Name ____________________________________________________
Activity 1 – Examining RBCs
- List three (3) functions of blood. _____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________ - Differentiate formed elements from the liquid component of blood. __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- Describe the composition of blood plasma. __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- Red blood cells or __________________ give blood its ___________________ appearance. They have a _____________________ shape which is important for transporting _____________________. Abnormal or low number of RBCs can lead to __________________________.
Examine Figure 2 and answer the following questions.
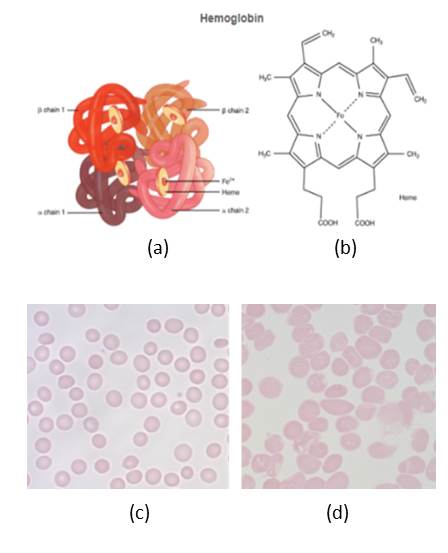
Figure 2. Hemoglobin and RBCs. (a) Structure of hemoglobin molecules. (b) structure of heme. (c) normal RBCs. (d) RBCs from a sickle cell patient. (Panels (a) and (b) credit: OpenStax Anatomy and Physiology CC BY 3.0. Panels (c) and (d) credit: Alcendor CC BY)
5. Which panel, (c) or (d), represents blood from a
a) normal individual __________
b) sickle cell individual __________
6. What two problems arise as a result of the shape of the sickle RBCs?
a) ____________________________________________________________________________________
b) ____________________________________________________________________________________
7. What is one of the biggest problems with individuals suffering from sickle cell disease? Give the name of the disorder and the condition associated with it.
_________________________________________________________________________________
Activity 2 – White Blood Cells and Platelets
1. Another name for white blood cells is __________________________________. One of their main functions is ______________________________ which includes eliminating pathogens.
2. Differentiate granulocytes from agranulocytes. ___________________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________________
3. Which mnemonic helps in remembering the list of WBCs from most to least abundant? ___________________________________________________________________________________________________
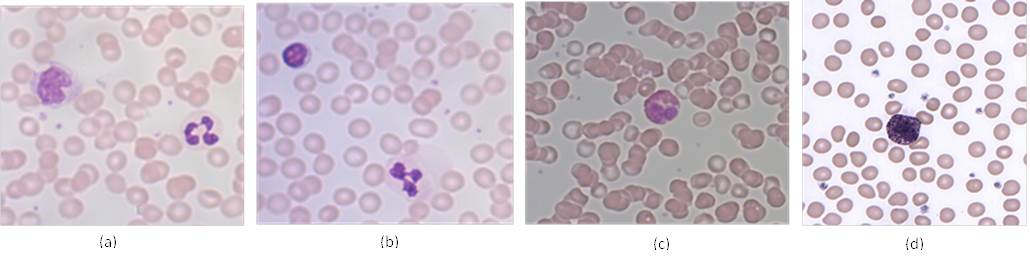
Figure 4. Blood cells from a blood smear. (Credit: (a) – (c) Alcendor, CC BY (d) Erhabor Osaro CC BY-SA 3.0)Examine Figure 1 and Figure 4 and answer the following questions.
4. Which panel(s) have
a. Neutrophil _________
b. Lymphocyte _________
c. Eosinophil _________
d. Basophil _________
e. Platelets _________
5. What features help identify the following cells?
a. Neutrophil ______________________________________
b. Lymphocyte ______________________________________
c. Eosinophil ______________________________________
d. Basophil ______________________________________
e. Platelets ______________________________________
6. Which blood cell type is likely to indicate or be involved in
a. Bacterial infection _________
b. Parasitic infection _________
c. Prevent excessive bleeding _________
d. Allergies _________
e. Phagocytizing and eliminating microorganisms and worn out cells. _________
f. Release antibodies _________
7. Based on Table 1, place the WBCs in order from most numerous to the least numerous.
_________________________________________________________________________________________
Activity 3 – Blood Smears
3. 1 – Blood Smear I
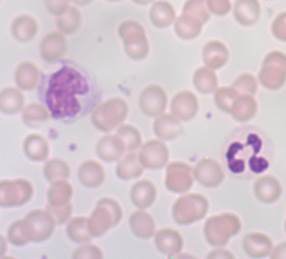
Examine the picture of the blood smear in Figure 5 and attempt the following questions.
a) How many complete red blood cells are there? ________________________________________________
b) Besides red blood cells what other specific formed elements are present?
_________________________________________________
c) What is the percentage of the various cell type identified? (percentage = number of cell type/total number of all cells x 100)
_________________________________________________
d) Determine whether the smear is from a healthy individual or from sickle cell patient. Give reason(s) for your answer.
