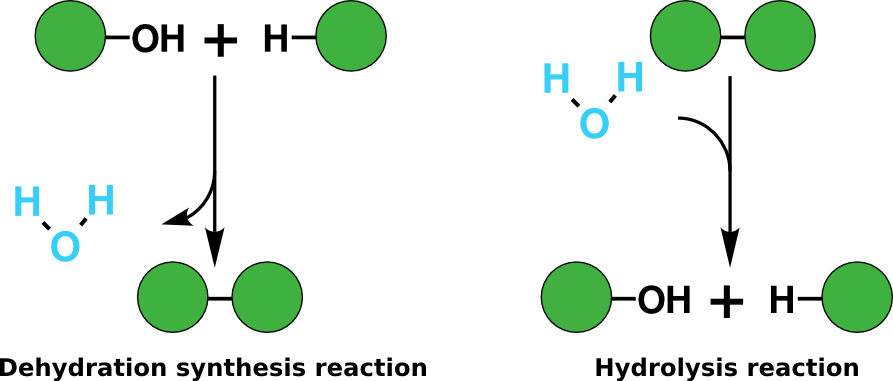
The common organic compounds of living organisms are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Each of these are macromolecules or polymers made of smaller subunits called monomers. The bonds between these subunits are formed by a process called dehydration synthesis. This process requires energy; a molecule of water is removed (dehydration) and a covalent bond is formed between the subunits. Because a new water molecule is formed, this is also referred to as condensation. The opposite where water and energy are used to break apart polymers into simpler monomers is called hydrolysis (hydro– water, lysis– to break or split).