Review Exercise
Male Reproductive System
- SELECT THE WORD OR TERM WHICH BEST FITS EACH SENTENCE BELOW. WRITE THE WORD IN THE SPACE PROVIDED.
Spermatogenesis Diploid Haploid Seminiferous tubules Mitosis
Spermatogonium Haploid Negative Spermatozoa Testis
Spermiogenesis Meiosis Spermatid primary Secondary
- The type of feedback involved in regulation of testosterone production. ________________________
- This type of cell division will lead to nonidentical cells .________________________
- ______________ is the male gonad producing gametes.
- Each spermatozoa is ______________, having just one set of chromosomes, while each sperm stem cell or ______________ ______ is ______________________ having two copies of each chromosome.
- At the end of mitosis 2 _______________ spermatocytes will be produced, while at the end of ________________________ four ________________________ spermatocytes will be produced.
- Within each ______________________ spermatozoa will be released into the lumen.
- The entire process of sperm production is called ______________________________ while formation of fully formed sperm is called ________________________________.
- At the end of ______________________2n cells will give rise to 1n
- A ________________________ is not yet a fully formed sperm. It is still lacking key structures.
- Spermatogonium divides by _______________________ to give rise to primary spermatocytes.
2. Match each description with the correct term. WRITE THE NUMBER OF THE TERM IN THE SPACE PROVIDED.
1. LH ____This gland directly controls sperm production.
2. FSH ____ Where sperm production takes place.
3. Testosterone ____ This hormone directly controls testosterone production.
4. GnRH _____Released from seminiferous tubules and inhibit release of FSH/LH
5. Testes _____This hormone stimulate spermatogenesis.
6. Interstitial region _____This gland’s secretion control pituitary hormones.
7. Leydig cells _____Produced by the hypothalamus.
8. Sertoli cells _____ This is where the leydig cells are found.
9. Anterior pituitary _____The cells will produce testosterone.
10. Hypothalamus _____Endocrine gland in males
11. Seminiferous tubules _____These cells nourish and protect spermatocytes
12. Inhibin ______Produced by leydig or interstitial cells
- List the cells and processes involved in spermatogenesis. Begin with spermatogonium and end with spermatozoa. Indicate where each process occurs.
- What are some of the effects faced by a thirty year-old if both of his testes are removed because of accidents or a particular disease.
- List the hormones involved in male reproductive system and indicate their main function or effects.
6. Label the following diagram with the terms given.
Anterior pituitary, Leydig cells, LH, FSH, GnRH
Inhibin, Hypothalamus, Testosterone
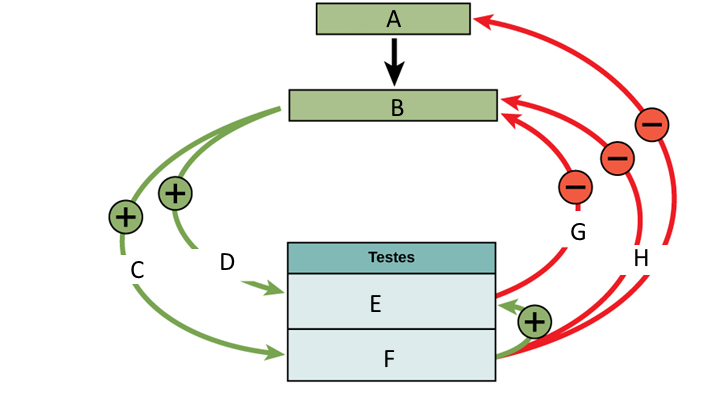
Figure 1 Hormones and the male reproductive system (Credit OpenStax Anatomy and Physiology CC BY 3.0)
Female Reproductive System
- SELECT THE WORD OR TERM WHICH BEST FITS EACH SENTENCE BELOW. WRITE THE WORD IN THE SPACE PROVIDED.
Oogonium Fallopian tube Polar body Medulla Primordial
Graafian Corpus luteum Mitosis Ovum Oocytes
Oogenesis Ruptured follicle primary Secondary Fertilization
- After ovulation the _________________ will become the corpus luteum.
- The process of egg production and maturation is known as ____________________.
- The structure formed from a ruptured follicle. _____________________________
- The ________________________is the inner region of the ovary.
- _____________________ will eventually mature to become an ovum.
- The mature follicle prior to ovulation is known as a _______________________.
- _________________ oocytes are formed after meiosis I while _________________ oocytes are form after meiosis II.
