Table of Contents
Pyruvate oxidation reaction
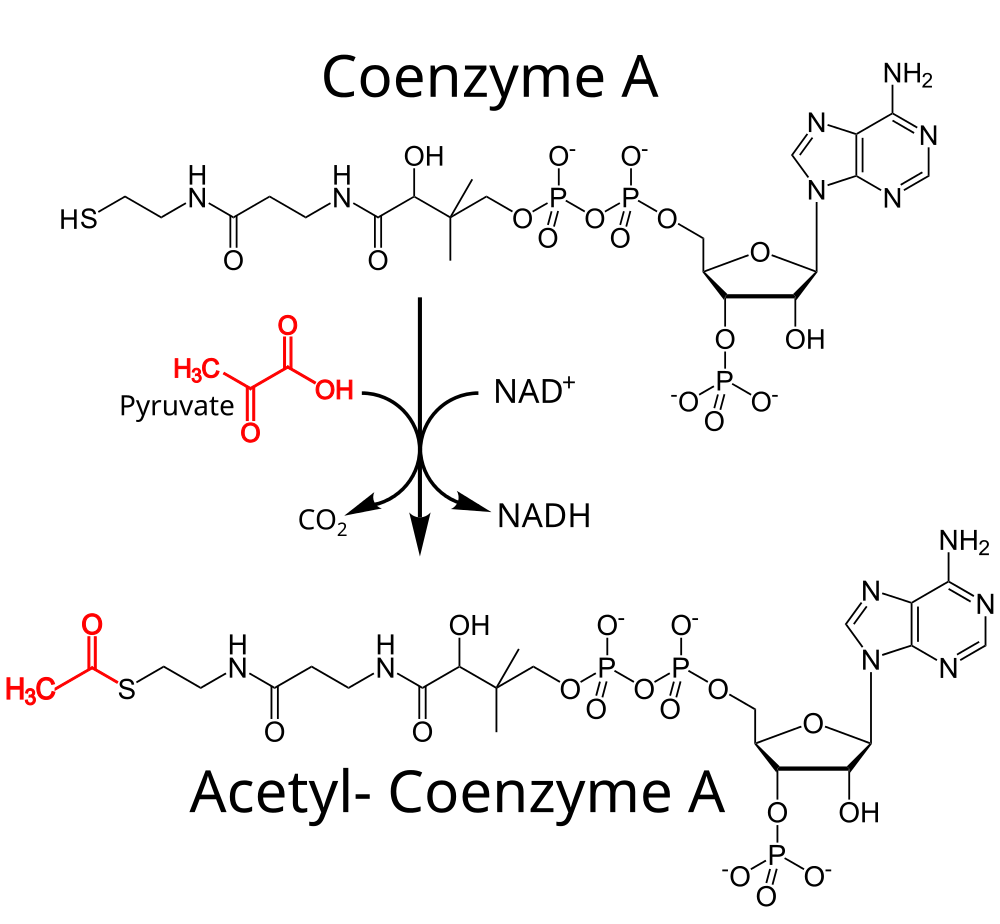
In the presence of O2, aerobic organisms will use a reaction of pyruvate decarboxylation in the cytosol. This reaction generates a molecule of Acetyl-CoA from the Coenzyme A which can enter the mitochondria.
Notice in the diagram, in red, the acetate group of pyruvate (that comes from glucose) is “activated” and will be incorporated in the Citric acid cycle.
When there is an excess of carbohydrates, the Acetyl-CoA is used as a starting point for long-term energy storage in lipid synthesis.



