Contents
Proteins are polymers of Amino Acids

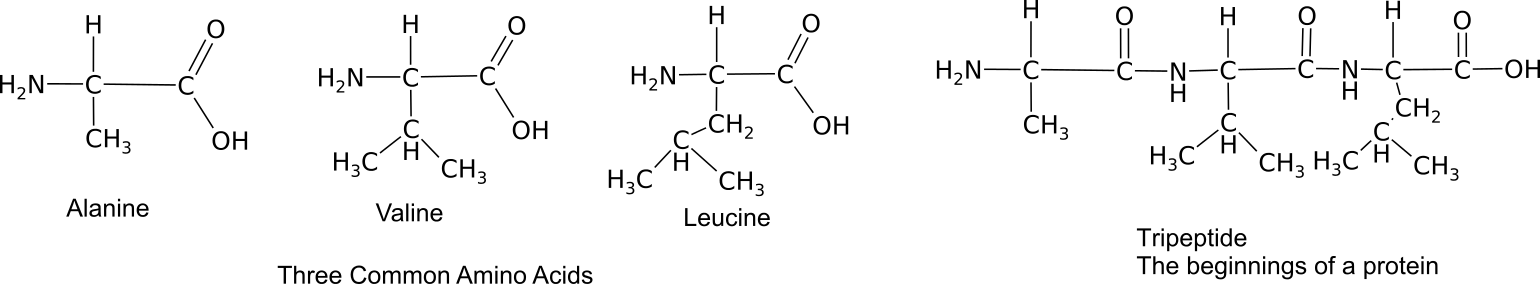
Proteins provide much of the structural and functional capacity of cells. Proteins are composed of monomers called amino acids. Amino Acids are hydrocarbons that have an amino group (-NH2) and an acidic carboxyl group (-COOH).The R group represents a hydrocarbon chain with a modification that alters the properties of the amino acid. 20 universal amino acids are used to construct proteins. The variation in functional groups along the amino acid chain gives rise to the functional diversity of proteins.

Monomers bond together through a dehydration synthesis reaction between adjacent amino and carboxyl groups to yield a peptide bond.
How amino acids interact with each other and the environment
Use the following simulation to test how a polypeptide chain with fold based on the type of solution it is in and the composition of the amino acids.
- Protein Folding Simulation (CC BY 4.0 Concord Consortium)
Levels of structure
- Primary Structure (1°): The sequence of amino acids read from the Amino or N-terminal end of the molecule to the Carboxyl or C-terminal end
- Tyr-Cys-Arg-Phe-Leu-Val-….
- Secondary Structure (2°): local three-dimensional structures that form from interactions of amino acids, like hydrogen bonding
- Alpha Helix – coils occurring from the H-bonds between N-H and C=O groups along the backbone of the protein
- Beta Sheets – laterally connected strands or sheets of amino acids occurring from the H-bonds between N-H and C=O groups along the backbone of the protein
- Tertiary structure (3°): overall 3-D structure of the peptide chain
- Quaternary structure(4°): multimeric protein structure from assembling multiple peptide subunits
Disruption to Structure
The weak interactions that govern the secondary and tertiary structure of proteins can be disrupted through the application of energy, removal of the water environment, alteration of salt content or changes in the pH. The unfolding or misfolding of proteins from these disruptions is called denaturation. Changes in salt and pH will disrupt the charges on amino acids to disrupt structure. Since eggs are mostly protein and water, it is understood how frying an egg can push the water out (as steam) to leave behind a a congealed gelatinous solid. Similarly, cooking generally works to denature proteins. As such, there are methods of cooking that rely , not only on heat, but on dehydration or curing (using salts) and changes in pH (using acids or bases).
Diversity of Proteins
Interactive Animation @ PDB :https://cdn.rcsb.org/pdb101/molecular-machinery/
Learn more about complexity of protein structures at the Protein Data Bank