- ___________________ occur when one sperm and one egg fuse.
- At puberty the _______________ follicles will mature to become an ovum.
- Oogonium divides by _____________ ________ resulting in primary oocytes.
- When oocytes divide the ______________________ will not have as much cytoplasm as the growing oocye.
- Most fertilization will occur in the _______________________.
- Like the sperm stem cell, the ___________ ________ will divide to give rise to primary oocyte.
- The __________________ is the mature egg capable of being fertilized.
2. Match each description with the correct term. WRITE THE NUMBER OF THE TERM IN THE SPACE PROVIDED.
1. LH _____ Produce and release LH and FSH
2. FSH _____ Refers to the time the ovum leaves the ovary.
3. GnRH _____ Occurs between day 7 and day 14 of the uterine cycle.
4. Uterus _____ The layer of the uterus affected during the menstrual cycle.
5. Uterine cycle _____ Produced by the developing follicles.
6. Ovarian cycle _____ Produced mostly by the corpus luteum.
7. Proliferative phase _____ The layer of the endometrium removed during menstruation.
8. Pituitary _____ Hormone responsible for initiating follicle maturation.
9. Estrogen _____ Consist of follicular phase and luteal phase
10. Endometrium _____ A surge in this hormone will lead to ovulation.
11. Functional _____ This hormone is produced by the hypothalamus.
12. Ovulation _____ Where implantation is expected to take place.
13. Progesterone _____ Consist of the menses, proliferative and secretory phases.
3. List the cells and processes involved in oogenesis. Begin with oogonium and end with the mature ovum. Indicate where each process occurs.
4. What are some of the effects faced by a thirty year-old if both of her ovaries are removed because of accidents or a particular disease.
5. List the hormones involved in female reproductive system and indicate their main function or effects.
6. Label the following diagram with the terms given.
hypothamus, Estrogen, Ovaries, Follicles
FSH, GnRH, Progesterone, Anterior pituitary gland
Endometrium, Uterus, Corpus luteum
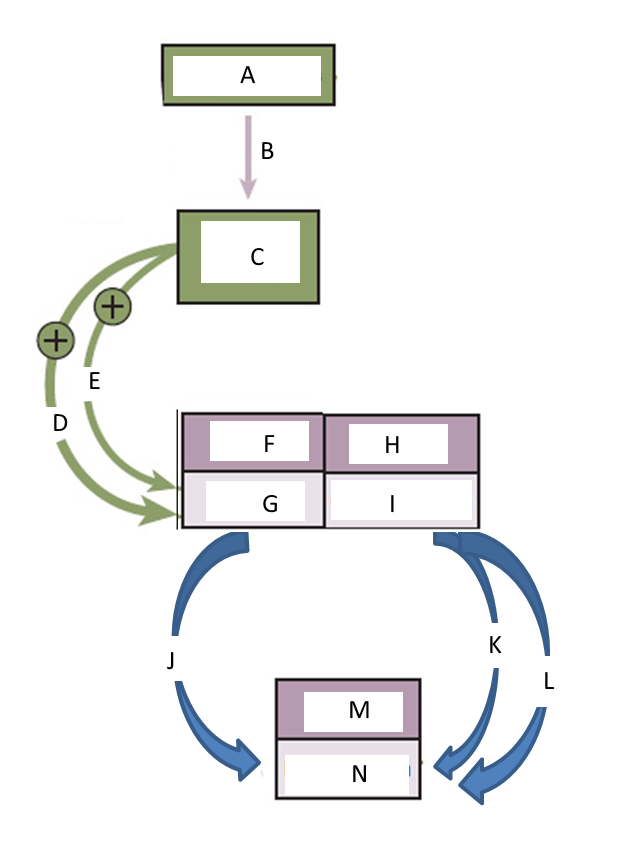
Figure 2 Hormones and the female reproductive system (Credit OpenStax Anatomy and Physiology CC BY 3.0)
7. Identify the various phases and hormones involved in the menstrual cycle. WRITE THE LETTER NEXT TO THE APPROPRIATE TERM.
- ______Hormone levels
- ______Uterine cycle
- ______Ovulation
- ______Luteal phase
- ______Corpus luteum
- ______Luteinizing hormone
- ______Progesterone
- ______Secretory phase
- ______Graafian follicle
- ______Proliferative phase
- ______Estrogen
- ______Follicle stimulating hormone
- ______Ovarian cycle
- ______Menses
- ______Follicular phase




