Table of Contents
Discovering Buffers
- Take a small beaker of distilled water and determine its pH. Add one drop of strong acid or of strong base to the water and observe the pH reading on the meter.
- Now take a small sample of either the standard pH buffer or of any other buffer solution in the lab and add a drop of either strong acid or strong base. Does the reading on the pH meter remain constant or does it change rapidly as it did with the distilled water?
Titration of Acetic Acid
Overview
In this activity, you will perform a titration of acetic acid (a weak acid) with sodium hydroxide (a strong base). The data you gather during class will be used to complete the Lab 3 assignment.
Materials
Each lab group will need the following materials:
- 50 ml of 0.1 M acetic acid
- 5 drops of phenolphthalein
- 0.1 N NaOH
- 250 ml beaker
- 50 ml buret
- ring stand with clamp
- pH probe
Method
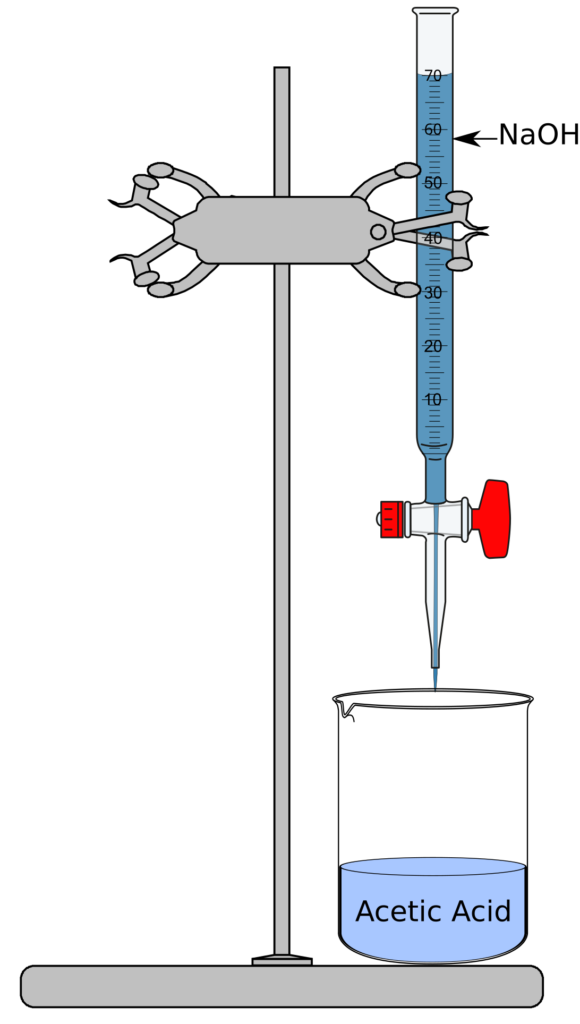
- Place 50 ml of 0.1M acetic acid into a 250ml beaker.
- Add 5 drops of phenolphthalein indicator to the acid and swirl briefly.

- Determine the initial pH with probe and record this in your data.
- Fill the buret with 0.1 N NaOH.
- Your set up should look like the image below.
- Open the tap of the buret to add 3 ml of NaOH and to the beaker and swirl briefly to mix.
- Use the probe to record the pH and observe the color of the solution. Record both pieces of data.
- Continue to add the NaOH in increments of 3 ml (with swirling) and record the pH and color of the solution until the pH reaches 10.
Scatterplot Tutorial
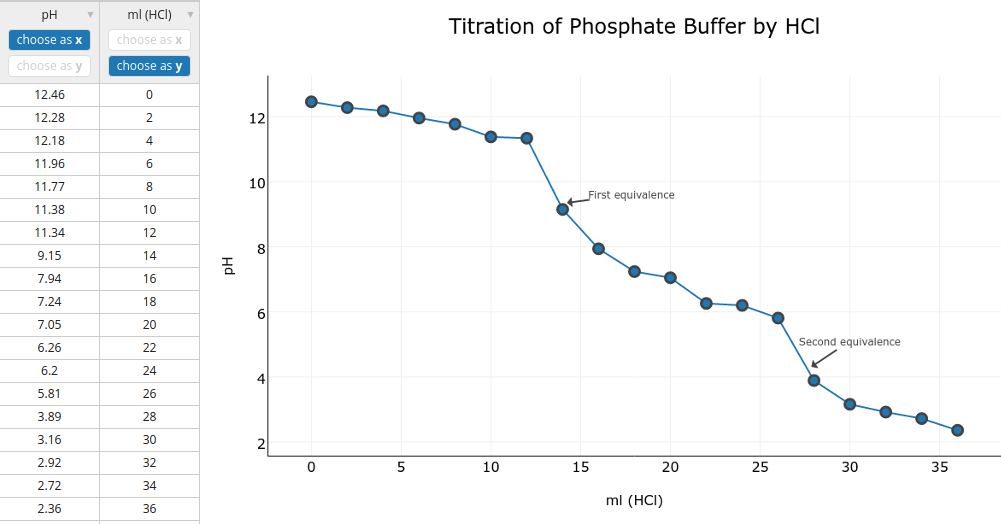
You will use the data you collected to create a scatterplot as part of the Lab 3 assignment. You will plot the pH readings on the y-axis and the volume of NaOH added on the x-axis. If you do not have access to Excel, you can make your scatterplot in Plot.y or Google Sheets.
Your scatterplot should resemble the example below:
You can download this practice data to try in Plot.ly. Follow this tutorial on using Plot.ly to generate a graph. However, do not draw a trendline.