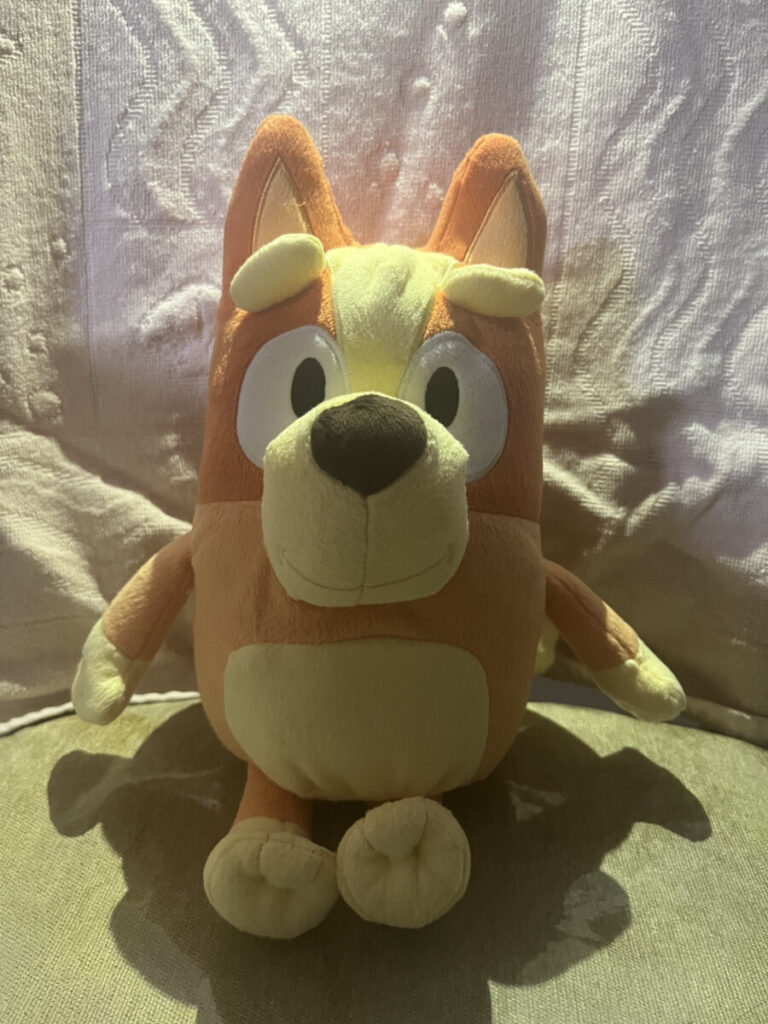


Direct Light and Direction
Front light comes from in front of subject from the camera position and the shadows fall behind the subject not concealing any details.
