Table of Contents
Elements and Compounds
Organisms are composed of matter. Matter is made of elements, which are the simplest forms of matter and cannot be broken down. Two or more elements can be chemically combined to form a compound. The ratio of elements in a compound is fixed. For example, the compound water will always consist of two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen. Changing the ratio changes the properties and identities of the compound–adding one more oxygen atom to water results in hydrogen peroxide.
Atoms
An atom is the smallest piece of matter that still has the properties of that particular element. Atoms are composed of three types of subatomic particles: the positive protons, the neutral neutrons, and the negative electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of the atom and make up most of the atom’s mass. Electrons are found outside the nucleus and are responsible for the specific chemical properties of that atom.
Atomic Number and Mass Number
The number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom give that atom its atomic number. Elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. The number of protons plus the number of neutrons in the nucleus make up the atom’s mass number.
All atoms of the same element have the same atomic number. However, atoms of the same element can have different mass numbers due to different amounts of neutrons. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes.

Ions
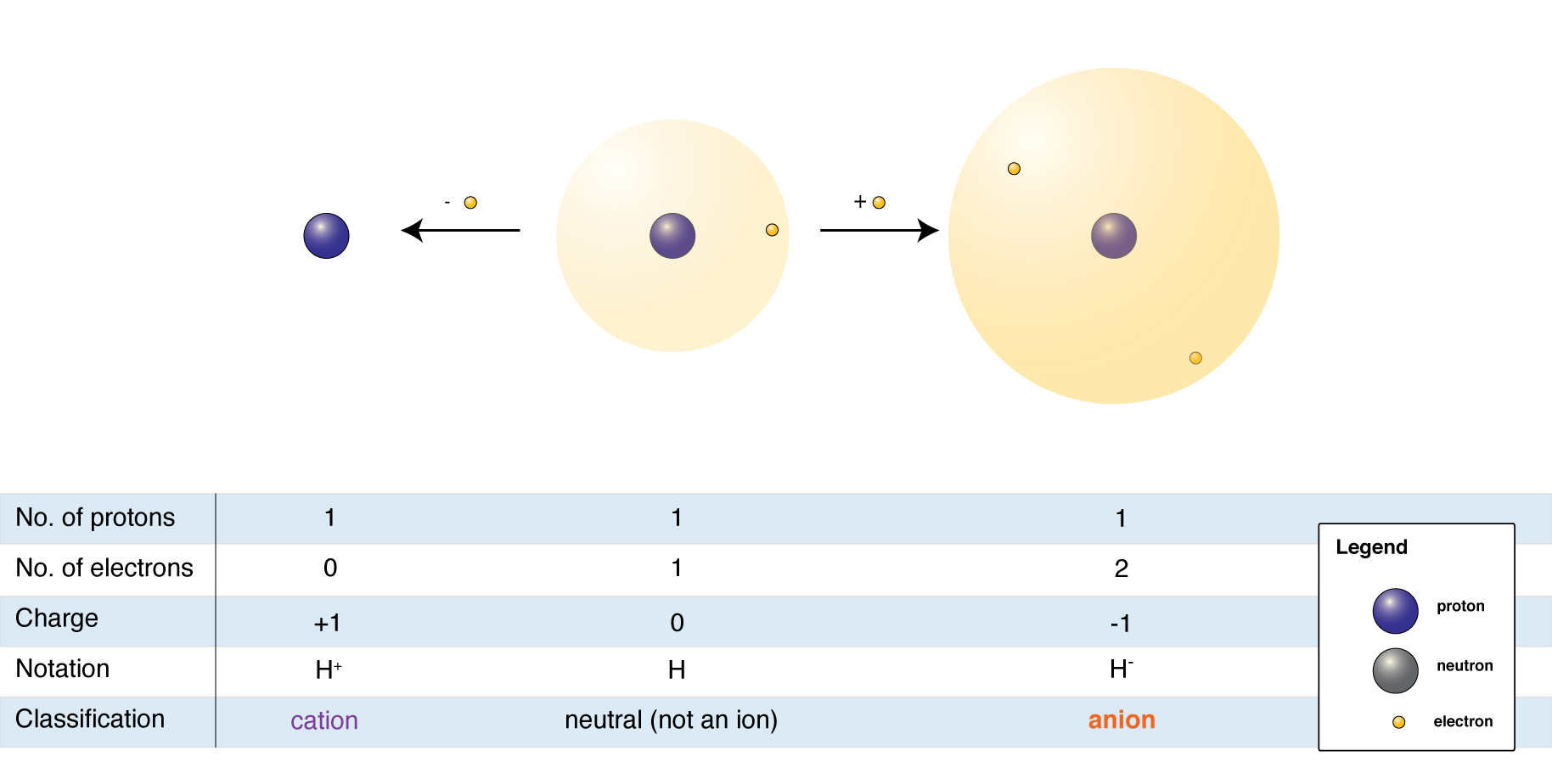
The elements on the Periodic Table are in their neutral state. This means that they have equal numbers of protons and electrons. When an atom loses one or more electrons, it becomes a positively-charged ion called a cation. When an atom gains one or more electrons, it becomes a negatively charged ion called an anion.
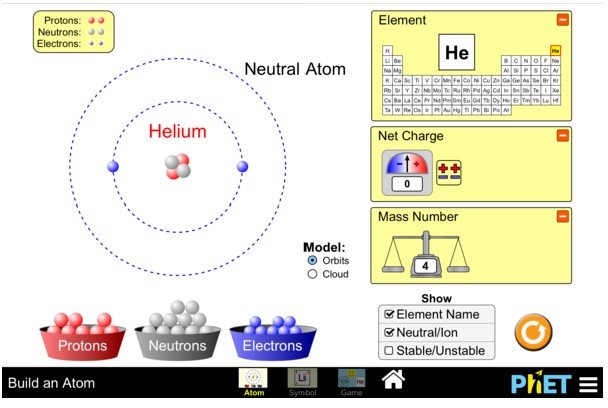
Practice: Building Atoms
- Start by adding protons to the atom one-by-one.
- What happens to the identity of the atom as you add protons?
- Build an atom that has 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons.
- What is the name of this element?
- What happens to the identity of this element if you add or remove neutrons?
- Build an atom that has 3 protons, 4 neutrons, and 3 electrons?
- What happens to the charge of the atom if you remove an electron?
- What happens to the charge of the atom if you add an electron?