USE OPENSTAX TEXT TO HELP TACKLE THIS ACTIVITY.
Activity One – Torso
One Torso per group.
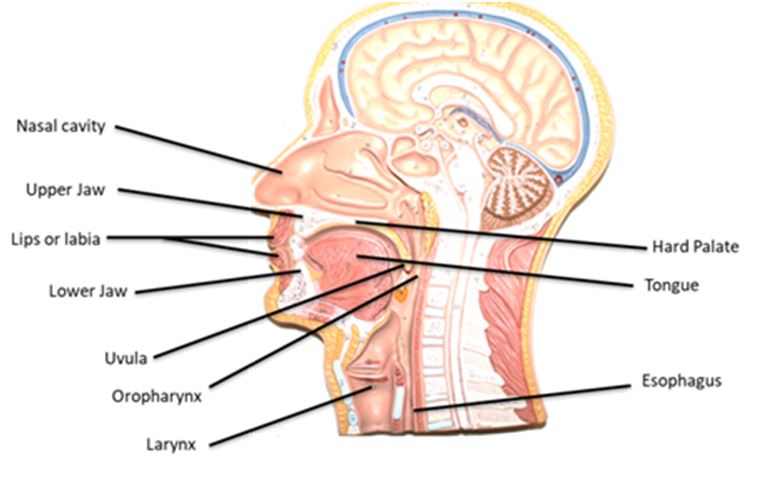
1. Identify the buccal cavity. This is where the food is physically manipulated by the tongue and teeth in order to get it to a form than can be swallowed. Chemical digestion of starch by salivary amylase begins in the buccal cavity. What forms the roof (top), floor and sides of the cavity? (imagine it is an opened mouth)
2. The lips or labia form the opening of the mouth (OpenStax). These are attached to the gums by the labial frenulum (Unable to see on the torso) but may be seen on each other. The space between the lips and the gun is called the oral vestibule. Pass your tongue over the gums in so doing the tongue will be in the oral vestibule.
3. List the accessory organs (OpenStax) of the GI tract found in or associated with the buccal cavity. Give the function of each.
4. A. Identify the uvula (flap-like tissue at the back of the oral cavity). It is an extension of which structure? ____________________________________________
B. What is the function of the uvula? ______________________________________
5. Identify the tongue. The tongue is made up of skeletal muscle which is why you have the ability to move it in various directions. What is the function of the tongue? _______________________________________________________________________________________________ Which tonsils are associated with the tongue? _______________________
6. The pharynx includes ______________ and ____________ (parts of the pharynx) which are both involved in passage of __________ and ______________. Which tonsils are associated with the oropharynx? ____________________________________
7. Identify the epiglottis. It is part of which system?________________________ When food is swallowed what will the epiglottis do? Why? ________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
 Figure 2. Organs of the digestive tract. Thoracic and abdominal organs. (Credit: Alcendor CC BY 4.0)
Figure 2. Organs of the digestive tract. Thoracic and abdominal organs. (Credit: Alcendor CC BY 4.0)
8. Describe the location of the esophagus to the trachea. The esophagus is a conduit for food heading to the stomach. No absorption of nutrients or chemical digestion takes place in the esophagus.
9. Compare the esophagus with the trachea. How are they similar? ______________________
__________________________________________ How are they different? ____________
_________________________________________________________________________
10. The first part of the esophagus is made up of skeletal muscles, the middle part is made up of skeletal and smooth muscles and the last part is made of smooth muscles. Which part of the esophagus does one have control of? Why?
11. Trace the esophagus as it passes through the thorax. Describe its location in relations to the bronchi and thoracic aorta. (Remove the heart and lungs to see these structures)
12. Identify the esophagus as it penetrates the diaphragm via the esophageal hiatus. The esophagus will join the ______________________ after passing through the hiatus. The connection is called _________________________.
