Lab 10 – Review Exercise
- Use the Lab activities and the slides to complete this exercise
Ureter Urethra Renal pelvis Adrenal glands Renal artery
Renal vein Hilum Bladder Retroperitoneal Capsule
Perirena fat Renal cortex Renal medulla Renal pyramid Calyxes
___________________ 1. Where structures enter and exit the kidney.
____________________2. These are found on top of each kidney.
____________________3. Found within the medulla and drains blood into the minor calyx.
____________________4. Tubular structure connecting the kidneys to the bladder.
____________________ 5. Each kidney is covered with this fibrous structure.
____________________ 6. Takes filtered blood away from the kidney.
____________________ 7. Takes urine away from the bladder.
____________________ 8. Layer of the kidney below the cortex..
____________________ 9. The kidneys, IVC and abdominal aorta are all _________________.
____________________ 10. These drain urine into the renal pelvis.
____________________ 11. Brings blood to the kidneys.
____________________ 12. The layer below the cortex.
____________________ 13. Funnel-shaped structure connecting urine from the calyxes.
____________________ 14. Act as a shock absorber and protects the kidney.
____________________ 15. Muscular sac stores urine until micturition.
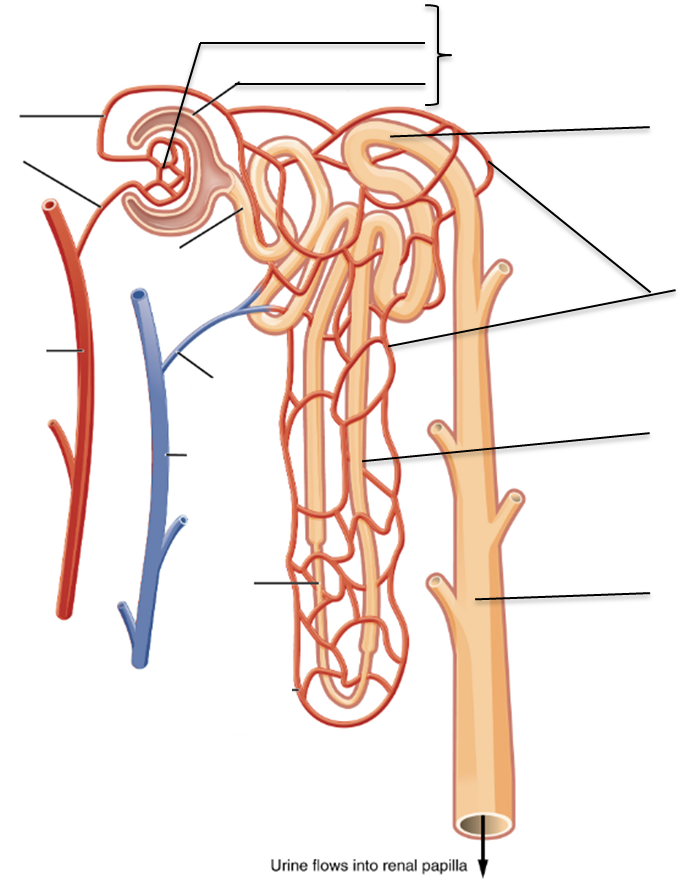
2. Label the diagram using the following terms.
Renal corpuscle Proximal convoluted tube Distal convoluted tube
Descending Loop of Henle Ascending loop of Henle Afferent arteriole
Collecting duct Peritubular capillary Glomerulus
Efferent arteriole Bowman’s capsule
3. Label the diagram using the following terms.
Cortex Medulla Renal Pyramid Renal Pelvis
Renal column Ureter Renal vein Renal artery
Minor calyx Major calyx Papilla Renal capsule
4. Give responses to the following questions.
A. Differentiate between the two types of nephrons.
B. list the type of capillaries associated with nephrons.
C. List, in order, the blood vessels of the kidney. Begin with the renal artery.
D. List the structures involved in the formation and flow of urine. Begin with the glomerulus and end with the urethra.
5. Select the term that best fits each statement below.
Glomerulus Renal corpuscles Afferent arteriole
Efferent arteriole Tubules Proximal C T
Distal CT Tubular reabsorption Tubular secretion
Glomerular filtration Nitrogenous wastes Juxtamedullary apparatus
1. Where absorption of most solutes take place. ______________________________
2. Returns blood to the kidney venous supply. ______________________________
3. Material like drugs are added to nephron tubules. ______________________________
4. The capillary network involved in filtration. ______________________________
5. Connects each nephron to a collecting duct. ______________________________
6. Uric acid and urea are examples of these. ______________________________
7. Made up of Bowman’s capsule and glomerulus. ______________________________
8. Involved in regulation of blood pressure. ______________________________
9. Takes blood to the glomerulus. ______________________________
10. First part of urine formation. ______________________________
11. Where secretion take place. ______________________________
12. Material gets back to the blood. ______________________________
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus
6. Select the term that best fits each statement below.
Renin Angiotensin I Angiotensin II Liver Afferent
Aldosterone ACE Adrenal Gland DCT Angiotensinogen
________________________ 1. Secreted by juxtaglomerular cells in response to signal from MD cells
________________________2. Part of the nephron tubule making up the juxtaglomerular apparatus.
________________________3. Converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II.
________________________4. Angiotensinogen is converted to _________________.
________________________5. The arteriole bringing in blood be filtered by each nephron.
________________________6. Makes and releases angiotensinogen in circulatory system.
________________________7. Released by the adrenal glands and help in Na+ reabsorption.
________________________8. Sits on top each kidney.
________________________9. Activated form of angiotensin I.
________________________10. Activated by renin.