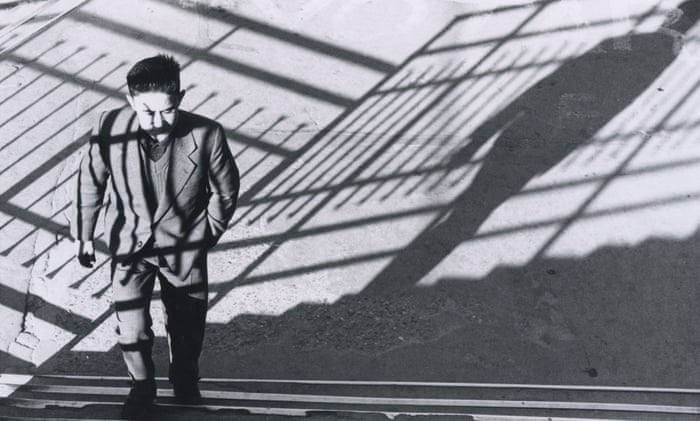
Side Light comes from 90 degrees to the camera. it adds dimension and texture to the subject.
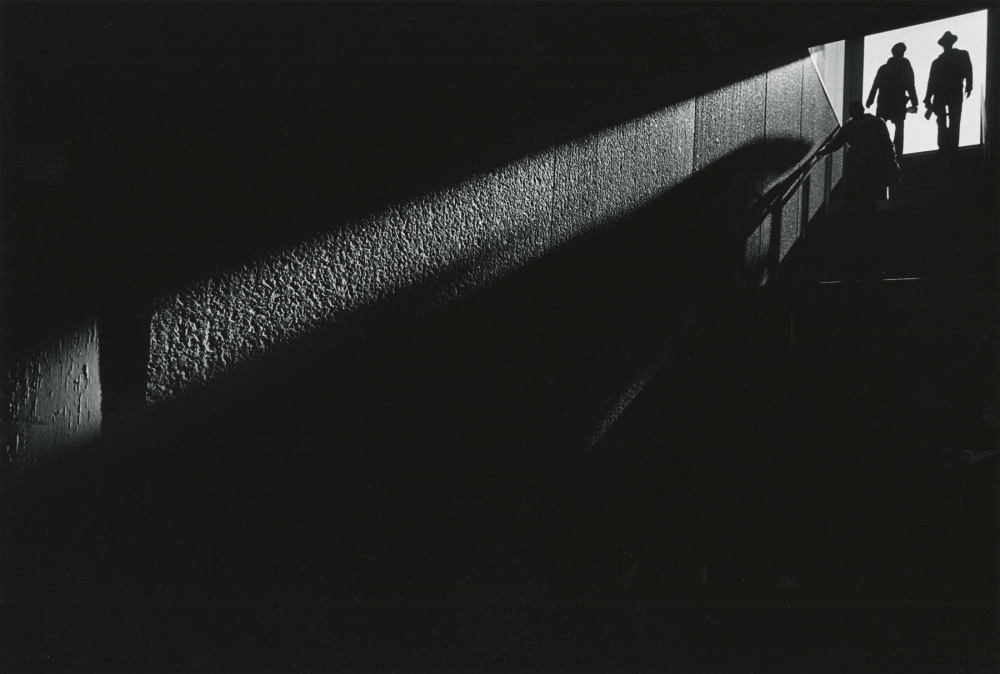
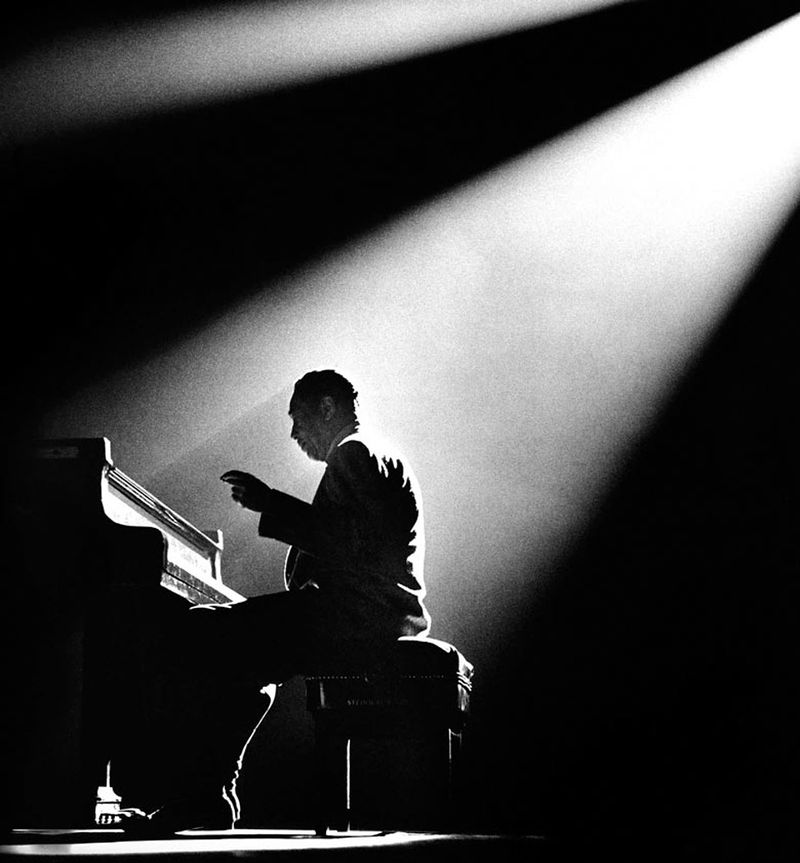
