Real Numbers
Any number we see that is in the categories of numbers is a real number represented by the symbol R except the complex numbers. Real Numbers consist of all rational and irrational numbers including fractions, decimals, integers, and whole numbers.
Subsets of Real Numbers
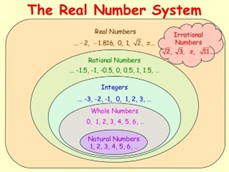
All numbers except complex numbers are real numbers. Therefore, real numbers have the following five subsets:
- Natural numbers: All positive counting numbers make the set of natural numbers, N = {1, 2, 3, …}
- Whole numbers: The set of natural numbers along with 0 represents the set of whole numbers. W = {0, 1, 2, 3, …}
- Integers: All positive counting numbers, negative numbers, and zero make up the set of integers. Z = {…, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, …}
- Rational numbers: Numbers that can be written in the form of a fraction p/q, where ‘p’ and ‘q’ are integers and ‘q’ is not equal to zero are rational numbers. Q = {-2, 0, -5, 3/5, 4.25}
- Irrational numbers: The numbers that are square roots of positive rational numbers, cube roots of rational numbers, etc., such as √2, come under the set of irrational numbers. (¯Q ) = {√3, -√7}
Symbol of Real Numbers
Real numbers are represented by the symbol R. Here is a list of the symbols of the other types of numbers that are all real numbers.
- N – Natural numbers
- W – Whole numbers
- Z – Integers
- Q – Rational numbers
- ¯Q – Irrational numbers
N, W, Z, Q, ¯Q belong to R.
Let’s look at this number system to visualize the classification of real numbers.

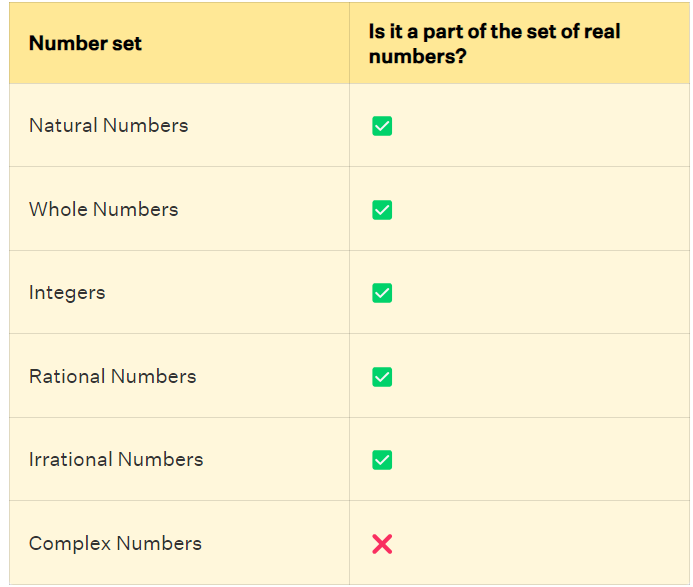
This Table shows the validation of sets of numbers that come under real numbers.
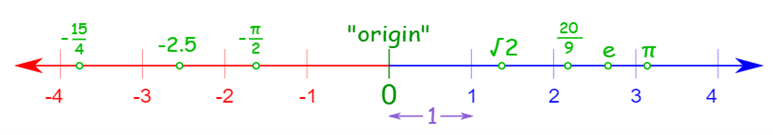
Real Numbers on a Number Line
A number line helps us to display numbers by representing them by a unique point on the line. Every point on the number line shows a unique real number.
Then what are not real numbers, we have complex numbers with the symbol C in the form of 2i, √−1, and infinity(∞).



Leave a Reply