Lab 12 – Anatomy of the Reproductive System
Review Exercise
Male Reproductive System
1. SELECT THE WORD OR TERM WHICH BEST FITS EACH SENTENCE BELOW. WRITE THE WORD IN THE SPACE PROVIDED.
Accessory glands Testosterone Spermatozoa Ejaculatory Testis
Cremasteric Vaginalis Epididymis Spermatic cord Ampulla
Albuginea Vas deferens Prostate Seminal vesicle Dartos
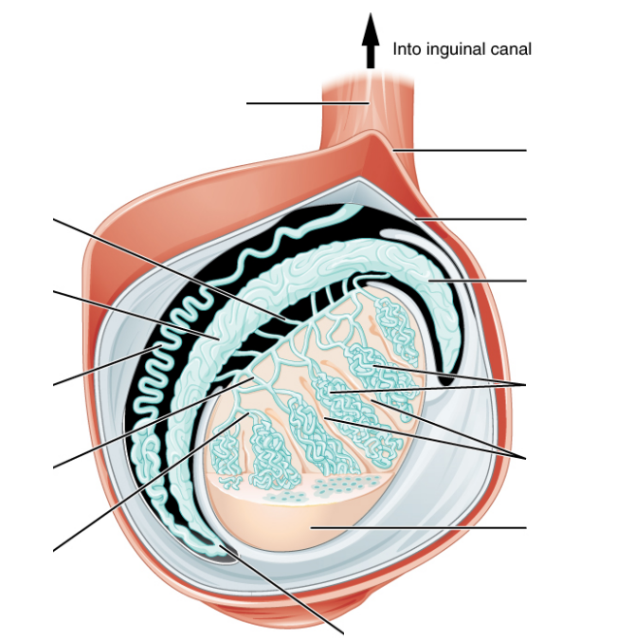
- This covering or structure has a parietal and a visceral layer. _______________
- This gland is the largest of the accessory glands. _______________
- The ______ muscle is closest to the skin of the scrotum. _______________
- One of the primary functions of the testes responsible for secondary characteristics. ______________
- The bulbourethral gland is an example of one of the _______ . _____________
- The _____ muscle functions in wrinkling of the scrotal sac while the _______ muscle moves the scrotal sac closer to the body. _______________
- Prior to entering the ejaculatory duct sperm leaving the vas deferens will enter the ______________. _______________
- Immediately leaving the epididymis sperm would enter the ______________ on the way to the ejaculatory duct. _______________
- In males the _____________ are the gonads and are responsible for production of sperm and testosterone._______________
- The connective tissue layer attached to the testis is the _________________._______________
- The ___________________ , one of the accessory glands, releases its fluid into the ejaculatory duct._______________
- Sperm after released from the seminiferous tubules will remain in the ___________._______________
- After sperm leave the ________________ they will enter the prostatic urethra._______________
- This structure has blood vessels, nerves and the vas deferens as it leaves the testicles._______________
- Mature sperm or ______________ are found in semen after ejaculation._______________
2. Match each description with the correct term. WRITE THE NUMBER OF THE TERM IN THE SPACE PROVIDED.
- Corpus cavernosa _________ These connect the seminiferous tubules to the rete testis.
- Efferent ductule _________ Has a parietal and visceral layer.
- Corpus spongiosum _________ connective tissue layer separating seminiferous tubules.
- Prostate _________ this erectile tissue is makes up most of the penis shaft.
- Straight tubule _________ connects the straight tubules and the efferent ductule
- Glans penis _________ The spongy urethra is found in this erectile tissue.
- Spongy urethra _________ directly connected to the head of the epididymis.
- Tunica vaginalis _________ The largest accessory gland.
- Tunica albuginea _________ the last part of the urethra in males
- Rete testis _________ forms the tip or top part of the penis.
3. ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS
3.1 During vasectomy which structure will be cut or ligated? Why will this prevent pregnancy?
3.2 If, as a result of testicular cancer, both testes are removed, what function of the male reproductive system would be affected?
3.3 Trace the path sperm would follow from where they are made to eventually leaving the urethra. List all structures involved.
LABEL THE FOLLOWING DIAGRAMS
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
4. SELECT THE WORD OR TERM WHICH BEST FITS EACH SENTENCE BELOW. WRITE THE WORD IN THE SPACE PROVIDED.
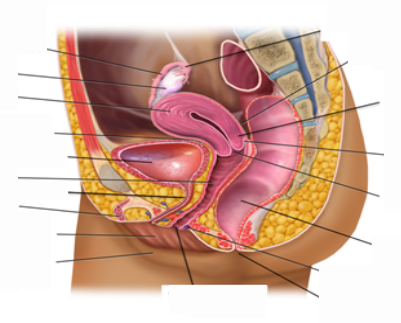
Ovaries Oocyte Endometrium Fundus Cervix
Myometrium Vagina Uterus Perimetrium Fallopian tube
Labia majora Vulva Labia minora Urethra Clitoris
- The muscular tube where sperm is deposited during sexual intercourse.
- The narrow inferior part of the uterus which is in direct connect with the vagina.
- This structure is similar to male penis.
- The gonads in females. They produce estrogen and gametes.
- This is the top part of the uterus superior to the opening of the fallopian tubes.
- The __________ is not part of the reproductive system in females.
- The largest skin folds forming part of the external genitalia.
- Formed by the external genitalia structures.
- oocytes when released will make their way to the uterus via the
- Muscular structure where implantation will normally take place.
- __________ are the smaller skin folds forming part of the external genitalia.
- The female gametes are called ____________.
- In the uterus, the thickest layer is the ___________________.
- The part of the uterus where implantation of the embryo takes place.
5. Match each description with the correct term. WRITE THE NUMBER OF THE TERM IN THE SPACE PROVIDED.
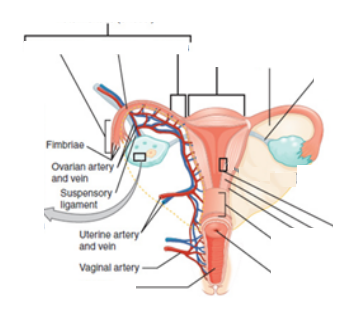
- Ovary ________ The birth canal and structure involved in sexual intercourse.
- Infundibulum ________ Cavity or space where the vaginal orifice is.
- Vagina ________ The external layer of the uterus.
- Fallopian tube ________ Part of the external genitalia and contains erectile tissue.
- Cervix ________ These produce the female gametes and produce estrogen.
- Urethra ________ Sperm enter this structure just before entering the uterus.
- Uterus ________ During menses this layer of the uterus will be passed as period.
- Vestibule ________ The most muscular structure of the female reproductive system.
- Perimetirum ________ Funnel shaped and is closest to the ovaries.
- Fimbriae ________ Passageway for urine.
- Clitoris ________ The middle and thickest layer of the uterus.
- Endometrium ________ Guide eggs or oocyte into the infundibulum.
6. ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS
6.1 During tubal ligation to prevent getting pregnant, which structure will be cut or ligated? Why will this prevent females from getting pregnant?
6.2 If, as a result of ovarian cancer, both ovaries are removed, what function of the female reproductive system would be affected?
6.3 Trace the path an oocyte would take during development until they are passed out during menses (list the stages beginning with the primordial follicle and all structures involved).
LABEL THE FOLLOWING DIAGRAMS