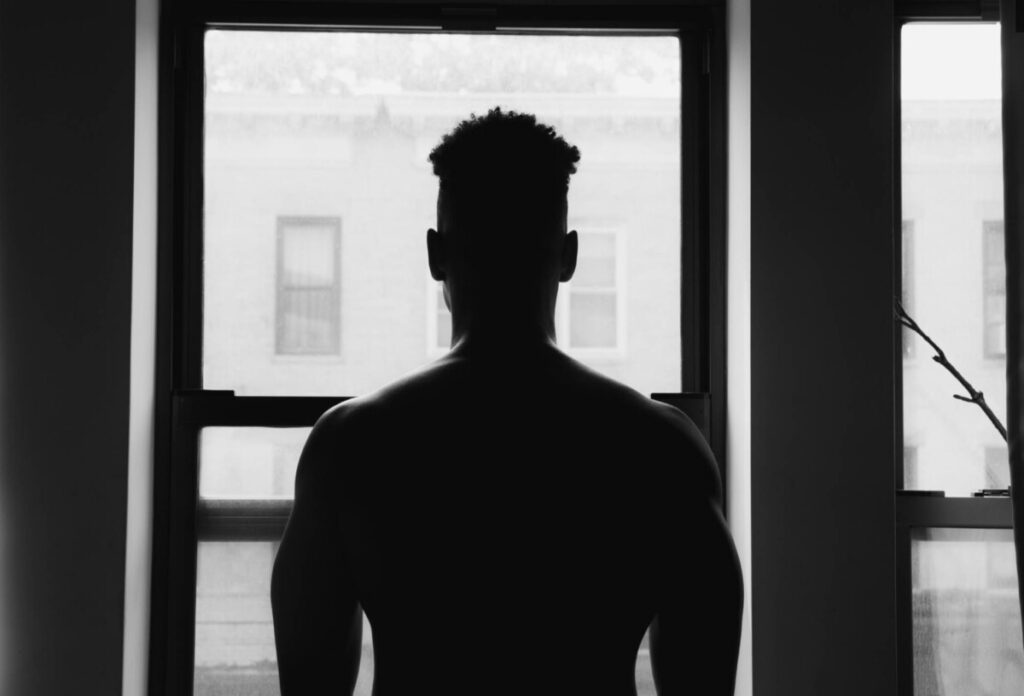
Backlight comes from behind the subject towards the camera.


Inspiration
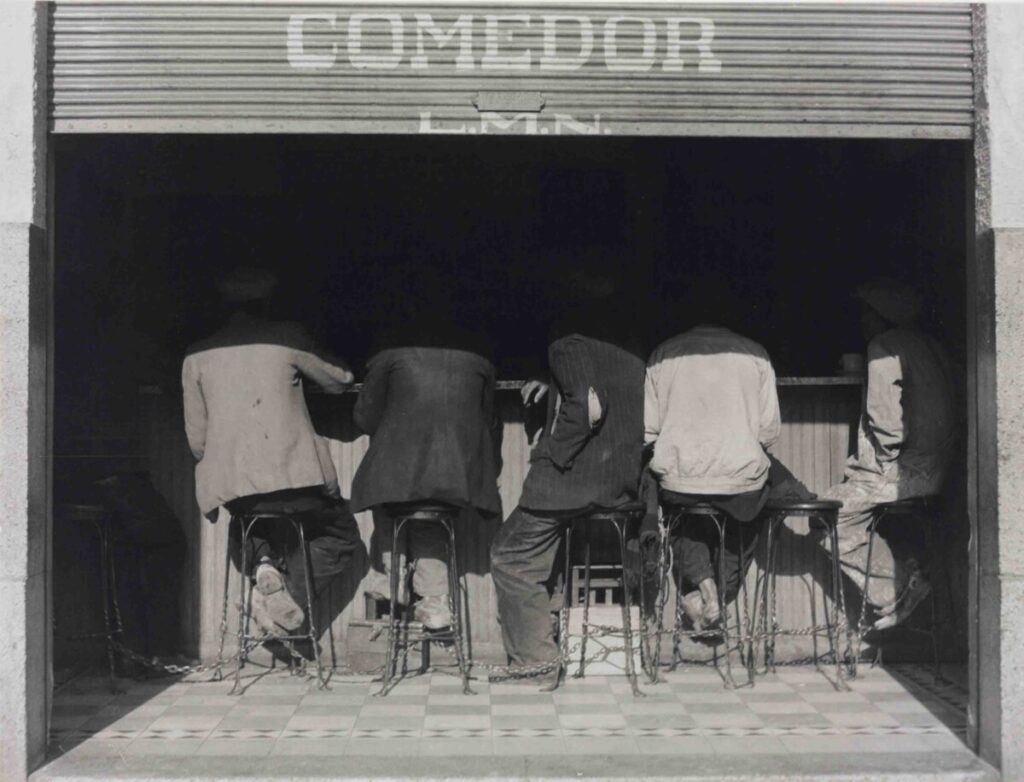

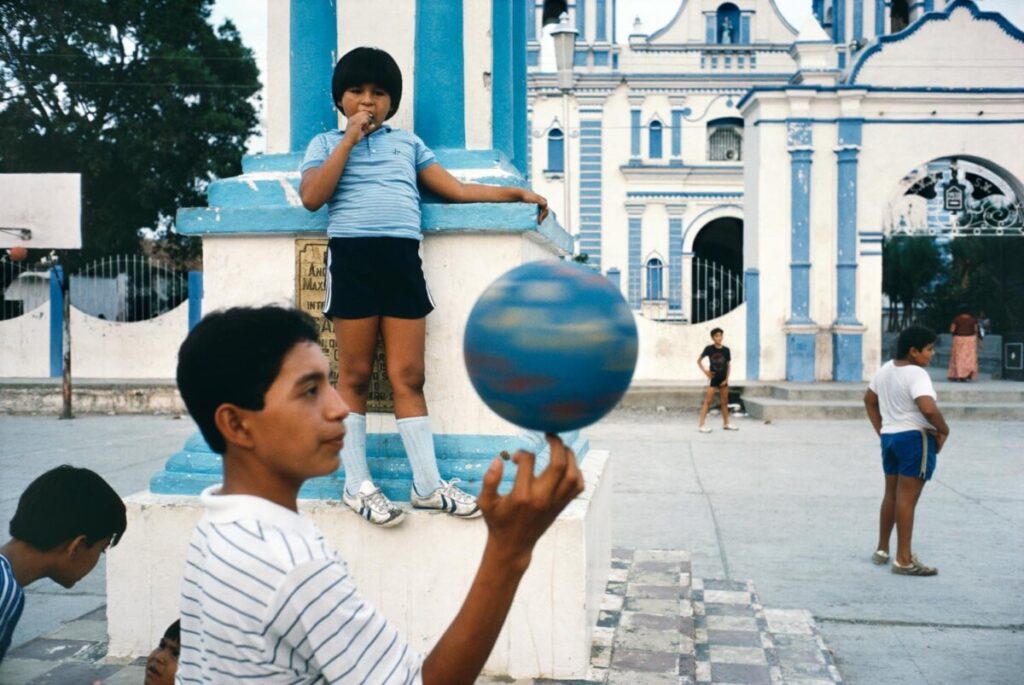
