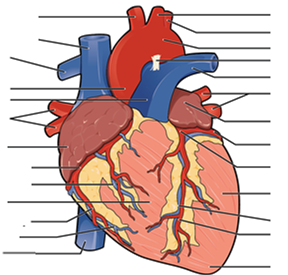
- Match the word to the correct description. Write the word on the line provided.
Mediastinum pericardium visceral parietal chordae tendineae
Cusps papillary muscles apex trabeculae carneae epicardium
Base pectinate myocardium cardiac skeleton pulmonary trunk
- The layer of the pericardium attacked to the fibrous pericardium. ________________
- All the four heart valves have more than one of these. ________________
- These muscular ridges are found in the atria. ________________
- The thickest layer of the heart muscular wall. ________________
- The layer of the pericardium attached to the heart. ________________
- Compared to bones, the heart has one made up of soft connective tissue. _________________
- The space where the heart is found in the thoracic cavity. ________________
- The inner layer of the pericardium. ________________
- Muscular ridges in the ventricles. ________________
- This part of the heart is found on the left side of the chest. ________________
- Muscular structures controlling the opening of the AV valves. ________________
- Forms a barrier around the heart. ________________
- Directly attached to AV cusps. ________________
- Largest region of the heart. ________________
- Takes deoxygenated blood away from the heart. ________________
- Give correct responses to each of the following.
- Trace the flow of blood from the vena cava to the lungs, back to the heart and out to the aorta. Trace by listing all blood vessels, structures and valves.
- Differentiate pulmonary circuit from systemic circuit.
- How are pulmonary arteries and veins different from regular arteries and veins?
- Base on your measurements of the arterial walls and septum, write a sentence comparing the thickness of the ventricles and septum.
- Match each structure with its function. Write the letter of the structure next to the correct function.
- Pulmonary circuit _______ found on the left lung.
- Systemic circuit _______ the pericardium is attached to it inferiority
- Fossa ovalis _______ prevents blood returning from the aorta
- Coronar circulation _______ to the lungs and back to the heart
- Left ventricle _______ returns blood directly to the left atrium
- Right ventricle _______ connected the pulmonary trunk to the aorta
- Aortic semilunar valve _______ takes blood all over the body
- Pulmonary semilunar valve _______ Blood to and from heart muscles
- Cardiac notch _______ remnant of an opening between the L and R atria.
- Diaphragm _______ has thick myocardium
- Ligamentum arteriosum _______ has the most papillary muscles.
- Pulmonary veins _______ prevents blood from returning to the R ventricle.
- Match the disease to its correct description
- Angina __________ abnormally slow heart rate
- Aortic aneurysms __________ heart defects like ventricular septal defect
- Cardiomyophathy __________ chest pain associated with heart attacks
- pericarditis __________ bulging of the aorta
- Tachycardia __________ buildup of fluid in pericardial space
- Congenital heart diseases __________ inflammation of the pericardium
- Bradycardia __________ heart muscles are too large or too thick.
- Cardiac tamponade __________ Abnormally fast heart rate
- Label the structures
Research
Select one of the heart disorders or diseases and write one paragraph providing information on the causes, signs and symptoms, treatments and prevention. Be sure to include your sources.