Contents
Review:
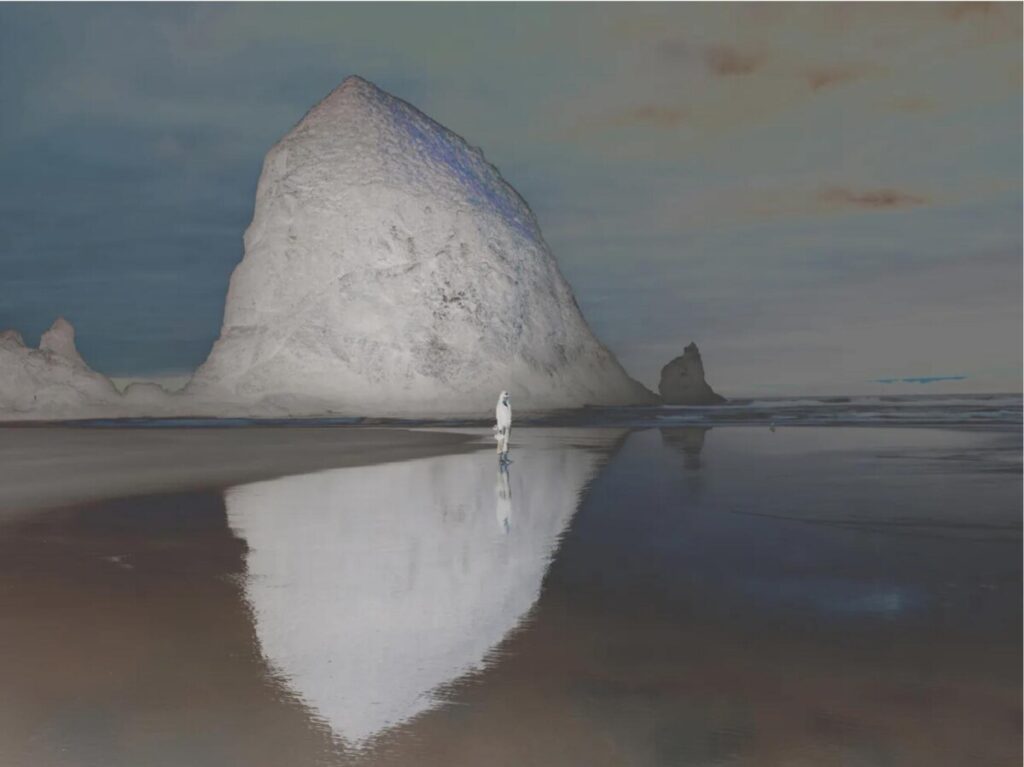
Lighting Quality
Diffused– light hits the subject from all directions and the shadows are soft
Direct– light hits the subject from one angle and the shadows are crisp with sharp edges


Lighting Direction
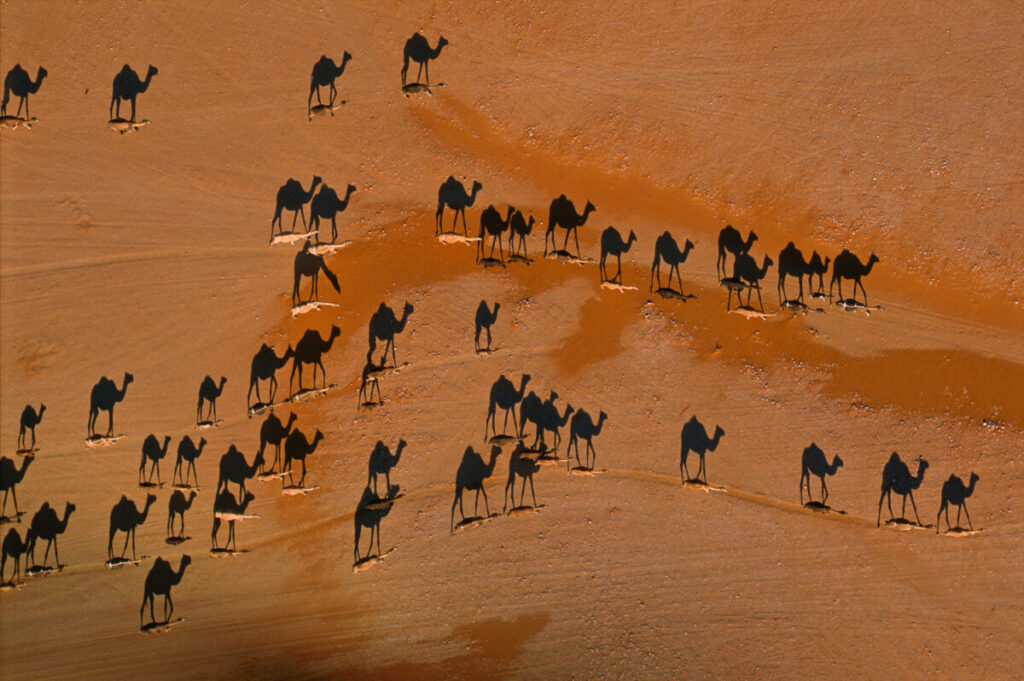
Front light – light comes from near the camera position.