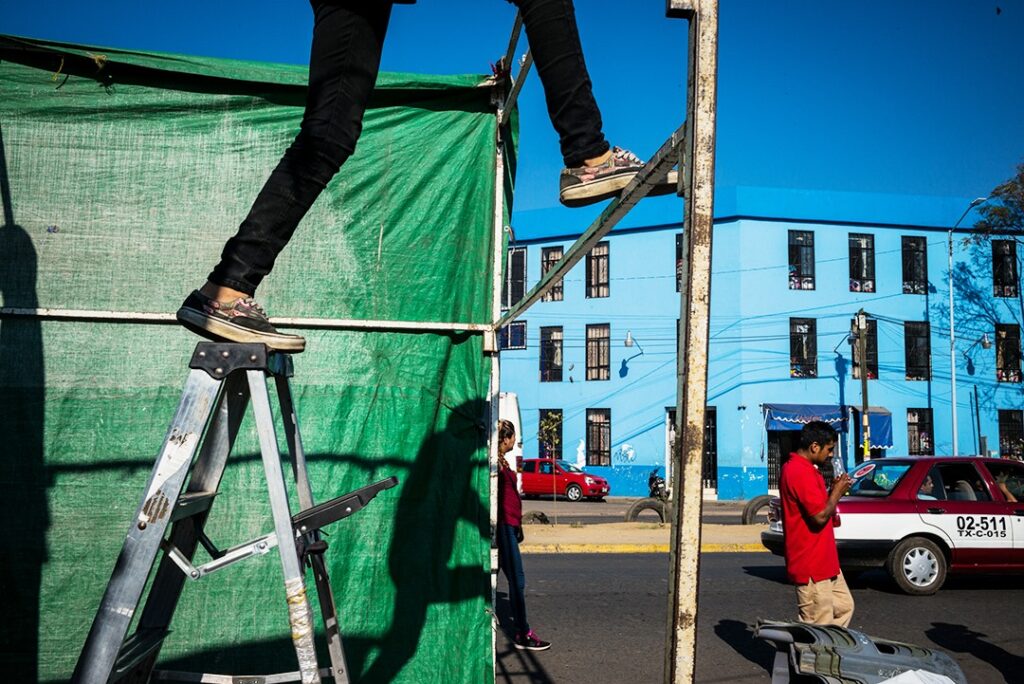
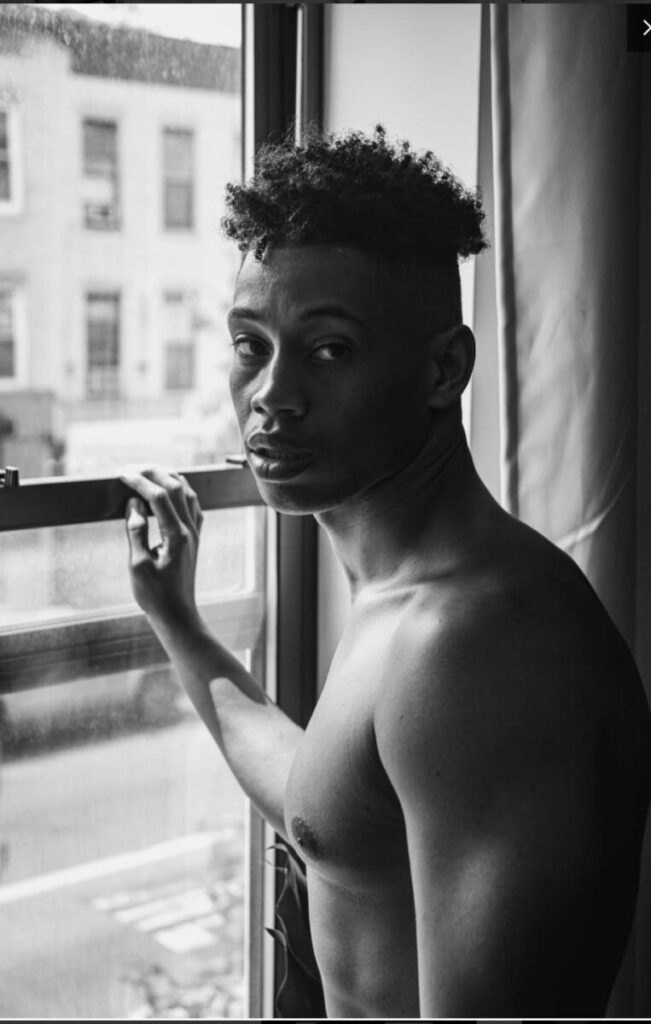
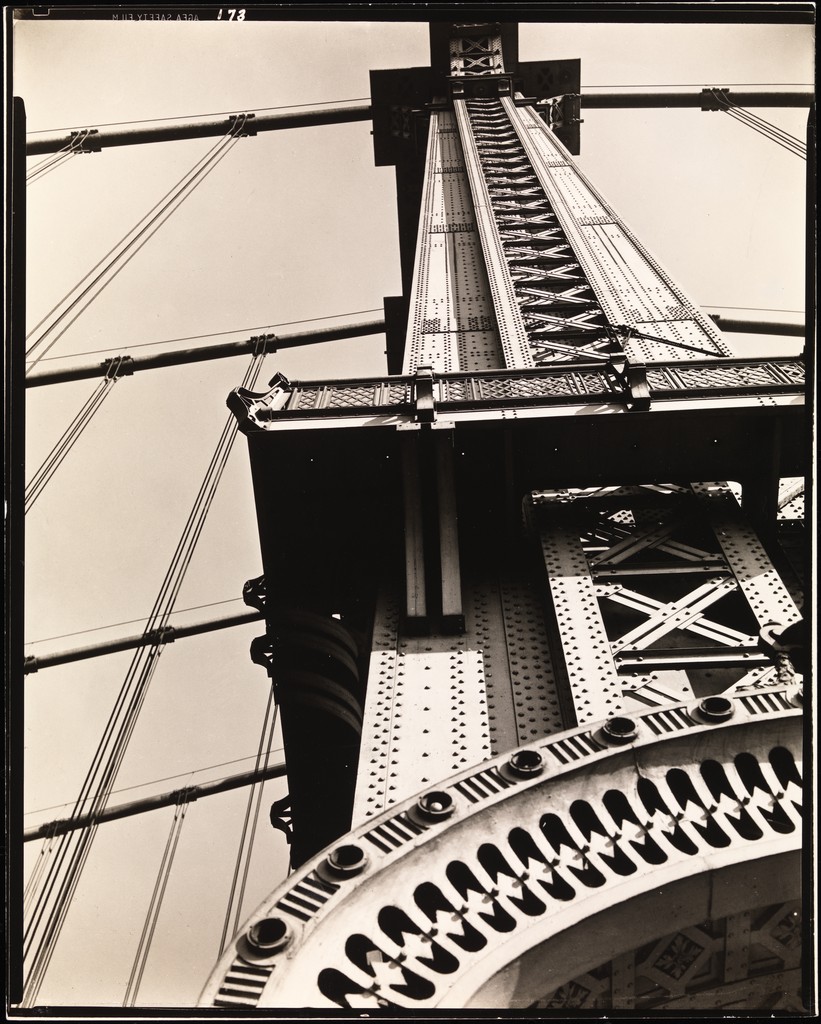
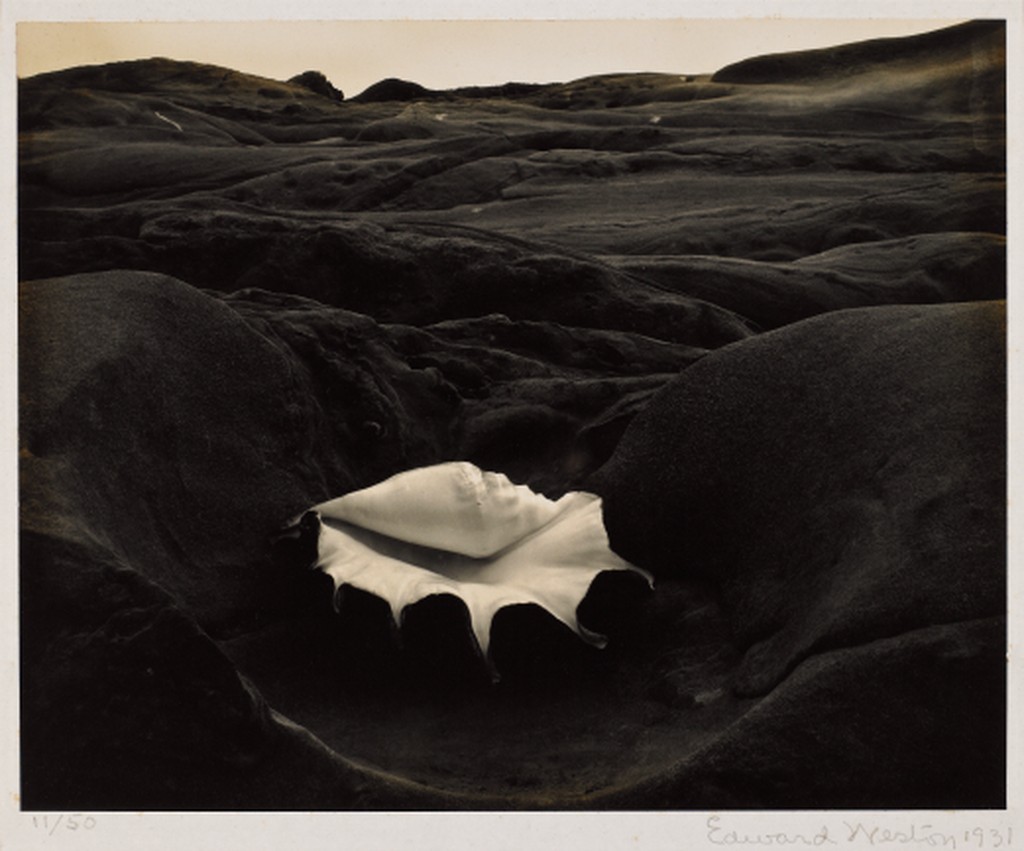
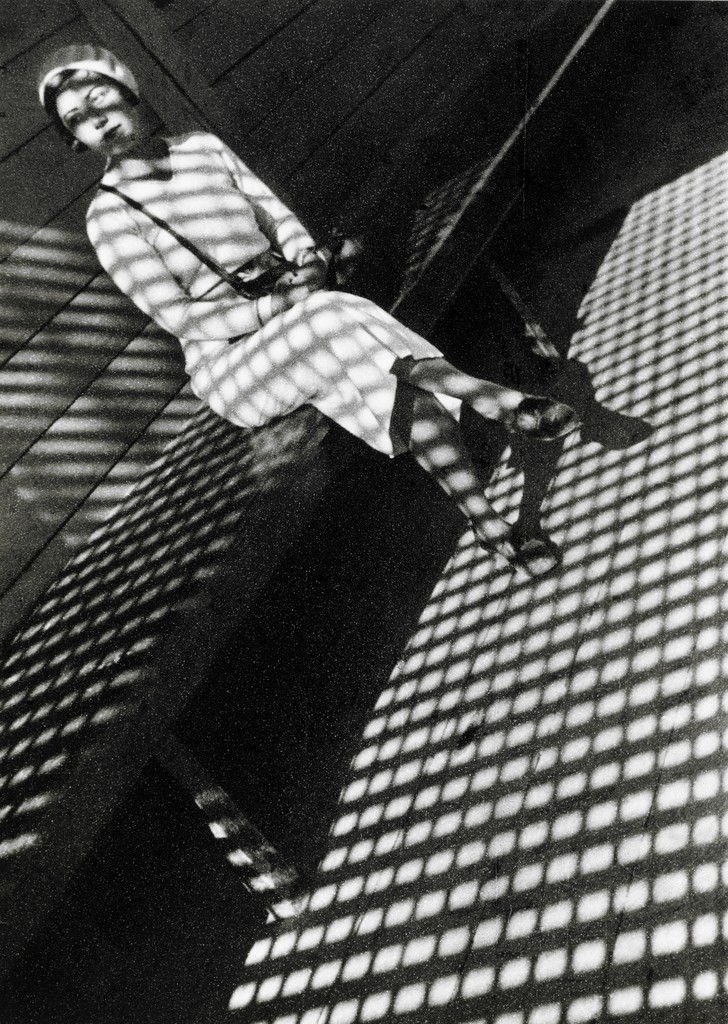
