In this section we will talk a little bit about the technical aspect of digital video and audio. You will get familiarized with the terms and vocabulary of the movie industry. It is also a preparation for your quizzes. You will have questions related to the topic in your first quizz.
Frame and Frame Rate
WATCH The Secrets Of frame Rates
- Frame rate (expressed in frames per second or FPS) is the frequency (rate) at which consecutive images called frames appear on a display. The term applies equally to film and video cameras, computer graphics, and motion capture systems. Frame rate may also be called the frame frequency, and be expressed in hertz.
What is the relationship between the frame rate and the quality of the video?
- Frame rate greatly impacts the style and viewing experience of a video. Different frame rates yield different viewing experiences, and choosing a frame rate often means choosing between things such as how realistic you want your video to look, or whether or not you plan to use techniques such as slow motion or motion blur effects.
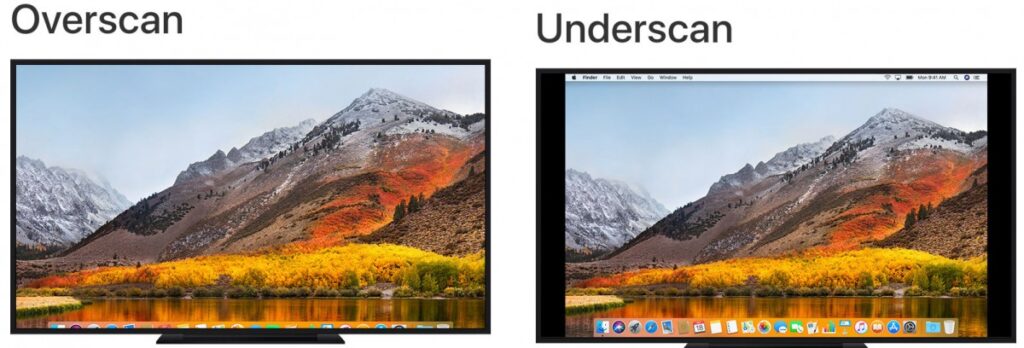
Overscan, Underscan and the Safe Zone
- Overscan: It refers to a cropped image on your TV screen.
- Underscan: The full image.
- Safe zone: The area that virtually all televisions would show, confirming that no text would be cut off.
Aspect Ratio
- An aspect ratio specifies the ratio of width to height.
WATCH what type of effects aspect ratios bring to movie.
Common Aspect Ratios in Digital Video
The commonly used aspect ratios are:
- Widescreen (16:9) It is the standard aspect ratio commonly shared by online videos, documentaries, and films. It captures a large amount of data with details.
- Vertical (9:16) It is the video recorded on your phone.
- Fullscreen (4:3) It is the aspect ratio that was used on television before widescreen was used. It focused on a particular element at a time.
- Square (1:1) It is a perfect square ratio that is commonly used on Instagram.
- Anamorphic (2.40:1) It is a wide widescreen often used in movies. It is similar to 16:9 but the top and bottom are cropped. This effect gives it a cinematic feel.
See on working with aspect ratio on Adobe Premiere.
Frame Sizes or Resolution for HD, FHD, QHD, 4K and 8K.
When high-definition TVs became the norm, manufacturers developed a shorthand to explain their display resolution.
The most common numbers you see are 720p, 1080p, 1140p or 4K. These shorthand numbers are sometimes used to describe computer monitors as well, even though in general a monitor is capable of a higher definition display than a TV.
Here’s how the shorthand translates:
- HD or “HD Ready” resolution > 720p = 1280 x 720
- FHD or “Full HD” resolution > 1080p = 1920 x 1080
- QHD or Quad HD resolution > 1440p = 2560 x 1440
It is typically seen on gaming monitors and on high-end smartphones. 1440p is four times the resolution of 720p HD or “HD ready.” To make things even more confusing, many premium smartphones feature a so-called 2960×1440 Quad HD+ resolution, which still fits into 1440p. - 4K, UHD or Ultra HD resolution > 4K or 2160p = 3840 x 2160
It is a huge display resolution, and it is found on premium TVs and computer monitors. 2160p is called 4K because the width is close to 4000 pixels. In other words, it offers four times the pixels of 1080p FHD or “Full HD.” - 8K > 8K or 4320p = 7680 x 4320
It offers 16 times more pixels than the regular 1080p FHD or “Full HD” resolution. For now, you see 8K only on expensive TVs from Samsung and LG.
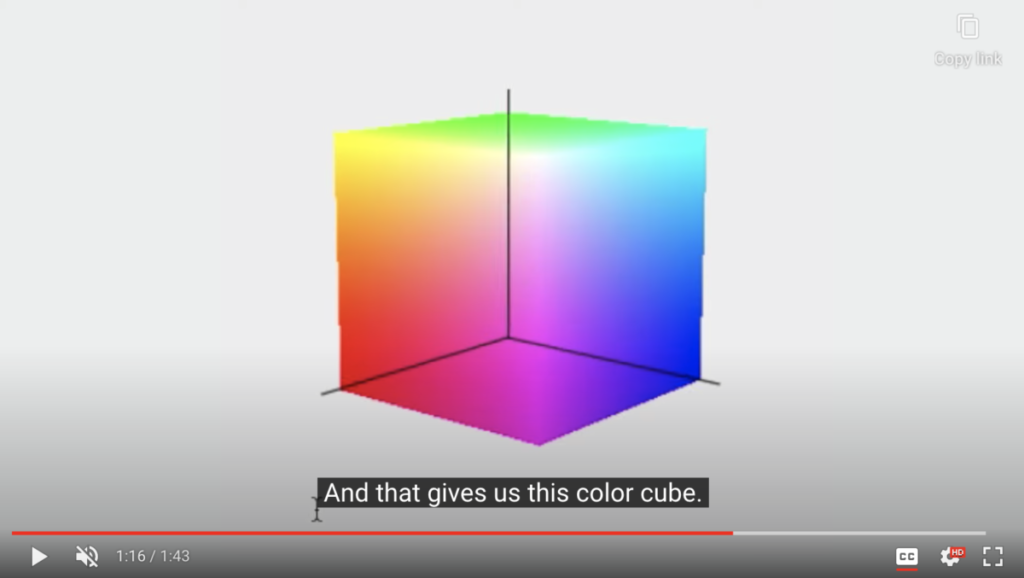
What is the color space for video?
The color space for video is RGB.
Check a video explaining what is color space from the Pixar Animation Studios and Khan Academy.
What are the key considerations in having a good sound for your video?
A professional microphone, don’t forget that audio is half of every video!
What are the strategies for reducing video file size?
- Reduce Video Length
If you have a long video, you may want to cut it into segments to reduce loading time. Try to keep your videos as brief as possible and cut out any unnecessary parts during the editing process. - Lower Video Resolution
The lower the resolution, the smaller your file. YouTube offers on the spot video compression, giving you the choice to adjust the resolution from the video player. Many videos on YouTube work well with a resolution of 360p, although there is support for HD. - Change the Video Codec
There are many codecs to choose from. The most popular lossless codec is H.264, which preserves HD quality. Other common codecs are AVI, WMA, XviD, Real Audio, and Apple Video. - Lower the Audio Bitrate
Audio tracks are appended to video files. Different codecs handle the audio compression. If high fidelity vocals, or music isn’t a priority, you can reduce the file size quite a bit by lowering the audio bitrate. - 3rd Party Video Hosting
You can also host your videos on video sharing sites to save space on your server. Video sharing sites like YouTube and Vimeo make it easy to distribute your videos.


