Table of Contents
Lesson Overview
Topic: Basic operation of computer, binary operations, clock speeds
Activities & Due Dates: [Activity 3] Use of Command Line
Opening
- In Raspberry Pi, you can use all UNIX commands. Below are common & useful commands that you will need to use all the time.
- LS – list the contents in the current working directory
- Ls –a <- list hidden files
- Ls –l <- list in long format
- Clear – clear console screen
- Echo – print command output
- Echo hello friend
- Man – Manual
- Man echo
- Mkdir – create directories
- Rmdir – delete directories
- Cd – change directories
Content 1 – What is Computer?
- Definition: A computer is an electromechanical device that can be programmed to change (process) information from one form to another.
- Digital devices: Understand only two different states (OFF and ON)
- How many computers do you use in your daily life?
- History of computing
- Abacus
- Mechanical computer – Blaise Pascal in 1645
- To add numbers and give a sum
- Calculators
- Babbage’s calculator – programmable calculator
- Punching card – Sort cards using a tabulator (Process) and record the result (Output)
- Electronic Computers
- ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer)
- By U.S. Army, 18,000 vacuum tubes
- Smaller and faster computers
- Semi-conductor

Content 2 – Computers live in the bit world
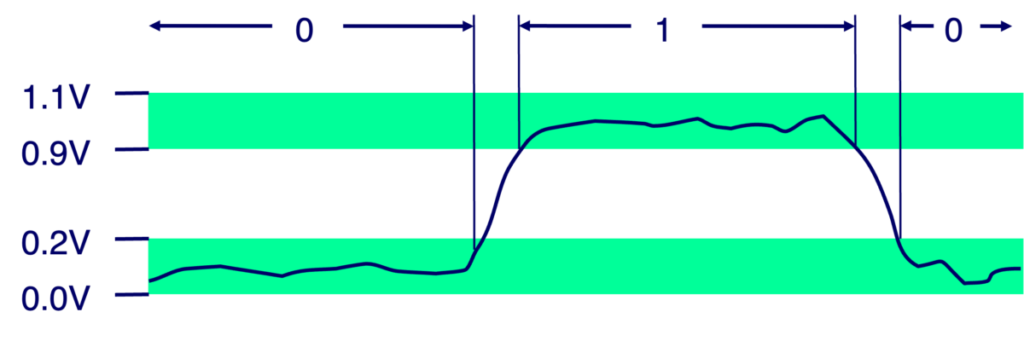
- Computers always use two types of signals: 1 for on, 0 for off.
- Each bit is 0 or 1
