Contents [hide]
Reading
- (OpenStax)Loading...
- 3.4 Proteins (CNX OpenStax)
- 3.5 Nucleic Acids (CNX OpenStax)
Learning Objectives
- Draw the basic structure of an amino acid, and explain the relationships between amino acids, proteins, and peptide bonds.
- Describe the levels of organization of protein in terms of its primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures.
- Define the term nucleic acid, give the subunits of a nucleotide, and name the two main types of nucleic acids found in living organisms.
- Explain why ATP is important and describe its general structure.
Proteins
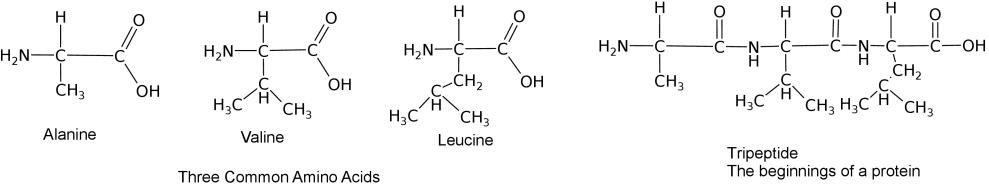
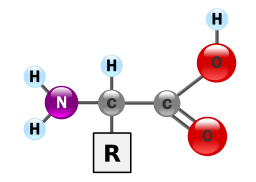 Proteins provide much of the structural and functional capacity of cells. Proteins are composed of monomers called amino acids. Amino Acids are hydrocarbons that have an amino group (-NH2) and an acidic carboxyl group (-COOH).The R group represents a hydrocarbon chain with a modification that alters the properties of the amino acid. 20 universal amino acids are used to construct proteins. The variation in functional groups along the amino acid chain gives rise to the functional diversity of proteins.
Proteins provide much of the structural and functional capacity of cells. Proteins are composed of monomers called amino acids. Amino Acids are hydrocarbons that have an amino group (-NH2) and an acidic carboxyl group (-COOH).The R group represents a hydrocarbon chain with a modification that alters the properties of the amino acid. 20 universal amino acids are used to construct proteins. The variation in functional groups along the amino acid chain gives rise to the functional diversity of proteins.

20 amino acids and their properties. A 21st amino acid on this table represents the non-universally found selenocysteine.
How amino acids interact with each other and the environment
Use the following simulation to test how a polypeptide chain with fold based on the type of solution it is in and the composition of the amino acids.
- Protein Folding Simulation (CC BY 4.0 Concord Consortium)
Protein Structure
- Primary Structure (1°): The sequence of amino acids read from the Amino or N-terminal end of the molecule to the Carboxyl or C-terminal end
- Tyr-Cys-Arg-Phe-Leu-Val-….
- Secondary Structure (2°): local three-dimensional structures that form from interactions of amino acids, like hydrogen bonding
- Alpha Helix – coils occurring from the H-bonds between N-H and C=O groups along the backbone of the protein

Side view of α-helix illustrating H-bonds in magenta between carboxyl oxygen (red) and amine nitrogen (blue) Credit: WillowW [CC-BY-SA 3.0]

Top-down view of an α-helix Credit: WillowW [CC-BY-SA 3.0]