Side light – light come from 90 degrees to the camera position.
Back light – light comes from behind the subject and aims towards the camera.
Contrast
Contrast: The measure of difference between bright areas (highlights) and dark areas (shadows) in a photo
High contrast : Large difference between highlights and shadows. Mostly lights and darks without many mid tones
Low contrast : Little difference between lights and darks. Mostly mid tones.
Inspiration
View:
http://filippodrudi.com/project-thefork.html
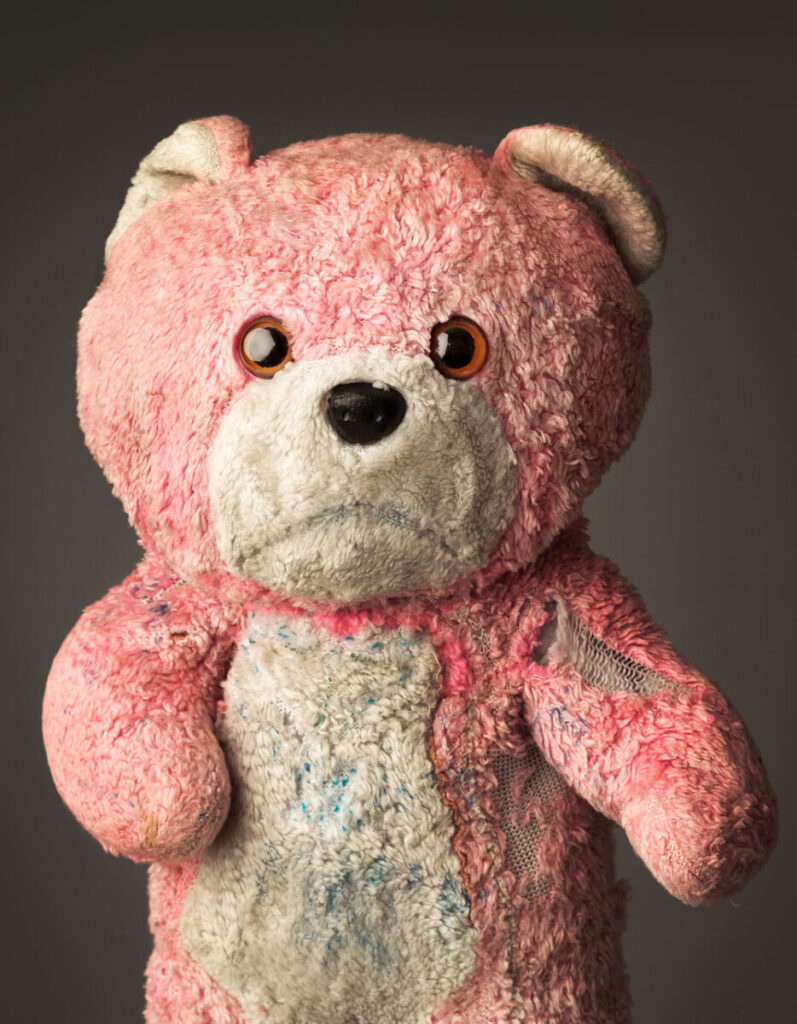
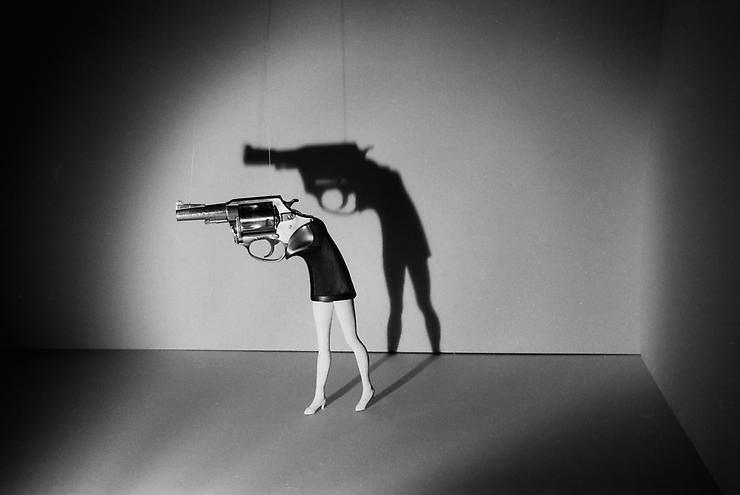
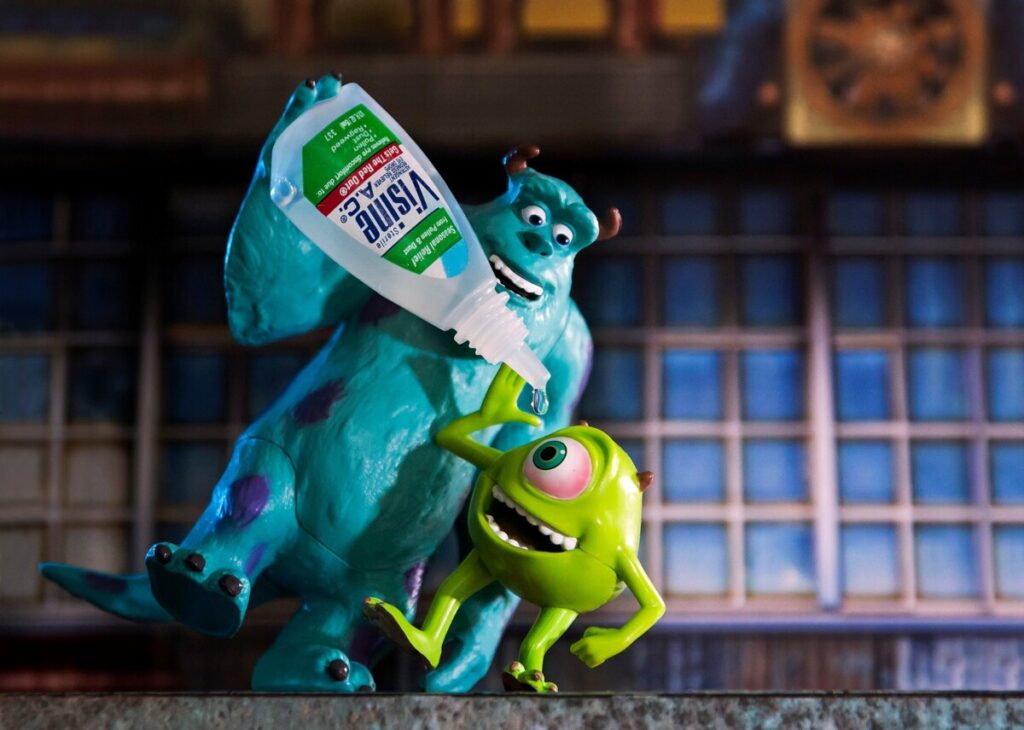
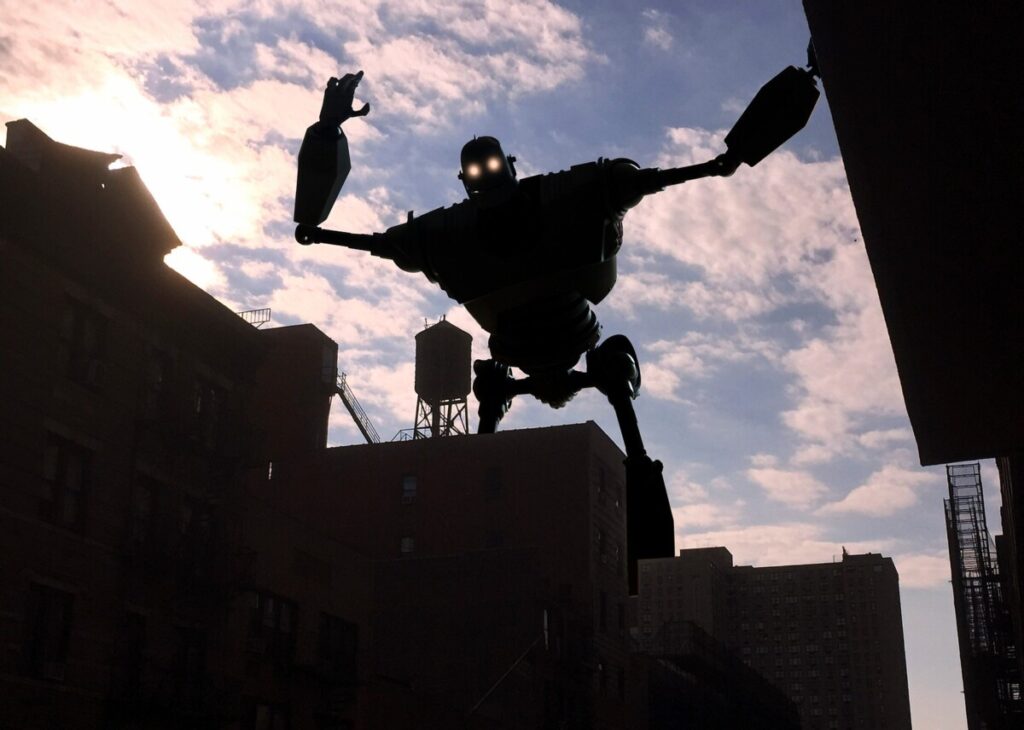












Other terms to know
Ambient Light-The light that is already there sometimes called available light
Continuous Lights-Always on, may be incandescent, halogen, fluorescent, LED
Strobe Lights – lights that fire when the exposure is made
Strobes have two bulbs:
- the modeling light which helps you see where the light will fall
- the flash bulb that fires when you press the shutter release
A trigger on the camera uses radio waves to tell the receiver to fire the light. The power pack stores the power used to make the exposure.
Modifiers
In studio photography, we put modifiers on the flash heads to change the quality of the lights. Two basic categories of modifiers are:
- Softboxes- these spread and diffuse the light. The light hits the subject from many directions making the shadows softer.
- Grids – these concentrate and focus the light. The light hits the subject from one direction making the light harsher and the shadows sharper.



Leave a Reply