Activity 1 – Heart location and external structures.

Figure 1: Location of the heart in the thoracic cage. Credit: OpenStax Anatomy and Physiology CC BY 3.0
Each group should work with one human torso to complete this activity.
- Remove the anterior chest wall, if present, to expose some major organs in the thoracic cavity. Observe the location the heart is in. What organs are found on the left and right side of the heart?
____________________________________________________________________________________
- One of the organs listed about has an indentation call a cardiac notch. This notch accommodates the heart. Which of the two organs have this indentation? Which part of the heart is found there?
____________________________________________________________________________________
- Observe the heart and the space it is in. What is this space called? Name three major blood vessels also located in this space.
____________________________________________________________________________________
- The heart is protected by a fibrous sac, which is not present. How is this sac called, and what are the two layers of this sac?
____________________________________________________________________________________
5. Which layer mentioned above has a parietal layer and a visceral layer? How are these two layers different?
____________________________________________________________________________________
6. Examine the right atrium. Which two blood vessels deliver blood into the right atrium? What type of blood is delivered in this chamber? Where is the blood coming from as they enter each of these vessels?
_____________________________________________________________________________________
7. Examine the aorta and the pulmonary trunk. Which of the two is more anterior and which is located closer to the superior vena cava?
_____________________________________________________________________________________
8. Examine the left and right ventricles. What external feature separates the left ventricle from the right ventricle?
_____________________________________________________________________________________
9. What feature helps identify the left ventricle?
_____________________________________________________________________________________
10. Name the four major coronary arteries and three cardiac veins located on the anterior surface of the heart.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
11. Remove the heart and examine the posterior side of the heart. Name the six blood vessels involved in taking blood away from and back to the heart atria.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
12. Name three cardiac veins, a sinus and two coronary arteries located on the posterior surface of the heart.
Activity 2 – Internal Structures of the Heart
Use a heart model to complete this activity
- Most of the hearts are 2-piece models. Remove the top part in order to see the inside of the heart. Examine the atria. How is the left different from the right?
___________________________________________________________________________________
- Blood flows from the right atrium to the right ventricle via the right AV valve. What is this valve called? How many cusps are present in each?
___________________________________________________________________________________
- How many papillary muscles are there in each ventricle?
___________________________________________________________________________________
- The papillary muscles are part of the heart wall. Give one function of these muscles.
___________________________________________________________________________________
- How are papillary muscles connected to the cusps of the valves? Although these are not designed by scale, how many are there in the right ventricle?
___________________________________________________________________________________
- Examine the right ventricle, is there a moderator band present? These muscular structure help conduct action potential from the interventricular septum to wall of the right ventricle. (Some models do not include these structures, but they are usually present in real hearts)
___________________________________________________________________________________
- Examine the layer of the ventricular walls. Are there ridge like muscular structures? What are they called? What function do they play?
____________________________________________________________________________________
- When the right ventricle contracts blood is pumped into the pulmonary trunk. Identify the valve located between the right ventricle and pulmonary trunk. How many cusps are there in each one?
____________________________________________________________________________________
- From the pulmonary trunk blood flows through to the pulmonary arteries. How many pulmonary arteries are there?
____________________________________________________________________________________
- From the pulmonary arteries where would you expect the blood to flow to? For what reason?
____________________________________________________________________________________
- Examine the left atrium. What vessels carry blood to the left atrium? How is this blood in the left atrium different from blood in the right atrium?
____________________________________________________________________________________
- From the left atrium blood flows to the ______________ via the ________________. How is the right AV valve different from the left AV valve?
____________________________________________________________________________________
- Identify the papillary muscles. How many are there in the left ventricle?
___________________________________________________________________________________
- How many chordae tendineae are there?
___________________________________________________________________________________
- Following blood from the left ventricle to the aorta, which semilunar valve will prevent back flow of blood?
___________________________________________________________________________________
- Compare the wall and the chamber of the left ventricle with the wall and chamber of the right ventricle. How are they different?
___________________________________________________________________________________
- What contributes to the differences in the left and right ventricular wall?
Activity 3 – Blood Flow
1. Trace the flow of blood from the right atrium to the lungs and from the lungs to the aorta by listing all structures involved. Indicate the presence of all valves.
2. Complete the table below by listing all blood vessels taking blood to and from the heart. For each vessel indicate whether it is involved in carrying oxygenated blood or deoxygenated blood.
 3. Veins generally carry deoxygenated blood while arteries carry oxygenated blood. Are there any exceptions in the table completed above? If yes which ones?
3. Veins generally carry deoxygenated blood while arteries carry oxygenated blood. Are there any exceptions in the table completed above? If yes which ones?
4. Trace blood flow through the following circuit.
pulmonary trunk
systemic circuit
Activity 4. Sheep Heart Dissection.
Use the sheep heart provided for this activity
- Examine the outer surface of the heart. While holding the heart which layer of the pericardium are you touching?
_______________________________________
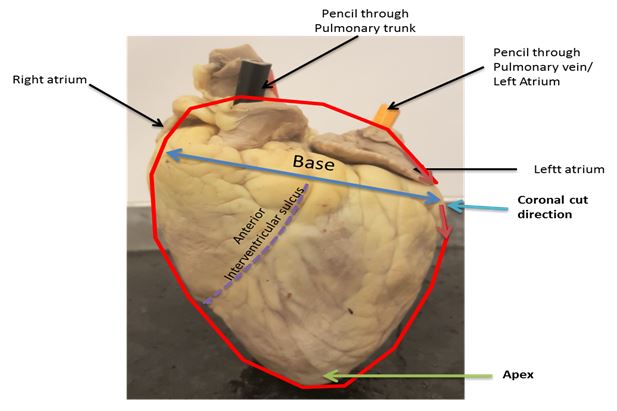
- Identify the apex and the base of the heart. The base follows the ring of adipose tissue surround the larger area at the top of the heart. The apex is the pointed portion of the heart.
