Contents
Heterologous expression in Tissue Culture
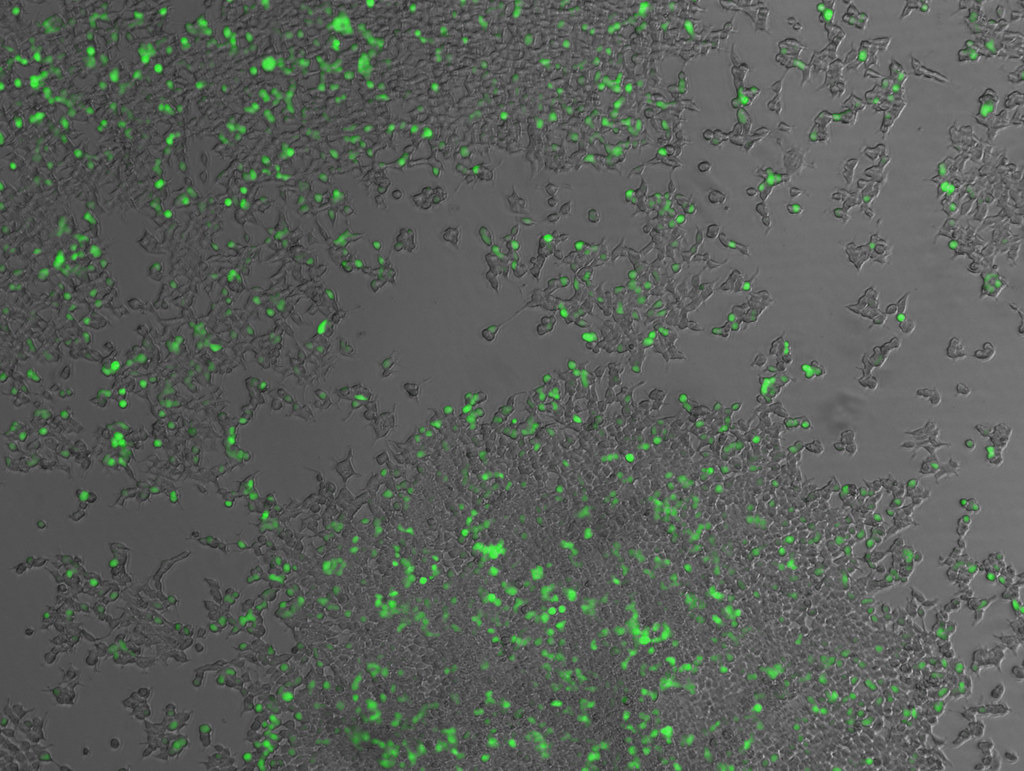
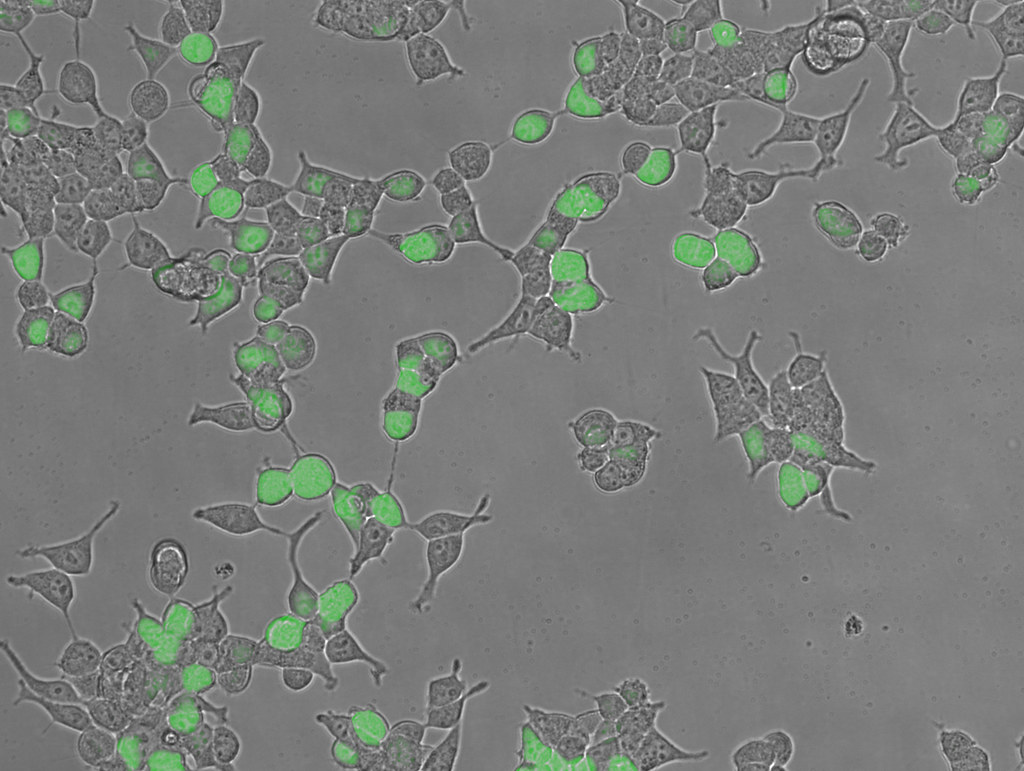
Plasmid Structure

Mammalian expression vectors contain the same hallmark features as bacterial plasmids: bacterial replication of origin and bacterial antibiotic resistance gene (β-lactamase or AmpR). General bacterial plasmid features allow for the carrying and propogation of the plasmid in a bacterial cell. Mammalian expression vectors additionally include a strong mammalian promoter (like CMV from the cytomegalovirus immediate early promoter) upstream of a multiple cloning site (MCS). Plasmids transfected into cells are transient in nature unless the DNA is selected for. The inclusion of a mammalian antibiotic resistance gene, like neomycin phosphotransferase (NeoR), allows for the integration of the plasmid into the genome of the cell by using high concentrations of Neomycin or the analog G418.
Lipofection
Cationic lipids can encapsulate plasmid DNA in liposomes. The cationic portions interact with the negatively charged plasma membrane to deliver the DNA into cells.
Calcium Phosphate Transfection
Calcium chloride solution can be used to incubate with plasmid DNA. When this solution is mixed with a HEPES-buffered saline solution (HeBS) containing phosphate ions, the solution precipitates onto the surface of mammalian cells where they are taken up with the DNA.
Tags: integration of knowledge, life-long learning, breadth of knowledge