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
3.2 – Blood Smear II (To be done in lab)
Use the slide provided in lab to perform a differential WBC count. Follow the steps below to perform the differential WBC count.
- Begin towards one end of the slide using the 40X objective lens.
- Move the slides in a straight line towards the opposite end, counting the different types of white blood cells seen.
- When the end of the smear has been reached, move the slide up or down and continue in the opposite direction (see Figure 6).
- Count a total of 100 WBCs, tallying the number of each WBC type.
- Record your numbers in the table below.
- Calculate the percentage of each cell type. Record your results in the table below.
Questions
1. Compare your results with the normal ranges found in Table 1. How do results match up with the normal ranges?
___________________________________________________________________________________________
2. Repeat using a sickle cell slide. How do these results match up with the normal ranges?
___________________________________________________________________________________________
3.3 – Virtual Microscope – WebScope 4 (To be done online)
Repeat the WBC count using the virtual microscope images given when the link above is selected or if you left click of Figure 7. Keep on clicking on the image to increase the size of the image so as to be able to distinguish the cell types. Count 100 white blood cells, keeping a tally of each type as you count. Record your results in the table below. calculate the percentage of each cell type.
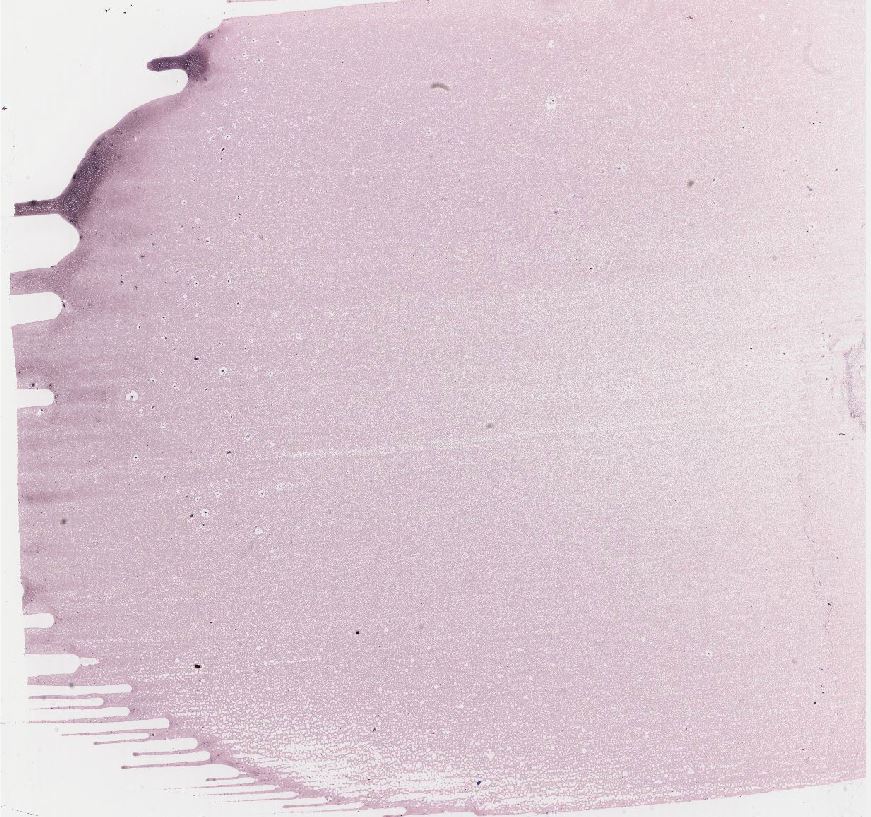
Figure 7. Virtual blood smear. (http://virtualslides.med.umich.edu)
Questions
1. Compare your results with the normal ranges found in Table 1. How do these results match up with the normal ranges?
Activity 4 – Blood Typing
- Each group should collect 4 plates – one for each of the 4 blood samples given, the four blood samples, and the three sera (Anti-A, Anti-b and Anti-Rh. One member from each is responsible for testing one of the 4 blood samples.
- Add a drop of each serum in an individual spot on the plates. The spots on the plates are already labeled.
- Add a drop of each blood sample to each of the three spots. Remember one blood sample for each plate.
- Use a tooth pick to stir the anti-serum/blood sample mixture.
- Observe for clumping. Clumping indicates that the blood sample as the antigen which matches the anti-serum.
- Record your results on the table below.
Questions
- Indicate the donor and recipient to which each blood type is compatible.
Recipient Donor
Sample 1 ____________________ ____________________
Sample 2 ____________________ ____________________
Sample 3 ____________________ ____________________
Sample 4 ____________________ ____________________
2. Which blood type is
the universal donor? _______________
the universal recipient? _______________
3. Match blood test to its correct outcome. Write the letter of test next to the correct outcome.
a) Tallquist method – __________ time it takes to stop bleeding
b) Hematocrit __________ Identifying type of Rh factor
C) Bleeding time __________ Hemoglobin concentration
D) Coagulation time __________ number of red blood cells
E) Blood typing __________ How it takes to clot