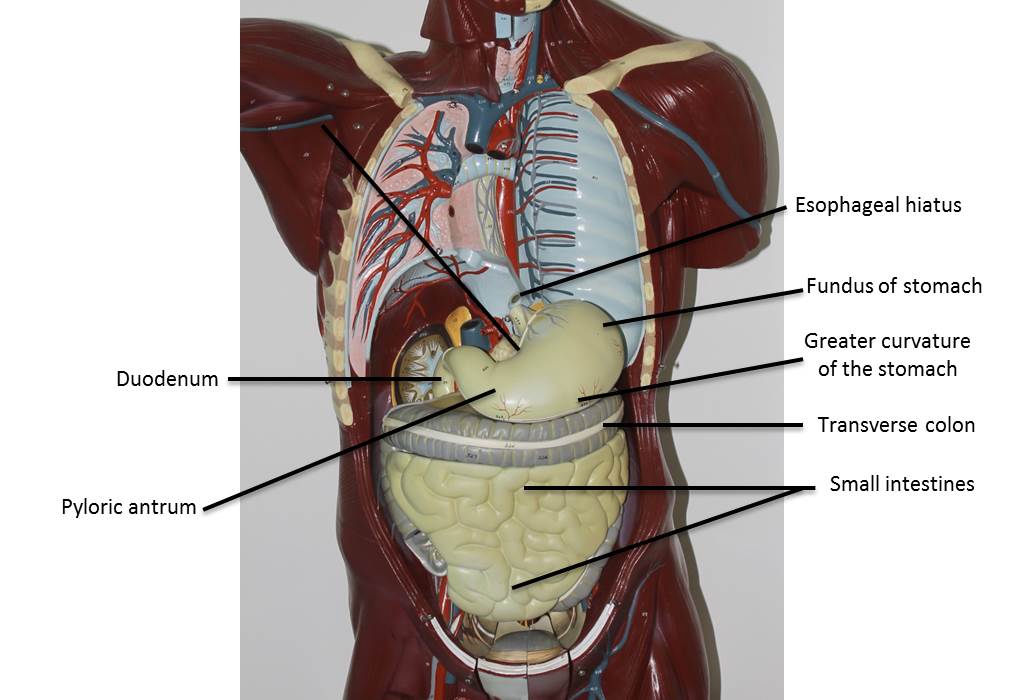
Figure 3. Organs of the digestive tract. Liver has been removed to show parts of the duodenum. (Credit: Alcendor CC BY 4.0)
13. Identify the stomach. Remove the liver to get a good view of the stomach. This sac or pouch receives the food from the esophagus. Describe the shape of the esophagus. Identify the fundus, the lesser curvature, the greater curvature, the body and the pyloric antrum. Draw a representation of the stomach and label the various parts.
14. The inferior part of the stomach that joins the first part of the intestines- the duodenum. Between the duodenum and the pylorus is the pyloric sphincter. What is the function of this sphincter?
15. The stomach has membranes called omentum attached to it. The lesser omentum attaches at the lesser curvature, while the greater omentum attaches to the greater omentum. Indicated which omentum is present on your torso.
The Liver and the Pancreas (OpenStax)
16. Identify the liver. The liver plays many functions such as detoxifying, production of bile, synthesis of proteins, metabolism of fats, proteins and carbohydrates. Describe the location of the liver in relation to the stomach. Which one is superiorly located and which one is inferiorly located?________________________
17. Count the number of lobes there are in the liver. How many are there? __________ Which is the largest? __________Which is the smallest? _________________
18. Which organ is intimately associated with the liver and one of the liver’s main products? _______________________
19. Compare the size of the liver to the other organs. ________________________________
20. Identify the pancreas. It is the master digestive enzyme producer. It releases enzymes for the chemical digestion of all macromolecules. Describe its texture and shape. ____________________________________________________________
21. Identify the head, body and tail of the pancreas. The head is closer to the first part of the ___________ and tail is closer to the ___________________.
22. The pancreas produces the most digestive enzymes. It produces enzymes to breakdown proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and nucleic acid. Follow the pancreatic duct and indicate where are the enzymes produced by the pancreas are released? _________________________
The intestines are involved in chemical digestion and absorption of nutrients. The first part of the intestines, the duodenum is primarily involved in chemical digestion. It is in this region that the pancreas releases its digestive enzymes.
23. Use figures 3 & 4 and identify the small intestine. The intestines are made up of three different parts. Nutrient absorption takes place in the small intestines particularly in the jejunum and ileum. Which part of the small intestine is located next to the head of the pancreas? ________________________________________ What are the three parts of the intestines? ____________________________________
24. The second part of the small intestines, the jejunum, does most of the absorption of nutrients. What nutrients are absorbed in the intestines? __________________________________________________________________________________________
25. Identify the large intestines (colon). Identify the various parts of. List the parts below.
26. Use arrows to indicate the follow of material from the three main parts of the colon.
27. Remove the intestines and observe the mesentery associated with them. The mesenteries are membranes, visceral peritoneum, associated with the intestines. How is the mesentery attached to the small intestine called? ___________________________________
28. What is the mesentery attached to the large intestine called? _______________________
29. The membrane associated with the abdominal cavity is called peritoneum; visceral and parietal peritoneum. The parietal is attached to the ___________________ wall while the _______________ is attached to the abdominal organs.
30. Name the last two segments of the GI tract. What is the main function of each?