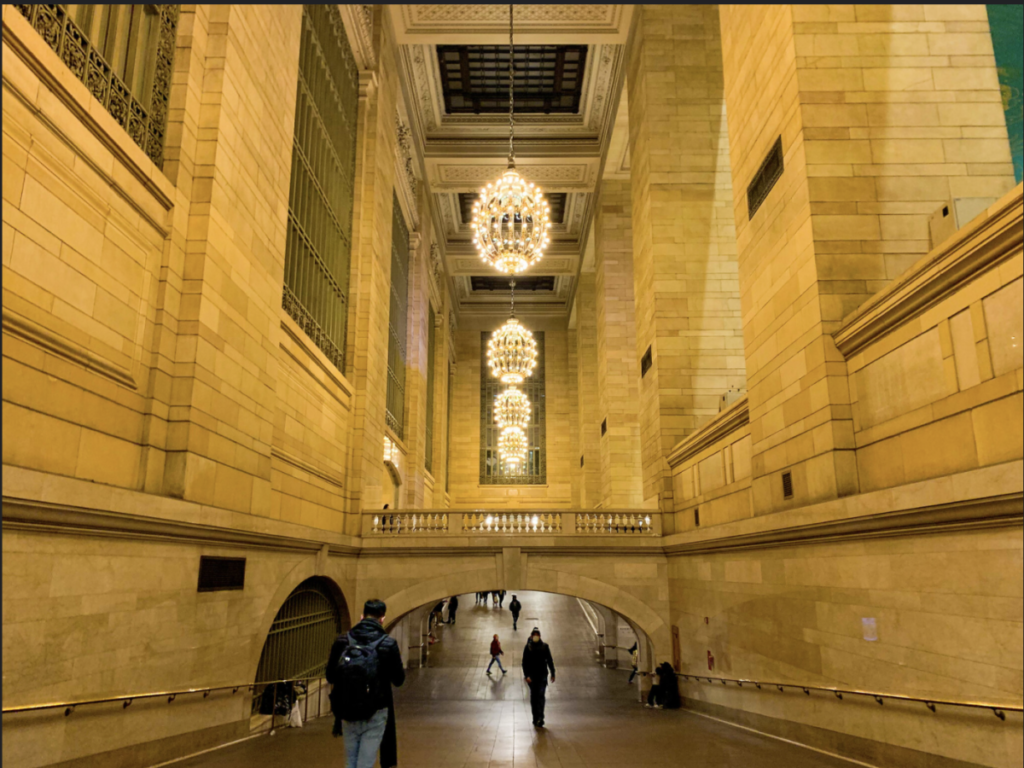
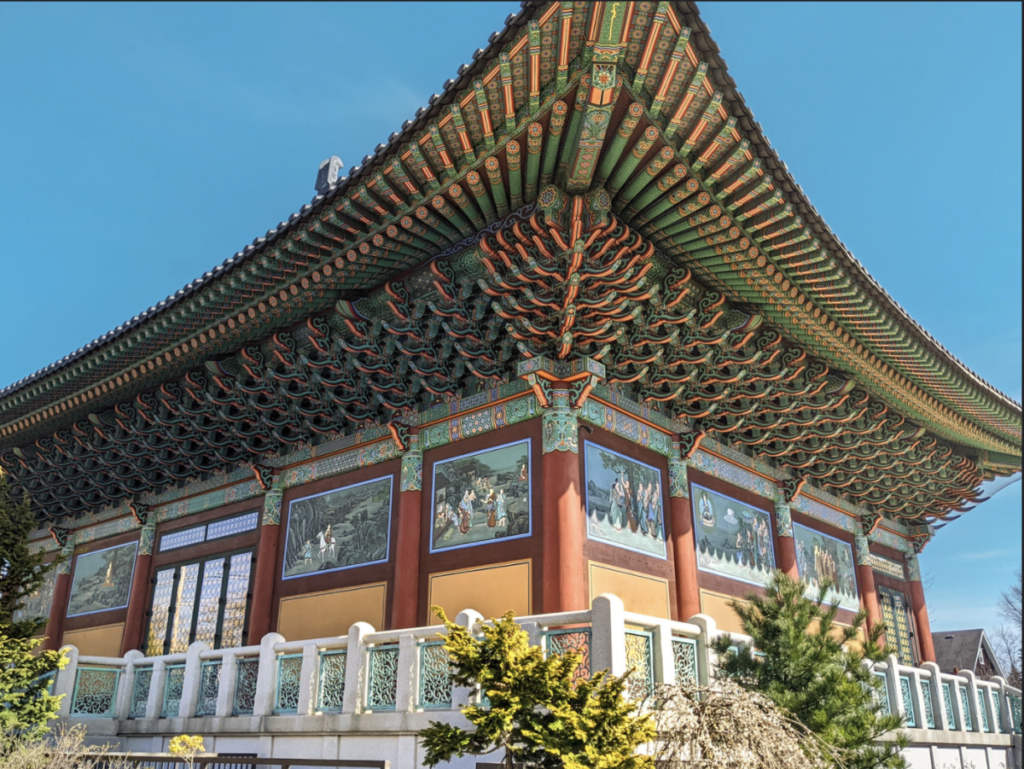
Find a photo from the Mid-term project of 2 different students that you find interesting. The photos should not be similar.
Write about each photo using some of the vocabulary below
Post the two photos with each student’s name and your comments in openlab to MT Critique in student posts
Vocabulary
Framing: How the frame brings together the elements inside the rectangle juxtaposing them, creating relationships between them
Types of shots: how much information is in the frame
- a long shot
- a medium shot
- a close up
- an extreme close up.
Frame within a frame – use elements in the frame to enclose the main subject and draw attention to it. A frame within a frame can be a window or door or it can be items in the foreground such as branches.
Angle of View: describes the camera position in relationship to the subject. The angle of view may be:
- a worm’s-eye view
- a low-angle
- eye-level
- a high-angle
- a bird’s-eye or aerial or overhead view
- an oblique angle.
Rule of Thirds – Instead of placing the main subject in the center of the frame, divide the frame into thirds horizontally and vertically and place the main subject at one of these intersections.
Fill the Frame – (get closer) – do not leave empty areas that do not add to the composition and plan to crop in later.
Diagonals – Sloping lines
Leading Lines – lines in the photograph that lead the eye to the main subject
Patterns – repeated elements. Break the pattern for visual interest
Figure to Ground -the relationship between the subject and the background sometimes described as negative and positive space.
Diffused light – light that comes from many directions and creates soft shadows
Direct light– light that come from one direction and creates hard shadows
Contrast: The measure of difference between bright areas (highlights) and dark areas (shadows) in a photo
High contrast : Large difference between highlights and shadows. Mostly lights and darks without many mid tones
Low contrast : Little difference between lights and darks. Mostly mid tones.







Recent Comments