Table of Contents
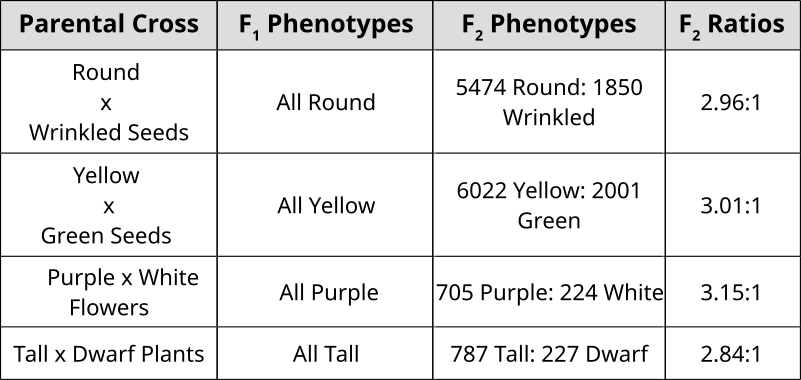
Mendel’s Observations
Mendel carefully recorded his results while breeding pea plants. He was able to track the inheritance of one trait on its own or two traits together. We call these monohybrid and dihybrid crosses and can predict their outcomes using Punnett squares.
We can use statistics to predict the outcomes of Mendelian crosses beyond that of a simple Punnett square.
Probability: Past Punnett Squares
Punnett squares are convenient for predicting the outcome of monohybrid or dihybrid crosses. The phenotypic ratio of the offspring of two heterozygous parents is 3:1 in a single trait cross or 9:3:3:1 in a two-trait cross. Performing a three or four trait cross becomes very messy. In these instances, it is better to follow the rules of probability. Probability is the chance that and event will occur expressed as a fraction or percentage. In the case of a monohybrid cross, 3:1 ratio means that there is a 3/4 (0.75 or 75%) chance of the dominant phenotype with a 1/4 (0.25 or 25%) chance of a recessive phenotype.
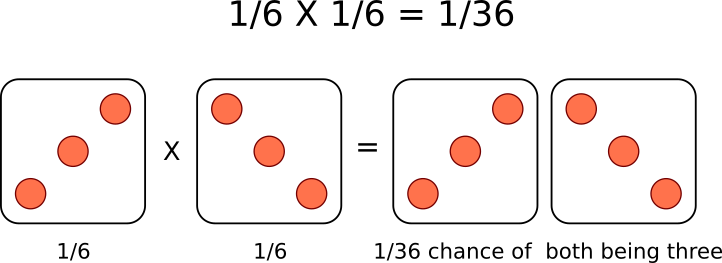
A single die has a 1 in 6 chance of being a specific value. In this case, there is a 1/6 probability of rolling a 3. It is understood that rolling a second die simultaneously is not influenced by the first and is therefore independent. This second die also has a 1/6 chance of being a 3.
We can use the multiplication rule to determine the probability of rolling two dice and having them both come up as 3:
We can understand these rules of probability by applying them to the dihybrid cross and realizing we come to the same outcome as the two monohybrid Punnett squares as with the single dihybrid Punnett square.
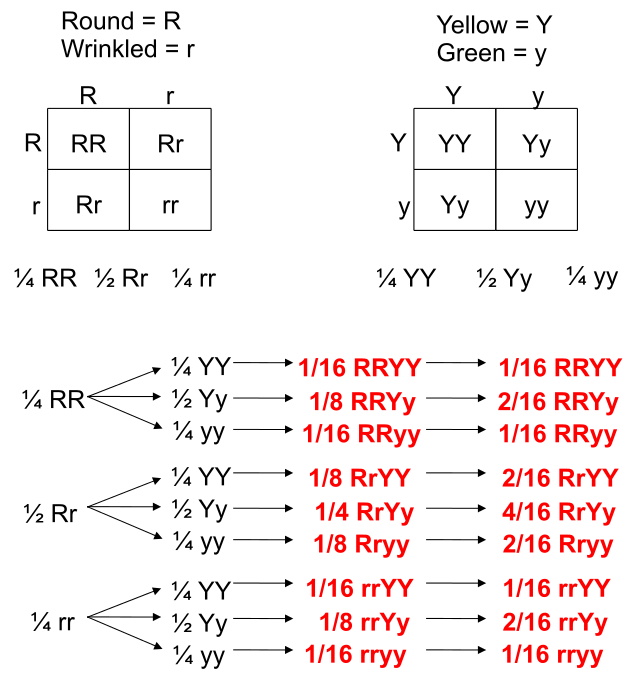
This forked line method of calculating probability of offspring with various genotypes and phenotypes can be scaled and applied to more characteristics.