- By encoding/interpreting sets of bits in various ways
- Computers determine what to do (instructions)
- … and represent and manipulate numbers, sets, strings, etc…
- Why do computers always use bits?
- Electronic Implementation
- Easy to store with bistable elements
- Reliably transmitted on noisy and inaccurate wires
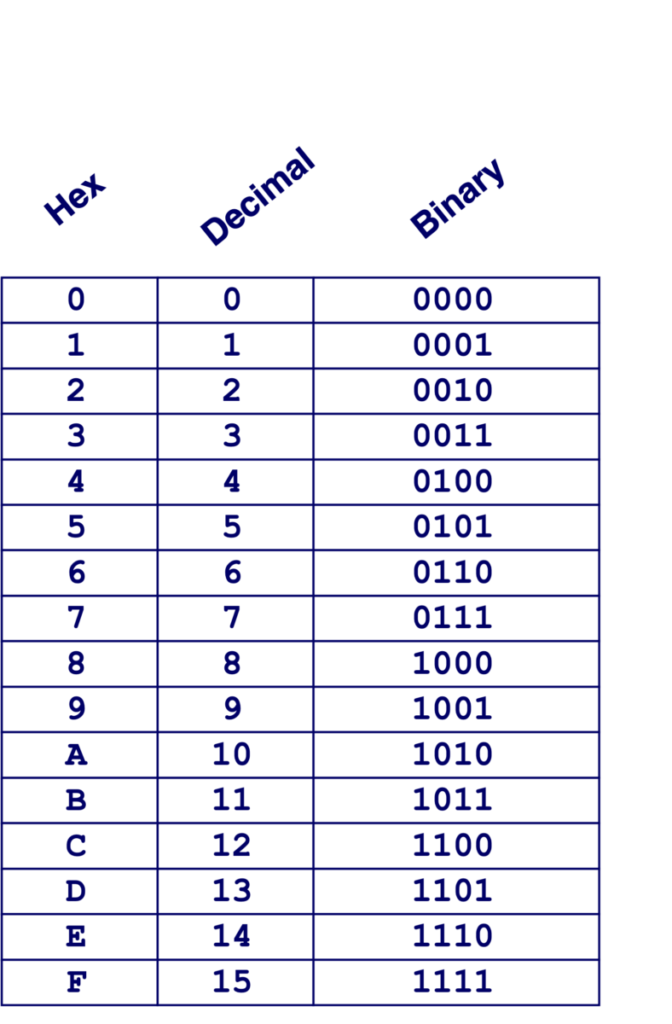
Content 3 – Encoding Byte
- Byte = 8 bits
- Binary 000000002 to 111111112
- Decimal: 010 to 25510
- Hexadecimal 0016 to FF16
- Base 16 number representation
- Use characters ‘0’ to ‘9’ and ‘A’ to ‘F’
- Write FA1D37B16 in C as
- 0xFA1D37B
- 0xfa1d37b
- Converting Binary to Decimal
- 1. Write the base 2 headings
- 2. Add base headings for 1s
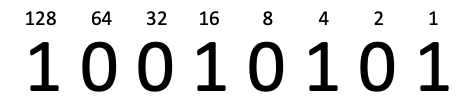
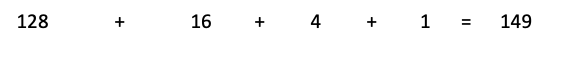
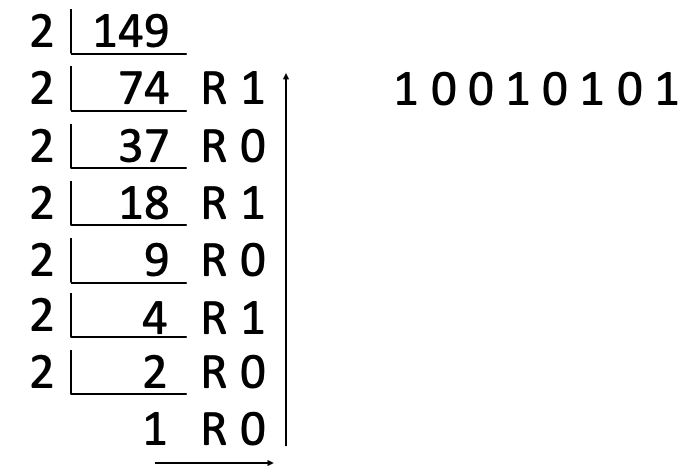
- Converting Decimal to Binary
- 149 -> binary. Divide it by 2 until the remainder turns to 1
Content 4 – Boolean Algebra
- Developed by George Boole in 19th Century
- Algebraic representation of logic
- Encode “True” as 1 and “False” as 0

Content 5 – Bit and Bytes
- Digital computers use a binary system of 0s and 1s
- Bytes: a group of 8 bits
- Kilobyte (KB): 1024 bytes
- Megabyte (MB): 1024 KB
- Gigabyte (GB): 1024 MB
- Terabyte (TB): 1024 GB
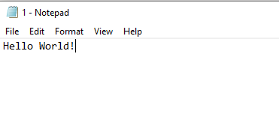
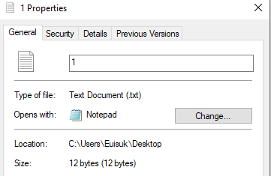
Activity 1 – Identify file size
- Open Notepad.exe
- Write Hello World!
- Close the file
- Check its file size
Activity 2 – ASCII Table
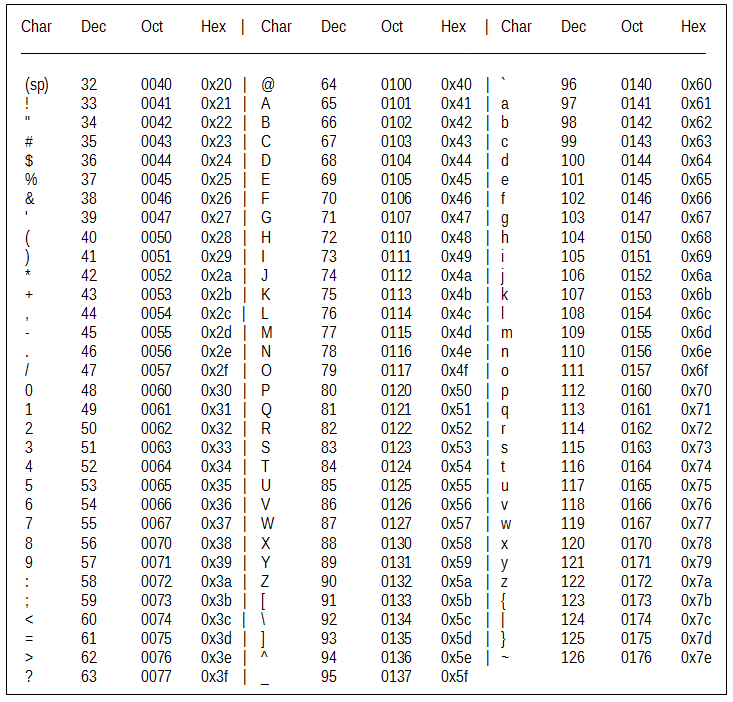