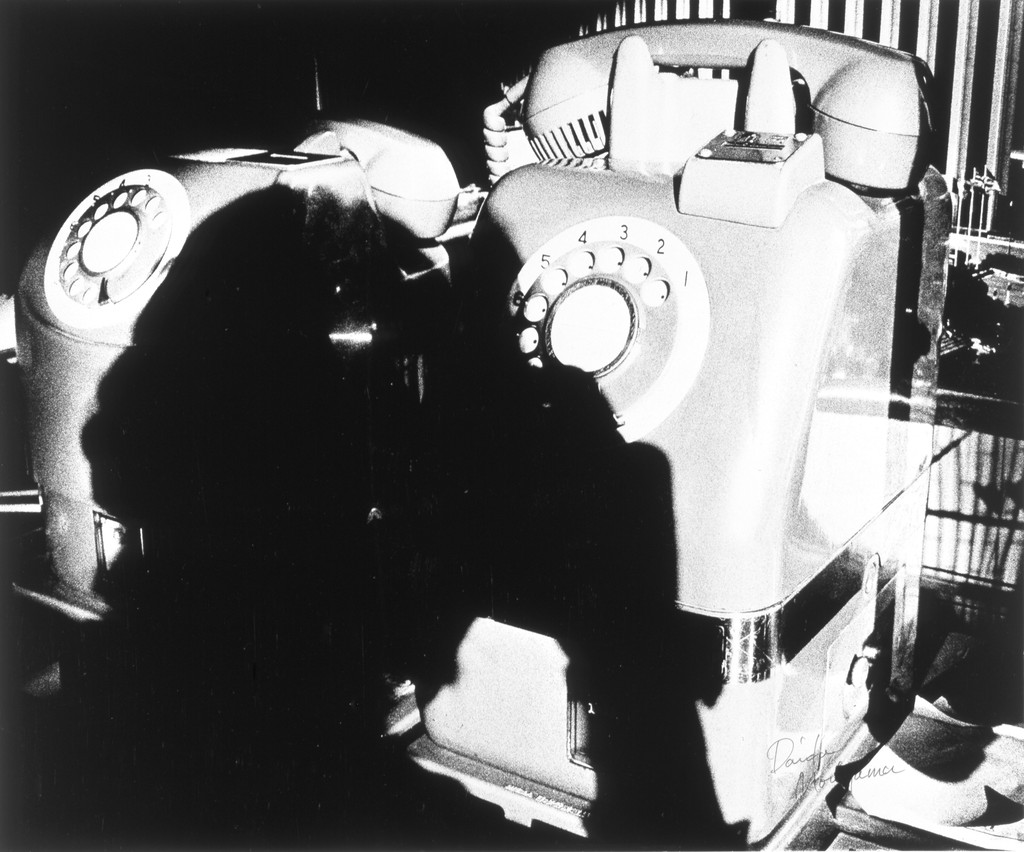
Photographer: Manual Alvarez Bravo
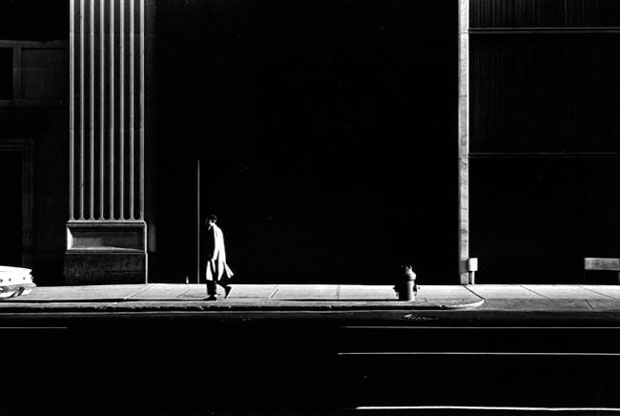

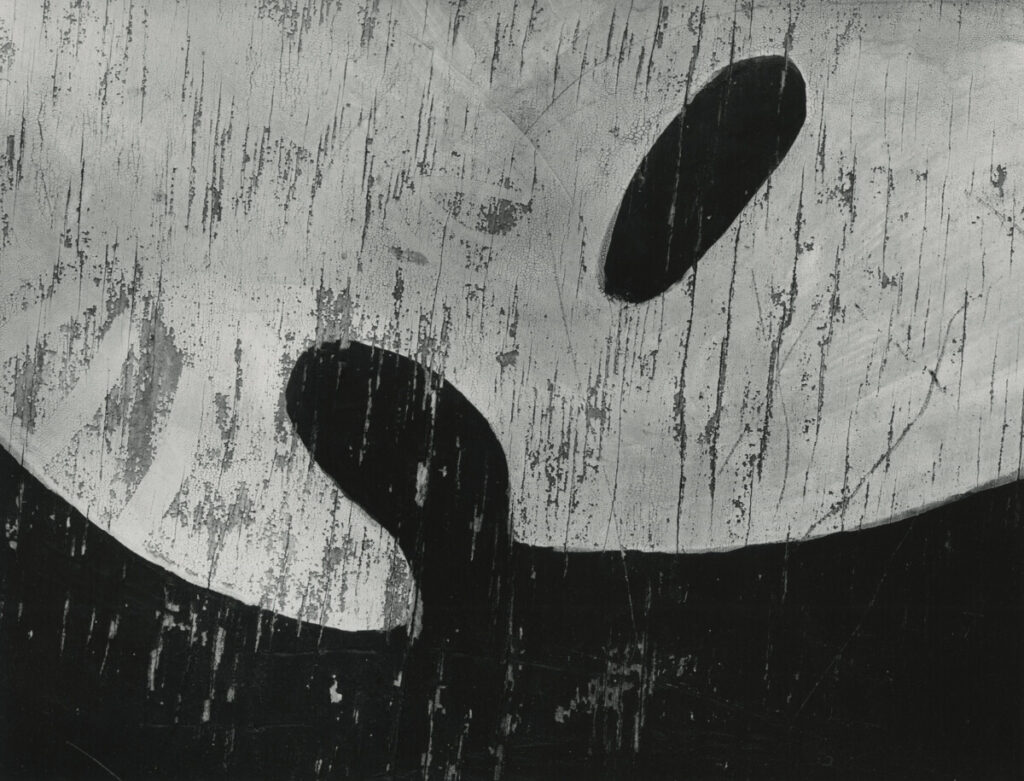
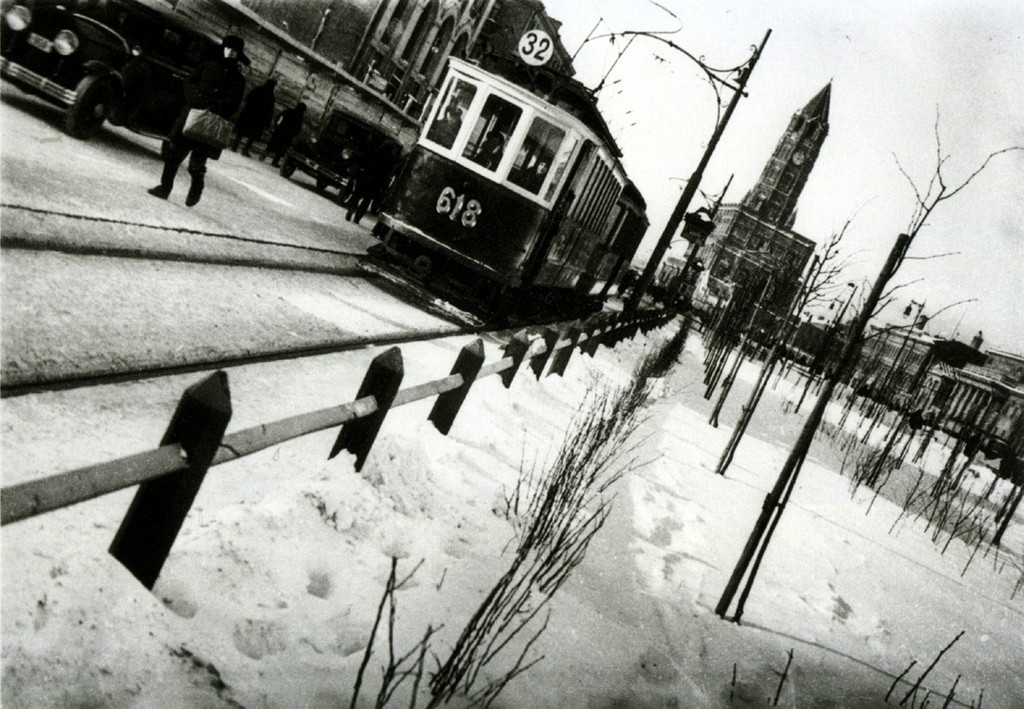
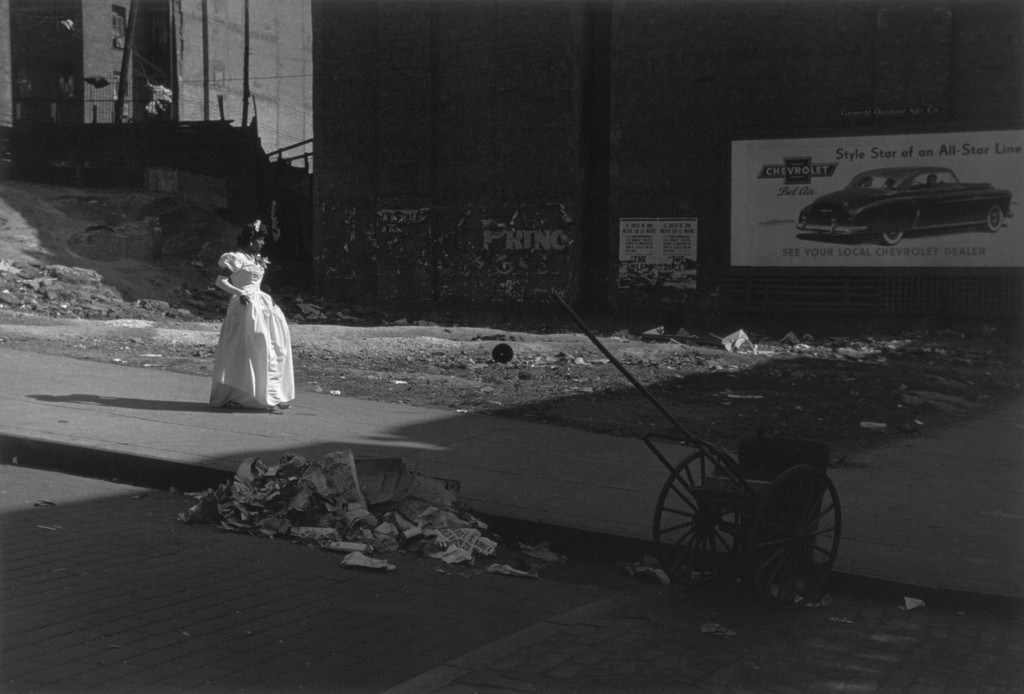
