Activity 1 – Human Torso
Use one human torso for this exercise.
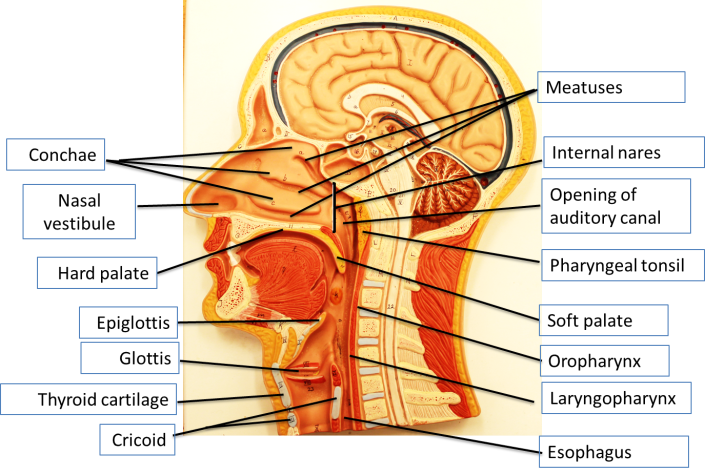
1. Identify the nasal cavity. The three bony structures found on the lateral wall of the cavity are called _______________ , ___________________, and ______________. Air getting to the cavity enters via the _______________, and exit via the ________________.
2. Identify the roof and the floor of the nasal cavity. The roof involves the _________ plate while the floor is made up of the _________________ palate.
3. The opening of the auditory is located closer to the ________________, the part of the pharynx involved only in the respiratory system.
4. Identify the location of the pharyngeal tonsils.
a. Describe its location in relations to the opening of the auditory tube.
b. Name the other two pairs of tonsils.
5. Follow the nasopharynx, oropharynx and laryngopharynx all the way to the larynx. What would you use to mark the beginning and ending of the oropharynx?
6. Identify the larynx.
a. The most visible portion is the _____________________ cartilage.
b. Inferiorly it is connected to the ______________ which forms a complete ring.
7. Continue inferiorly tracing the trachea. Count the number of C-ring cartilages. ___________.
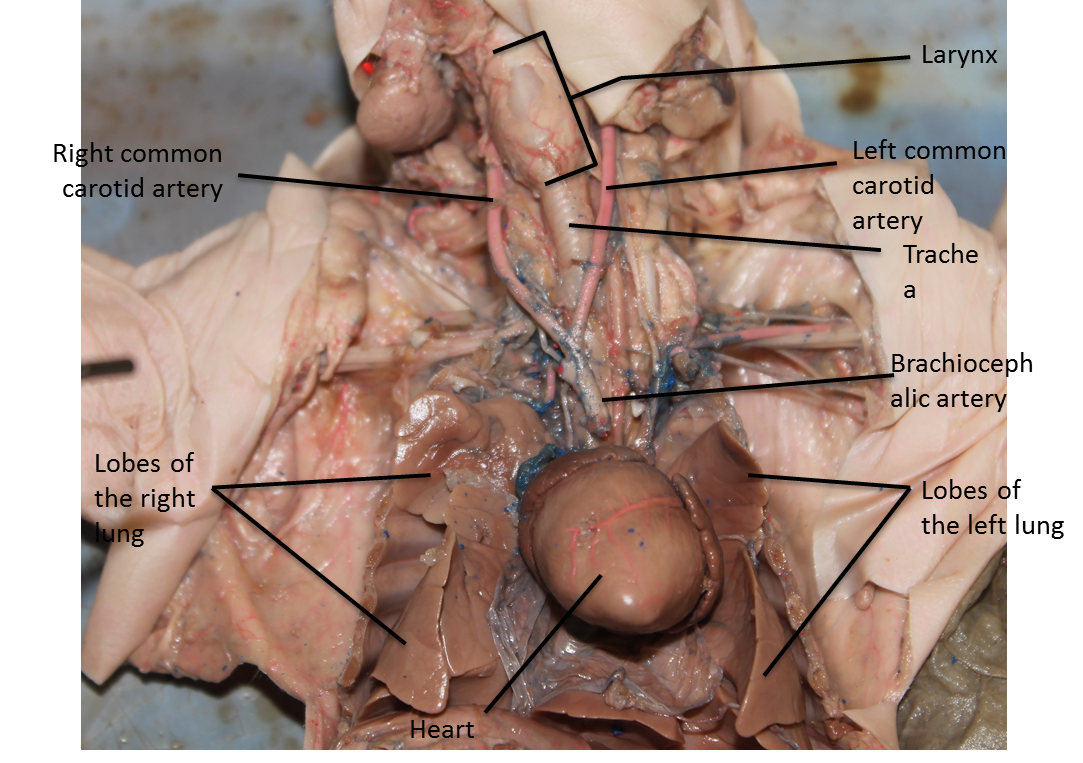
8. Examine the left and right lungs.
a. How many lobes are there in each? The right has ____________________, while the left has _______________.
b. What separates each lobe (be specific) ________________.
9. Examine the left and right lungs. Which lung shows bronchi and bronchioles? ___________________.
10. Remove the heart, if present. Follow the trachea as it bifurcates into left and right bronchi. The cartilage at the middle of the bifurcation marks the carina, an area which contains specialize nerve cells. Give one function the carina may be involved in.
11. Between the left and right primary bronchi which one is longer? How many secondary bronchi are present in the left ______________ and right _____________ lung?
12. Identify the diaphragm. How is its function in respiration?
Activity 2 – Fetal Pig Dissection
Dissection of fetal pig respiratory system.
1. Identify the nostrils or external nares, part of the pig’s snout. Where do these openings lead to? What structures, based on human anatomy, would you expect to find in the nasal cavity?
2. To examine the epiglottis and the entrance of the larynx, cut on either side of the mouth and separate the upper and lower jaw. The hard palate forms the floor of the nasal cavity but the roof of the oral cavity. Describe the texture of the hard palate and soft palate.
3. Identify the opening of the nasopharynx, the oropharynx. Which one is only involved in the passage of air?
4. Identify the epiglottis and the glottis. How can you tell one from the other?
5. Move to the neck region, and identify the larynx. Palpate the larynx. This structure is the thyroid cartilage. It is the largest of the 9 cartilages making up the larynx.
a. What cartilage is it made up of?
b. List the other cartilages and the number of each found.
c. Which cartilage is connected inferiority to the trachea?
6. Remove extra tissue from the trachea all the way to the different bronchi heading to the lungs. Attempt counting the number of c-shaped or tracheal cartilages. How many did you count? ______________
7. How many bronchi, these are primary bronchi, branches directly from the trachea? ________________ How is this different from humans? ____________________________________
8. Count the number of lobes found on each lung, left and right. There should be seven lobes all together. Can you identify them? ______________ on the right and ______________ on the left.
9. Cut through the right lung by following one of the main bronchi. Describe the appearance of the lung tissue.
10. Observe that the lungs are collapsed; they do not fill up the thoracic region. What do you think contribute to this?
11. Lungs that were functioning when the organism was alive will be filled with air. Fetal pigs lung have never been used. What would you expect to happen if you put lungs that were functioning and lungs that never functioned in a container of water? Why?
12. a. Identify the diaphragm; the flat muscle posterior or caudal to the lungs. What is the diaphragm attached to?
b. How does this contribute to the function of the diaphragm during inhalation?