Side view of ribbon diagram of α-helices traversing a membrane. Credit: Andrei Lomize [CC-BY-SA 3.0]
- Beta Sheets – laterally connected strands or sheets of amino acids occurring from the H-bonds between N-H and C=O groups along the backbone of the protein
- Alpha Helix – coils occurring from the H-bonds between N-H and C=O groups along the backbone of the protein
- Tertiary structure (3°): overall 3-D structure of the peptide chain
- Quaternary structure(4°): multimeric protein structure from assembling multiple peptide subunits
Disruption to Structure
The weak interactions that govern the secondary and tertiary structure of proteins can be disrupted through the application of energy, removal of the water environment, alteration of salt content or changes in the pH. The unfolding or misfolding of proteins from these disruptions is called denaturation. Changes in salt and pH will disrupt the charges on amino acids to disrupt structure. Since eggs are mostly protein and water, it is understood how frying an egg can push the water out (as steam) to leave behind a a congealed gelatinous solid. Similarly, cooking generally works to denature proteins. As such, there are methods of cooking that rely , not only on heat, but on dehydration or curing (using salts) and changes in pH (using acids or bases).
Diversity of Proteins
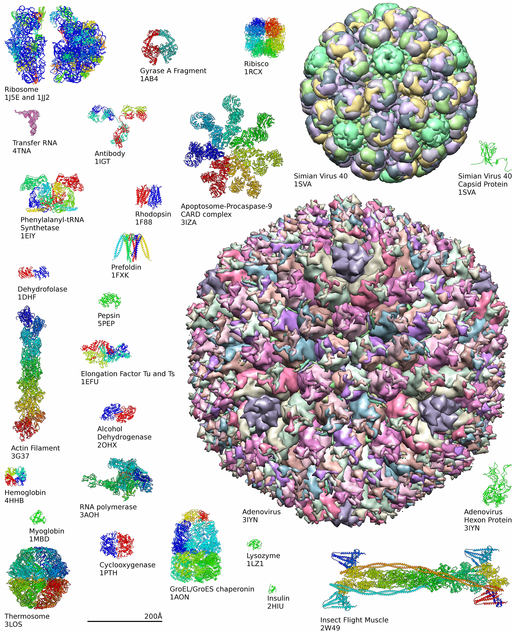
Credit:Axel Griewel [CC-BY-SA 3.0]
Protein Function
Interactive Animation @ PDB :https://cdn.rcsb.org/pdb101/molecular-machinery/
- Enzymes
- Help “catalyze” chemical reactions
- Structural Proteins
- Give support, strength, flexibility
- Examples: collagen, elastin, keratin
- Storage Proteins
- Storage of amino acids, for building proteins later or energy
- Examples: egg albumin (ovalbumin), Casein (in milk)
- Transport Proteins
- Examples: Hemoglobin (O2), H+ pump
- Signaling Proteins
- Hormonal Proteins and receptor proteins
- Example: Insulin and Insulin receptor
- Motor Proteins
- Actin and myosin perform muscle contraction
- Immune Defense Proteins
- Antibodies help fight infection
Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids are polymers that were named because they were first described in the nucleus. There are 2 types, deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid (DNA & RNA). DNA is the storage vessel for genetic information and RNA largely plays a role in expressing this genetic information.
Their monomers are called nucleotides, which are made up of individual subunits. Nucleotides consist of a 5-Carbon sugar (a pentose), a charged phosphate and a nitrogenous base (Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, Cytosine or Uracil). Each carbon of the pentose has a position designation from 1 through 5. One major difference between DNA and RNA is that DNA contains deoxyribose, and RNA contains ribose. The discriminating feature between these pentoses is at the 2′ position where a hydroxyl group in ribose is substituted with a hydrogen.
The following video illustrates the structure and properties of DNA
DNA is a double helical molecule. Two anti-parallel strands are bound together by hydrogen bonds. Adenine forms 2 H-bonds with Thymine. Guanine forms 3 H-bonds with Cytosine. This AT & GC matching is referred to as complementarity. While the nitrogenous bases are found on the interior of the double helix (like rungs on a ladder), the repeating backbone of pentose sugar and phosphate form the backbone of the molecule. Notice that phosphate has a negative charge. This makes DNA and RNA, overall negatively charged.
ATP
- ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is composed of adenine, ribose, and three phosphates
- In cells, one phosphate bond is hydrolyzed – Yields:
- The molecule ADP (adenosine diphosphate)
- An inorganic phosphate molecule
- Energy used for work in the cell

The structure of ATP. Credit: Smokefoot [CC-BY-SA 4.0]

Energy is released from the hydrolysis of the terminal phosphate. Credit: Muessig [CC-BY-SA 3.0]
Additional Resources
- Fats and Proteins http://www.visionlearning.com/en/library/Biology/2/Fats-and-Proteins/62