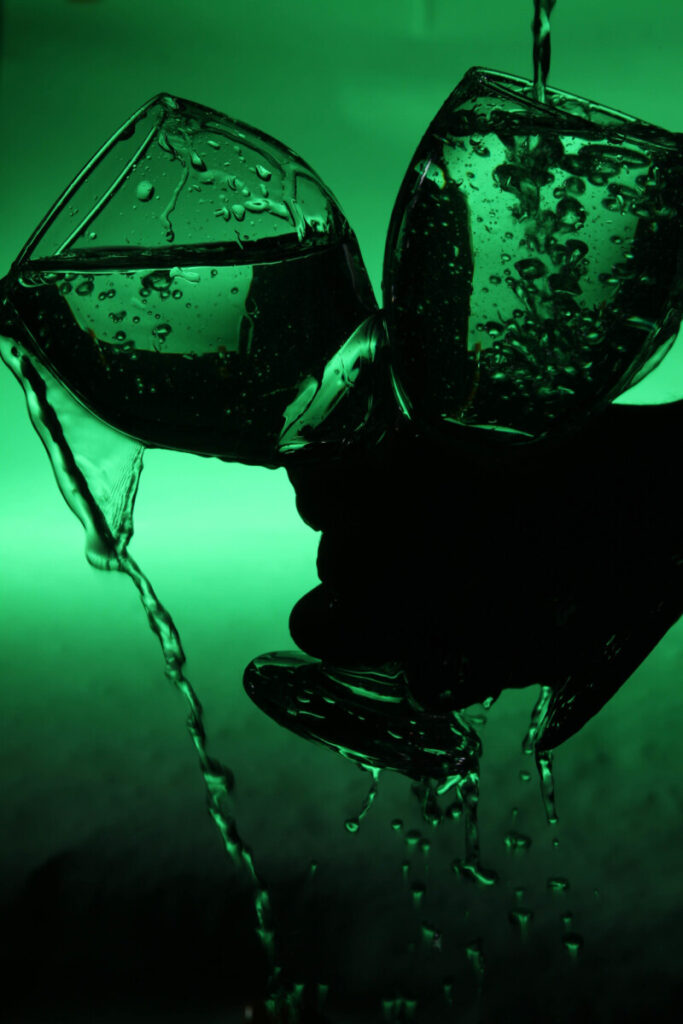
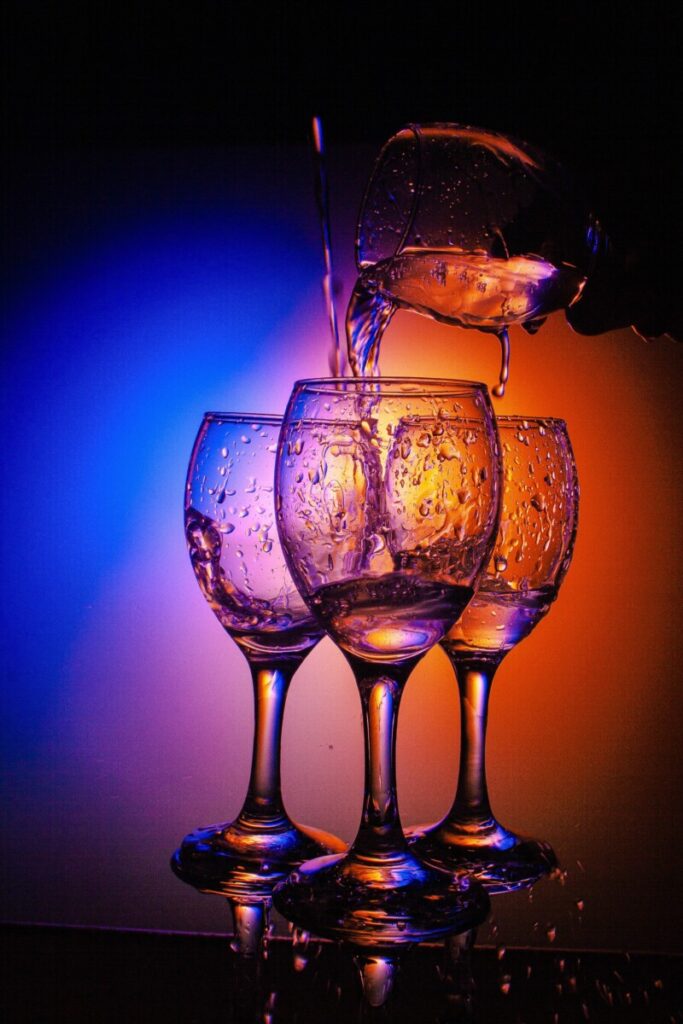
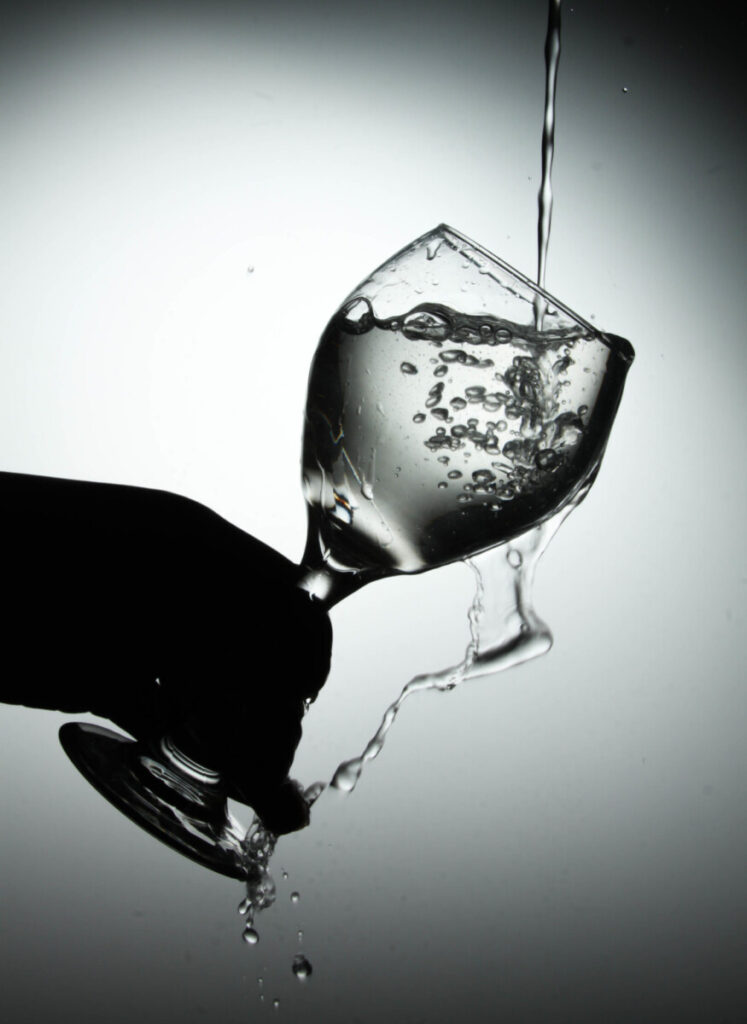
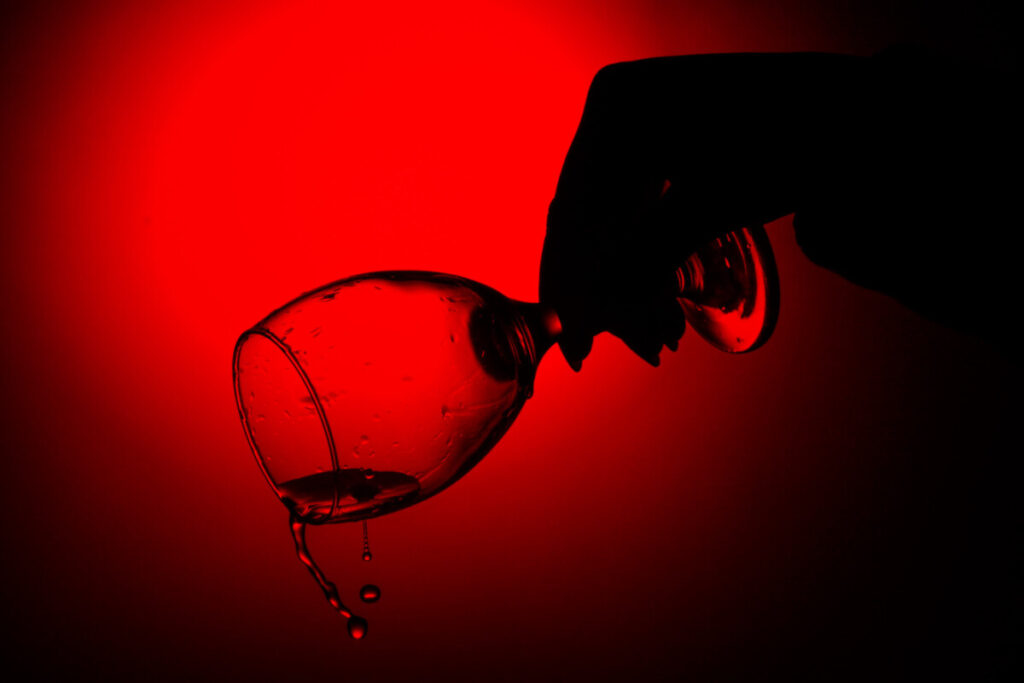
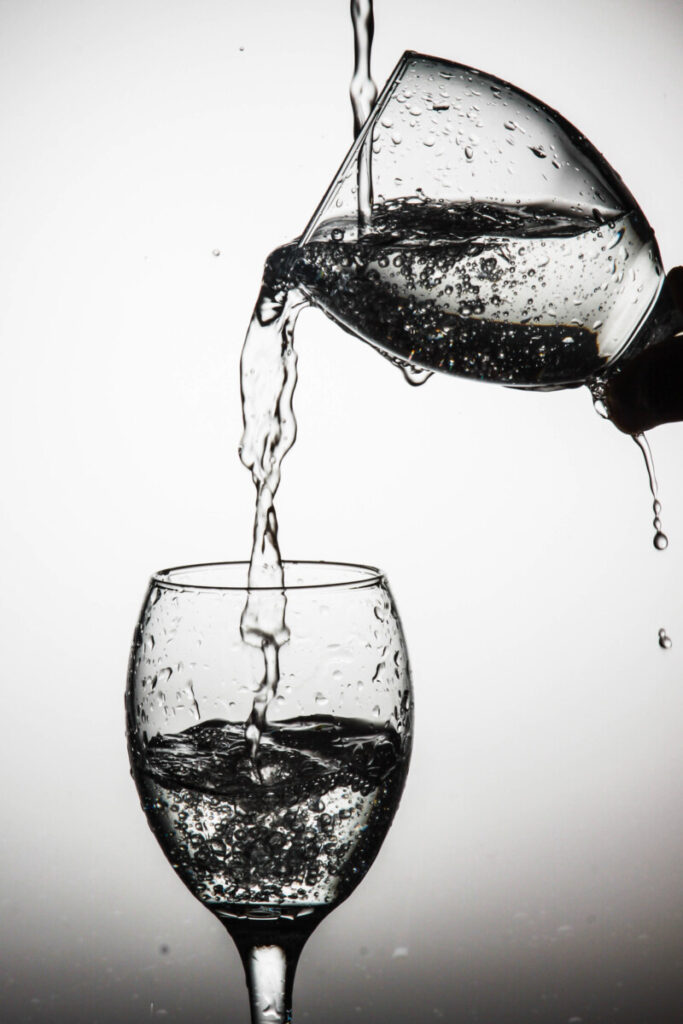





In making photographs of water and glass, you have to be concerned with the direction of the light. If you point a light at glass, it will produce a direct reflections which are mirror images of the light that produced them.
Even though glass produces direct reflection, it is transparent. In the above a diffused light is placed behind the glass. The light defines the edges and shape of the glass and water.
We use the strobe light to use a faster shutter speed and lower iso to capture motion
Terms to know for introduction to studio photography using strobe lights
Ambient Light-The light that is already there sometimes called available light
Continuous Lights-Always on, may be incandescent, halogen, fluorescent, LED
Strobe Lights – lights that fire when the exposure is made
Strobes have two bulbs:
- the modeling light which helps you see where the light will fall
- the flash bulb that fires when you press the shutter release
A trigger on the camera uses radio waves to tell the receiver to fire the light. The power pack stores the power used to make the exposure. Light meter is used to give proper exposure. Main light is set up first producing sense of direction of light and defining texture Fill light is light that is used to lighten shadows. It can be a light or a reflective surface.
Modifiers
In studio photography, we put modifiers on the flash heads to change the quality of the lights. Two basic categories of modifiers are:
- Softboxes- these spread and diffuse the light. The light hits the subject from many directions making the shadows softer.
- Grids – these concentrate and focus the light. The light hits the subject from one direction making the light harsher and the shadows sharper.



Leave a Reply