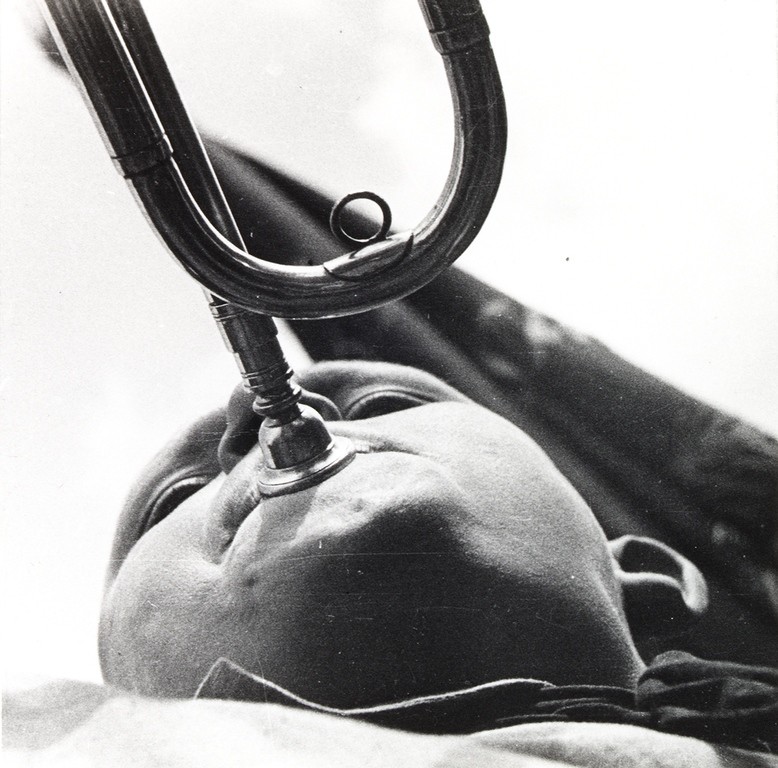
Photographer: Ray Metzker
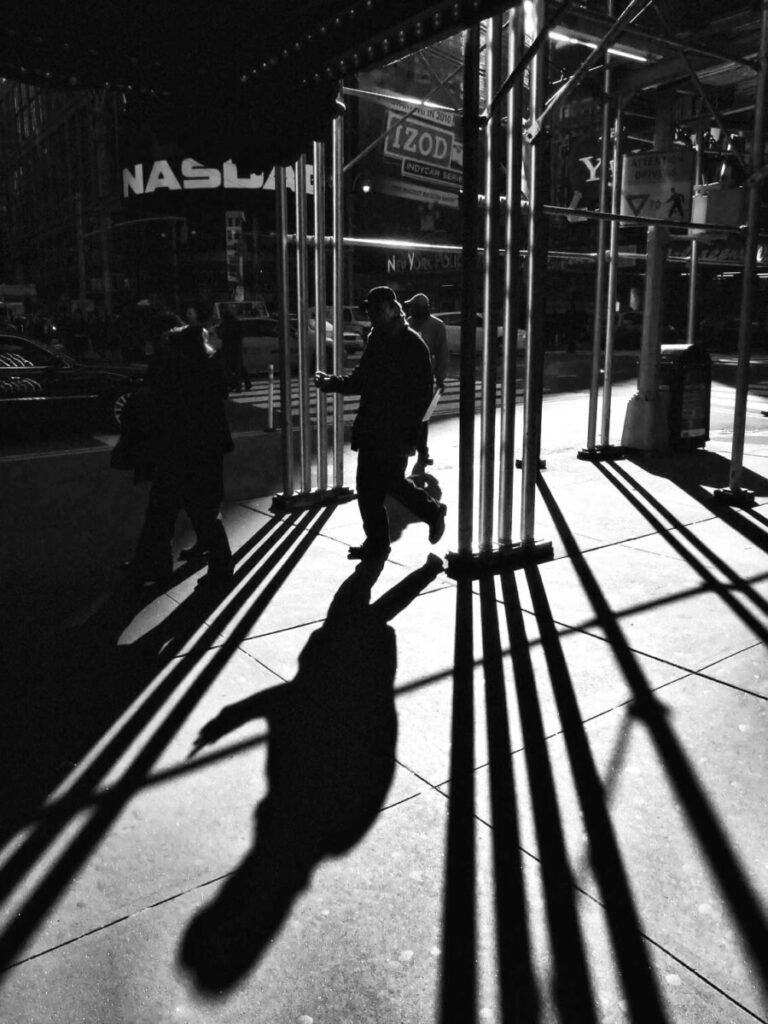

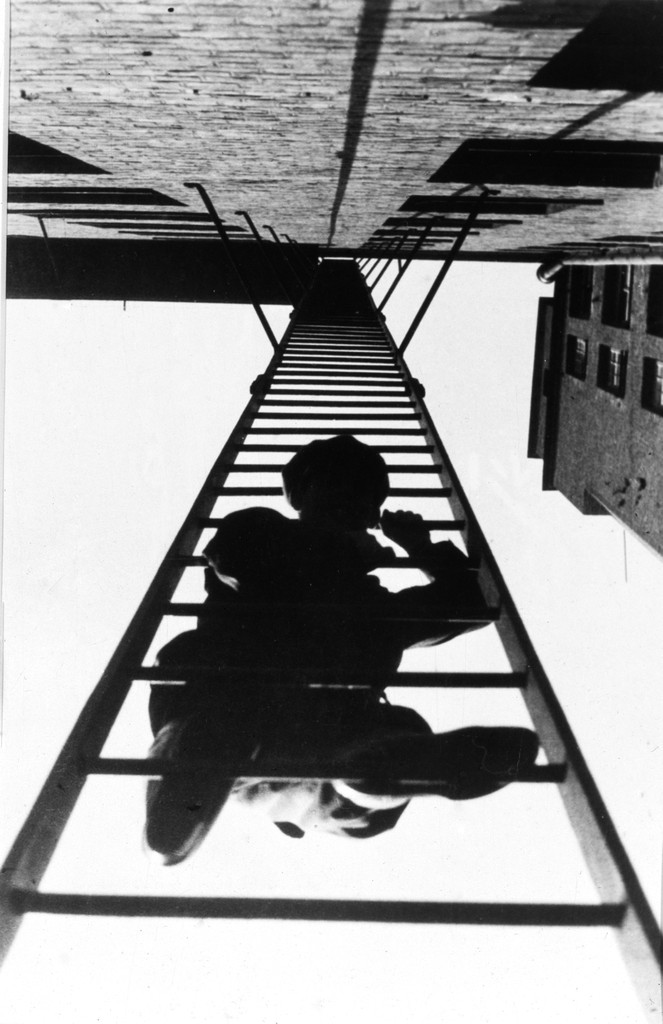
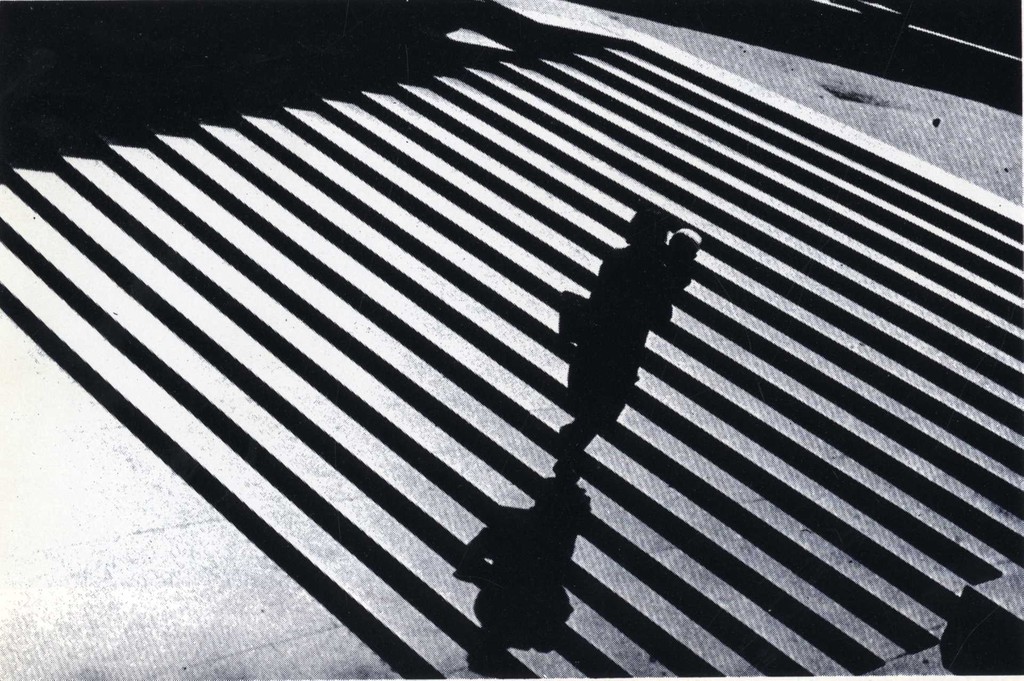