- ASCII refers to American Standard Code for Information Interchange
- 1. Visit https://www.onlinehexeditor.com/
- 2. Upload the “Hello World!” file
- 3. Report HEX codes
Activity 3 – Exploring Raspberry Pi
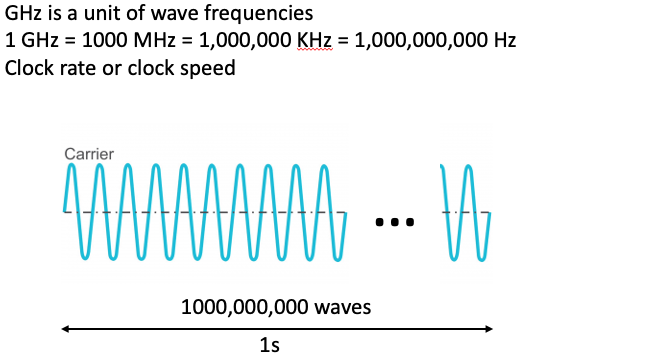
- A 1.4GHz 64-bit quad-core ARM Cortex-A53 CPU
- Dual-band 802.11ac wireless LAN and Bluetooth 4.2
- Faster Ethernet (Gigabit Ethernet over USB 2.0)
- Power-over-Ethernet support (with separate PoE HAT)
- Improved PXE network and USB mass-storage booting
- 1 GB RAM
Activity 4 – Use of command line in Raspberry Pi
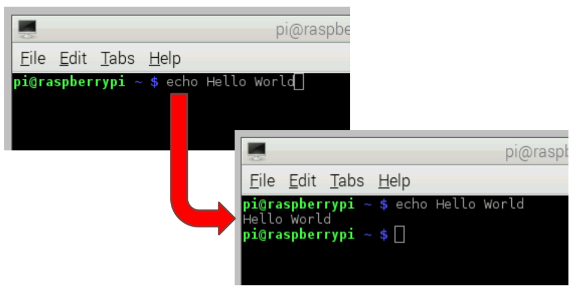
- We can communicate with Raspberry using the command line
- Learning how to use the command line
- Echo will print the argument to the console.
Activity 5 – Manual Command
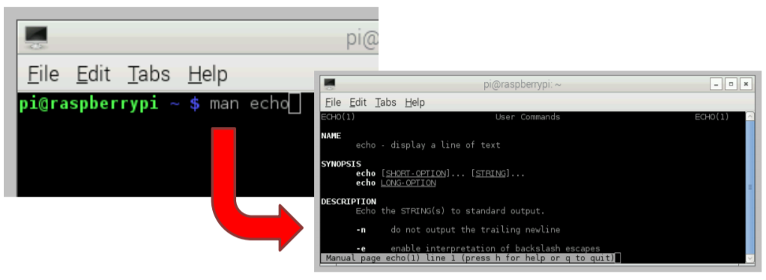
- Man will show you the manual page for the argument. Press Q on the keyboard to exit the manual page.
Activity 6 – Apropos Command
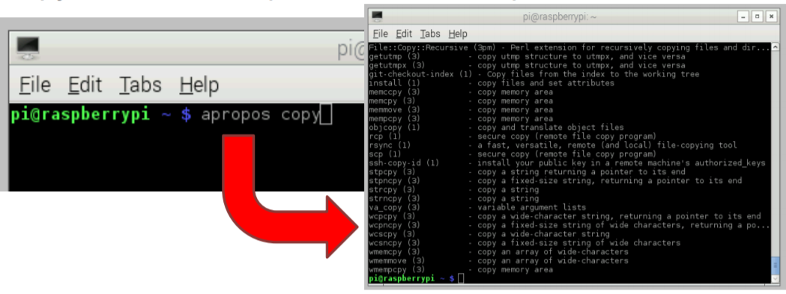
- Apropos is used to search the manual page descriptions for the specified keyword. You can find commands with “copy” in their descriptions as an example.
Activity 7 – Clear Command
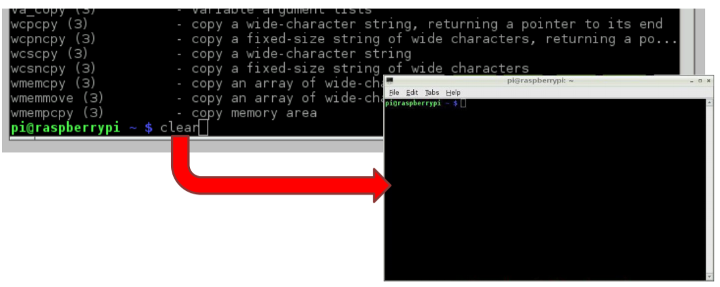
- Clear will move the prompt to the top of the console window. This effectively clears the console.
Activity 8 – LS Command
- Ls will list the directories in the current working directory.
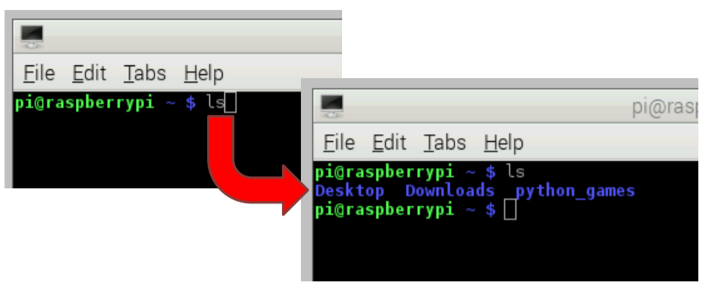
- Ls will list the directories in the current working directory.




