Review Exercises
1. Select the word or term which best match each statement given. Write the word in the space provided.
Systole Diastole Cardiac Cycle Passive
First sound Second sound Cardiac output Isovolumetric contraction
EDV ESV SV Isovolumetric relaxation
1. _____________________ one complete heart beat
2. _____________________ amount of blood left in the ventricles after one cycle
3. _____________________ sound heard from closure of the AV valves
4. _____________________ blood enters the ventricles before atrial contraction
5. _____________________ ventricles are contract by no change in blood volume
6. _____________________ contraction of anyone of the four chambers
7. _____________________ Amount of blood ejected in one minute
8. _____________________ the volume of blood in the ventricles before ejection
9. _____________________ ventricles are in diastole without change in volume
10. _____________________ sound heard after closure of the semilunar valves
11. _____________________ the amount of blood ejected from the ventricles after one cycle
12. _____________________ when the chambers are relaxed.
2. Place the following in correct order.
1. Isovolumetric relaxation
2. Ventricular contraction
3. Atrial contraction
4. Isovolumetric contraction
5. Ventricular ejection
6. Ventricular filling
1. ____________ _2. __________________ 3. ____________________
4. ______________5. ___________________6. _____________________
3. Complete the following using the appropriate terms.
1. Valves open and close as a result of a change or increase in ____________________.
2. When the chambers eject blood the volume in these chambers will ____________________.
3. The ventricles eject 120 ml of blood in the aorta leaving 40 ml in the ventricles. That 40 ml is the _______________________.
4. Increasing HR without an increase in SV will ________________ cardiac output.
5. Decreasing the SV without changing the HR will __________________ cardiac output.
6. The difference between systolic and diastolic pressure is _________________.
7. The extra sound heard as a result of the problem with heart valve is called a ______________.
8. Blood pressure is typically taken using the _____________________ artery.
9. All valves will open and close as a result of _______________________.
10. The average pressure of blood within the arteries is known as the __________________.
4. Indicate whether BP will increase or decrease under the following conditions.
1. High levels of calcium ion _______________________
2. Low levels of sodium ion _______________________
3. Injecting someone with digitalis _______________________
4. A room with abnormally low oxygen _______________________
5. Too much carbon dioxide in the blood _______________________
6. Taking in high amount of caffeine _______________________
7. Injecting epinephrine in someone’s thigh _______________________
8. Increase in temperature _______________________
9. High levels of H+ in the blood _______________________
10. Not able to take in oxygen _______________________
5. Complete the sentences below using appropriate terms.
1. When taking BP measurements the first Korotkoff sound while deflating the cuff is the ______________ reading.
2. The diastolic reading is the _____________________ Korotkoff sound.
3. The diaphragm of the stethoscope is placed on the _______________ artery when taking blood pressure.
4. Pulse rate is usually taken using the ________________ artery.
5. If your pulse rate is high it is expected that your ______________(BP/HR) most also be high.
6. Exercise is expected to ________________________ cardiac output.
7. SV will be expected to _____________________ during exercise.
8. An increase in HR and SV will lead to an _____________________ in cardiac output.
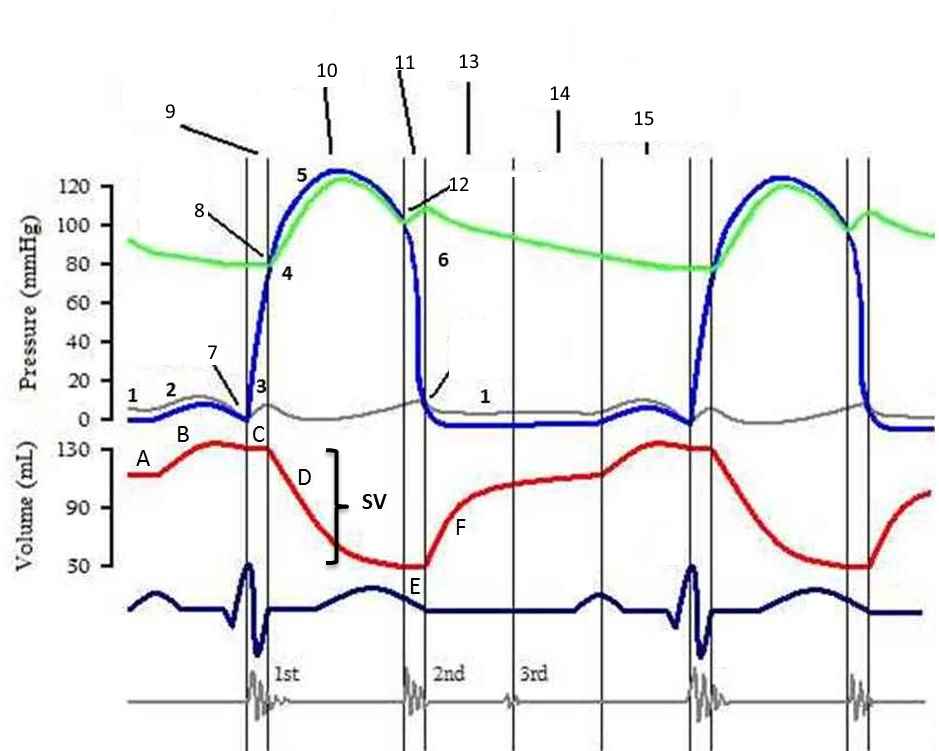
6. Label the following diagram using the terms given below
ESV EDV
SV aortic valve open
Atrial diastole AV-valves open
Decrease in ventricular volume Increase in ventricular pressure
Aortic valve close AV-Valves closed
Isovolumetric contraction isovolumetric relaxation