__________________________________________________________
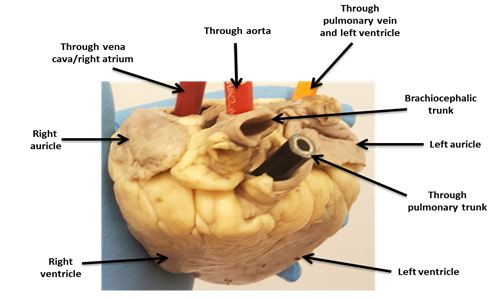
- Name the large vessels connected at the base of an intact heart. Identify the opening of the pulmonary trunk and the aorta. Which one is more anterior?
______________________________________________________
- Place a probe through the aorta and one through the pulmonary trunk. In which chamber does each of these probes end up?
______________________________________________________
- If both auricles, the extension of the atria, are present indicate which one appears larger.
________________________________________________________
- Identify the apex. On which side of the thorax would you expect the apex of the heart to located? Which chamber the apex is part of?
_______________________________________________________
- Identify the anterior interventricular sulcus. Which chambers are separated by this sulcus?
__________________________________________________
- Get a sense of the musculature of the two chambers separated by the anterior interventricular sulcus by squeezing each one repeatedly. How is the right one different from the left one?
___________________________________________________
- Examine the posterior aspect of the heart. Posteriorly what separates the left ventricle from the right ventricle?
___________________________________________________
- Although the blood vessels taking blood to the lung and back to the heart are not visible, list them and indicate the type of blood passing through them.
__________________________________________________
- To examine the internal structures, a coronal cut through the heart can be made. You should cut so as to split each auricle in two. See the fig.
__________________________________________________
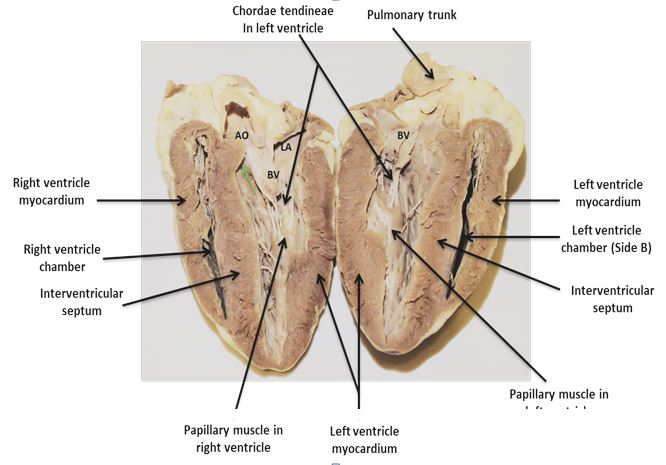
- After cutting through and separating the two halves, identify the left and right ventricles. How are they different?
__________________________________________________
- Measure the length and width of the interventricular septum. Measure at the center of the septum.
__________________________________________________
- Measure the width of the left and right ventricular wall. Take three measurements for each. One at the base, another at the middle and the last one close to the apex.______________________________________________________
- Identify the papillary muscles in the left ventricle.
- How many are there?___________________________
- Count the number of chordae tendineae each one has attached (Count only chords directly attached to the papillary muscle).
__________________________________________________
- Identify the papillary muscles in the right ventricle. You will have to carefully expose the chamber without destroying the structures in it.
- How many are there?________________________________
- How many chordaea tendineae are attached to each? ______________________________________
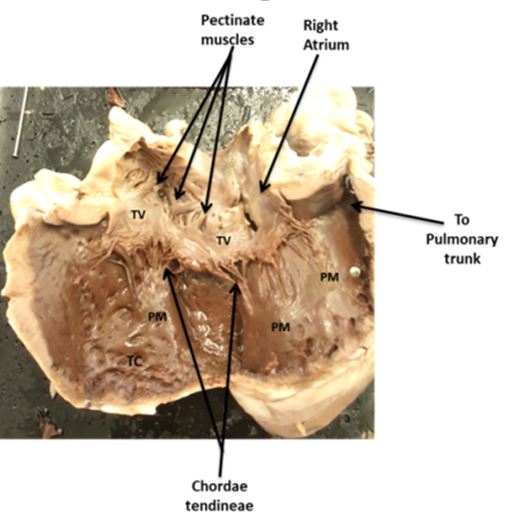
- Observe the pectinate muscles and the trabeculae carneae.
- How are they different? ___________________________________
- What function do they have in common? ______________________
- Examine the four valves.
- How many cusps are there in
- Bicuspid or mitral valve
- Tricuspid valve
- Pulmonary semilunar valve
- Aortic semilunar valve
- How many cusps are there in
b. How are the AV valves similar?
_______________________________________________
c. How are the two semilunar valves similar?
_______________________________________________
d. How are the AV valves different from the semilunar valves?
________________________________________________
19. Examine the right ventricle and look for the moderator band. Indicate whether it is present or absent.
________________________________________________________
20. In the right atrium, identify the fossa ovalis. It is on the same side as the interventricular septum. Try placing a blunt probe. The probe should not appear in the left atrium Why?
_____________________________________________________________
21. Compare the data your group collected with other groups. Use the tables below to input the data. What conclusion can be made about
a. IVS, LV and RV?
b. LV and RV?
c. the number of papillary muscles?
d. the number of chordae tendineae?
___________________________________________________________________________________
Use the table below to input your data from the class. Calculate the individual averages and use this average to answer question 21.
Use the table below to input your data from the class. indicate the number of chords per papillary muscle (PM)