Table of Contents
Explore the geometry of molecules
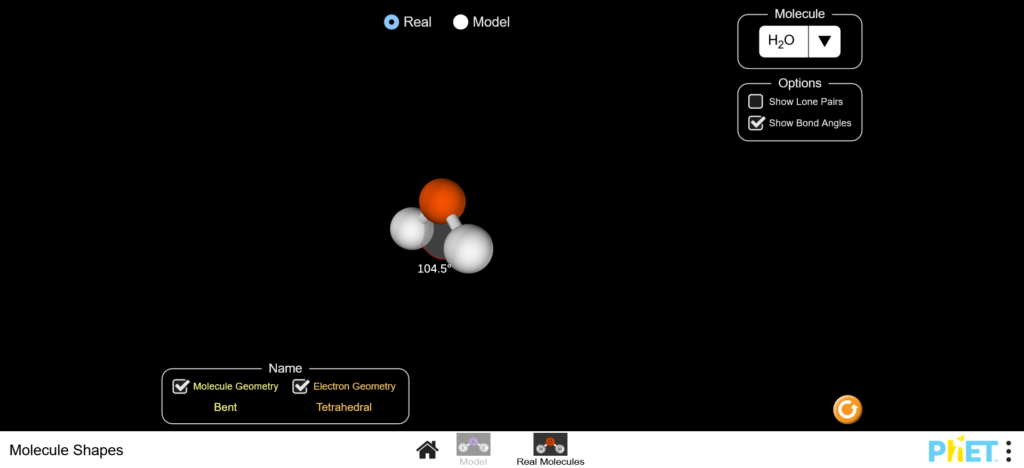
In this simulation, explore the molecular and the electronic geometry of model or real molecules.
Example: water’s electronic geometry is tetrahedral whereas the molecule is bent.

Importance of organic compounds
Living things are composed of organic molecules primarily made up of the elements carbon and hydrogen. Molecules of hydrogen and carbon (referred to as hydrocarbons) have the property of being non–polar. Yet 70- 90% of cells are composed of water (a polar compound). Polar substances mix with other polar substances. Likewise, non-polar substances interact with other non-polar compounds. Polar and non-polar compounds are immiscible (unable to mix).
So how do cells keep from falling apart in a water environment?
The answer is: functional groups!