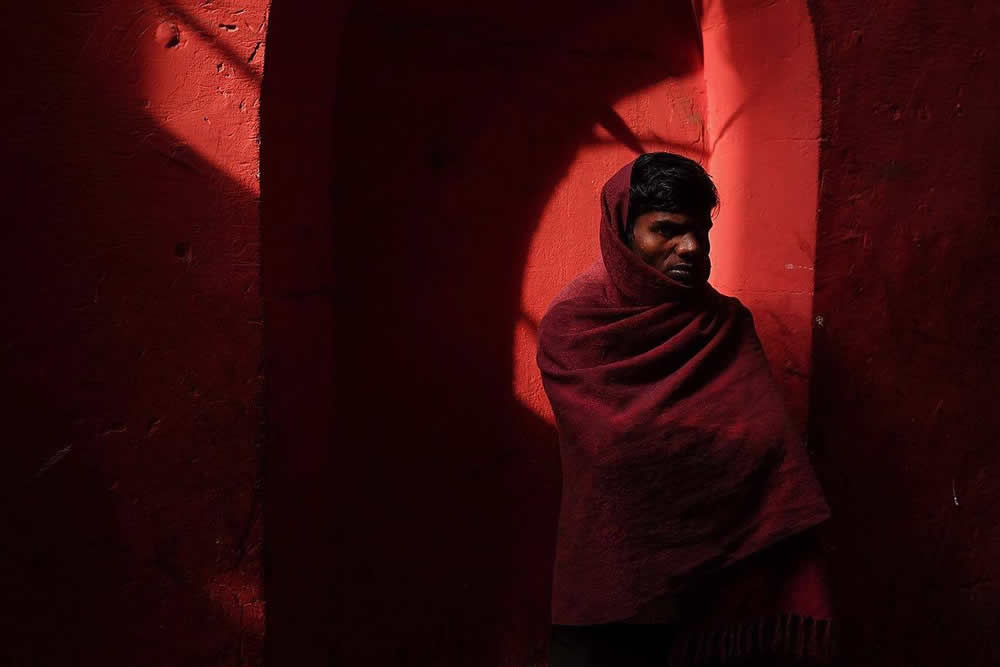
Photographer: Ray Metzker
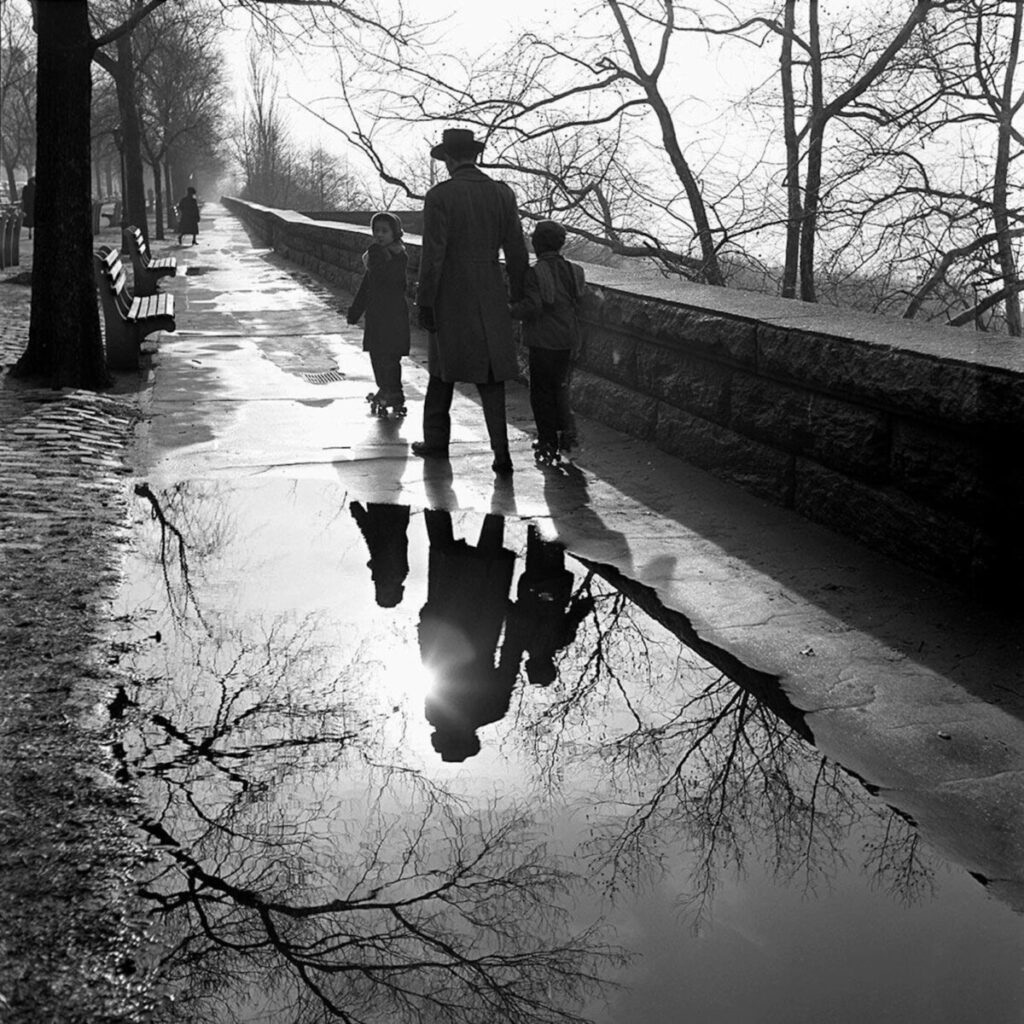






Labs
Lab 4: Continuous lights in the Studio
Homework
HW 4: Something Near and Something Far
Class Schedule
Feb 27th: Field Trip to the Oculus and Brookfield Place
March 5: Quiz 1, Lightroom: Global Corrections, Midterm support
March 12: Midterm Presentations














































Recent Comments