Table of Contents
Lesson Overview
Topic: ITEEA Learning Standards, Graphic Communication, Elements of communication system. Understanding of Raspberry Pi
Lesson Objectives
Students will be able to:
- Explain how computers work.
- Explain how microchips process information.
- Explain the configuration of Raspberry Pi 3.
Opening
Review ITEEA’s Standards for Technological Literacy related to Communication Systems. (ITEEA, 2000/2002/2007).
- Information and communication technologies include the inputs, processes, and outputs associated with sending and receiving information.
- Information and communication systems allow information to be transferred from human to human, human to machine, machine to human, and machine to machine.
- Information and communication systems can be used to inform, persuade, entertain, control, manage, and educate.
- Communication systems are made up of source, encoder, transmitter, receiver, decoder, storage, retrieval, and destination.
- There are many ways to communicate information, such as graphic and electronic means.
- Technological knowledge and processes are communicated using symbols, measurements, conventions, icons, graphic images, and languages that incorporate a variety of visual, auditory, and tactile stimuli.
Activity 1 – Graphic Communication.
- See the assembly guide for furniture.
- Discuss how the graphical illustrations of the guide are effective. Why the guide did not include any languages?
- Identify the best method that you can communicate with somebody in the situations below.
- When helping your friend know the way to go to library
- Teach how to assemble an IKEA furniture
- Teach how to do video editing
- Share how fun the football game played the last night
- When want to inform students not to make noise in the hallway
Content 1- Types of Communication Systems
There are so many ways to communicate with others. The types of communication can be folded into four ways.
- Text-based communication: Email, text messages, Social media
- Pros: Fast and precise, lightweight data
- Cons: Subject to interpretation, static
- Visual communication: Photos, images, videos
- Pros: connect remote people in real-time
- Cons: heavy data, less precise
- Audio communication: Phone, microphone
- Pros: connect remote people
- Cons: Need a microphone
- Multimedia communication: More than two media, video conferences, TV, and others
- Pros: multiple media
- Cons: heavy data
Content 2 – Input of Communication Systems
Communication systems can be explained using the Universal Systems model. The system model has the four elements, input-process-output-feedback. The input of the system includes people, capital, time, information, energy, materials, and tools & machines.

Activity 2 – Understanding Raspberry Pi 3.
- What is Raspberry Pi?
- Developed by the University of Cambridge’s Computer Laboratory
- Lower barriers to microcomputers.
- Designed for education
- A credit card-sized PC
- Plugs into a TV or monitor Inexpensive(ish) ~$35 each
- Capability: Programming, Electronic Projects, Office, Play HD Videos
- Variations of Raspberry Pi
- Hardware platform
- Raspberry Pi Zero ($5)
- Raspberry Pi
- Raspberry Pi 2
- Raspberry Pi 3 (with Wifi + Bluetooth)
- Software platform
- Noobs
- Raspbian
- 3rd OS
- https://www.raspberrypi.org/downloads/
- Structure of Raspberry Pi
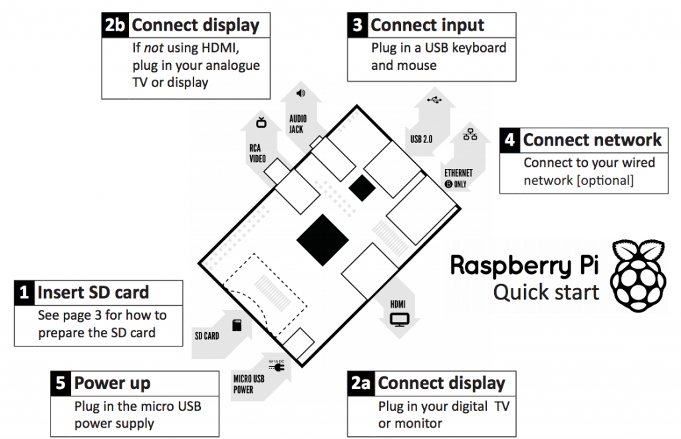
- Compare the structure of Raspberry Pi and a traditional computer. What are the differences between modules and the structure of Raspberry Pi?
Closing
Identify a situation that graphical communical is effective.
List the types of communication methods.
List the elements of input of the communication system with a communication device.



