From what I read in this chapter he explained the means of egress which is going out or leaving a place, as well as stair design which includes the different types of stairs and the reasons behind handrails, treads, risers, their dimensions and etc. Every building has an occupant load and that is the number of people that may occupy a building or portion. This plays a role when it comes to building stairs because these passageways should be as direct as possible and obtain safe egress. Exits are also very important because an exit must provide an enclosed and protected means of evacuation for the occupants of a building in the event of fire. In the section where he speaks about stair design he explains that the dimensions of risers and treads in a stairway should be proportioned to accommodate our body movement, also the occupant load which is based on the use group and the floor area served, determines the required width of an exit stairway. As you can see in this chapter the reasoning behind the way stairs, exits, and the specific dimensions chosen are made because of building codes which accommodate us while either leaving the building going in or going from different floors.
Page 13 of 13
Egress is the ability to leave a building to go to a large area or place in case of emergencies. Egress is defined in three different parts; exit access, exits, and exit discharge. Ching divided all of these into separate parts, giving them each their own definition. An exit access is the passageway leading to the exit, an exit is a corridor that leads to the outside of the building, and an exit discharge is the safe place that is at the end of the exit.
There was also a section on stairs in the chapter, where stairs are made up of treads and risers, which act as the “slope” of each step. The design of each staircase depends on the building code, a set of rules that the building places for constructed objects, whether it could be only a certain size, or a certain material. Stairways also have different designs, such as a spiral staircase, a half and a quarter stairwell, a straight run stairwell, winding stairwell, and a circular stairwell
Francis Ching, the author of “Building Construction Illustrated” talks about means of egress in one of his chapters. According to him, and online sources, means of egress is an unobstructed path which allows individuals occupying the building to exit safely. The three components a means of egress (or a way to exit) need to have are: Exit access, Exit, and Exit discharge. The width of any exit depends on the number of people occupying a portion of the building (square feet per occupant). Ching stresses that any exit must be unobstructed, lit by emergency lighting, and as direct as possible for occupants to reach and exit court at ground level.
In chapter nine, Ching focuses on the components, rules, and requirements of stairs. Generally, stairs consist of risers and treads. To generate stairs you need to have the formula for it. First, take the height of floor finish to floor finish and divide it by the preferred riser height. The rounded off quotient is a whole number of risers. Then divide the total rise by the quotient and the answer would be the riser height. There is always a minimum of three rises per flight to prevent tripping.
Moreover, the width of the stairs depends on the number of people occupying the floor area. Typically, the minimum width is 44 inches or 36 inches for 49 people or less.
Building code requires that the handrails must be on both sides on the stairs unless allowed otherwise, and should not be interrupted by a newel post. Most handrails should be 34 inches to 38 inches high and should extend 12 inches parallel to the landing.
Ching goes on to discuss the different types of stairs and their requirements. The straight-run stairs, which lead to one level to another without any winders. Quarter turn stair is an ‘L’ shaped. Half turn stair creates a semi circle at an angle of 180 degrees at intervening landings. Winding stairs are often restricted because of their small foot landing. Circular stair are usually helpful if the inner radius is twice the width of the stairs. And finally, spiral stairs are not recommended but they occupy the least amount of space.
Everyone,
I have added 2 new pages to the Course Coordination Site on the black menu bar:
Please review them before doing Reading #1 and apply strategies are you read and take notes.
Best,
Prof. Montgomery
AS I type the word count at the bottom
Welcome to Building Tech I. In this course we will be using this site as an active learning space. Please be sure to become a member of the course by following this link to the course profile page and clicking the membership button under the icon.
Everyone,
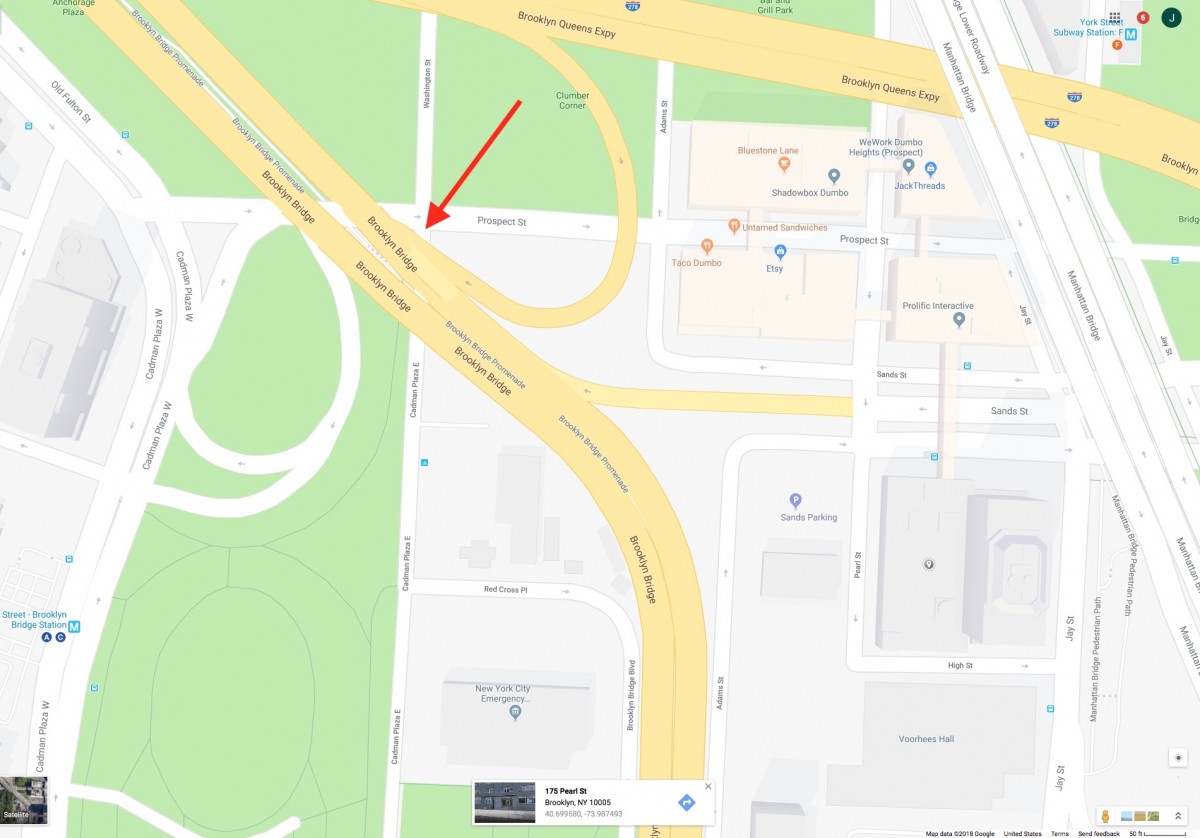
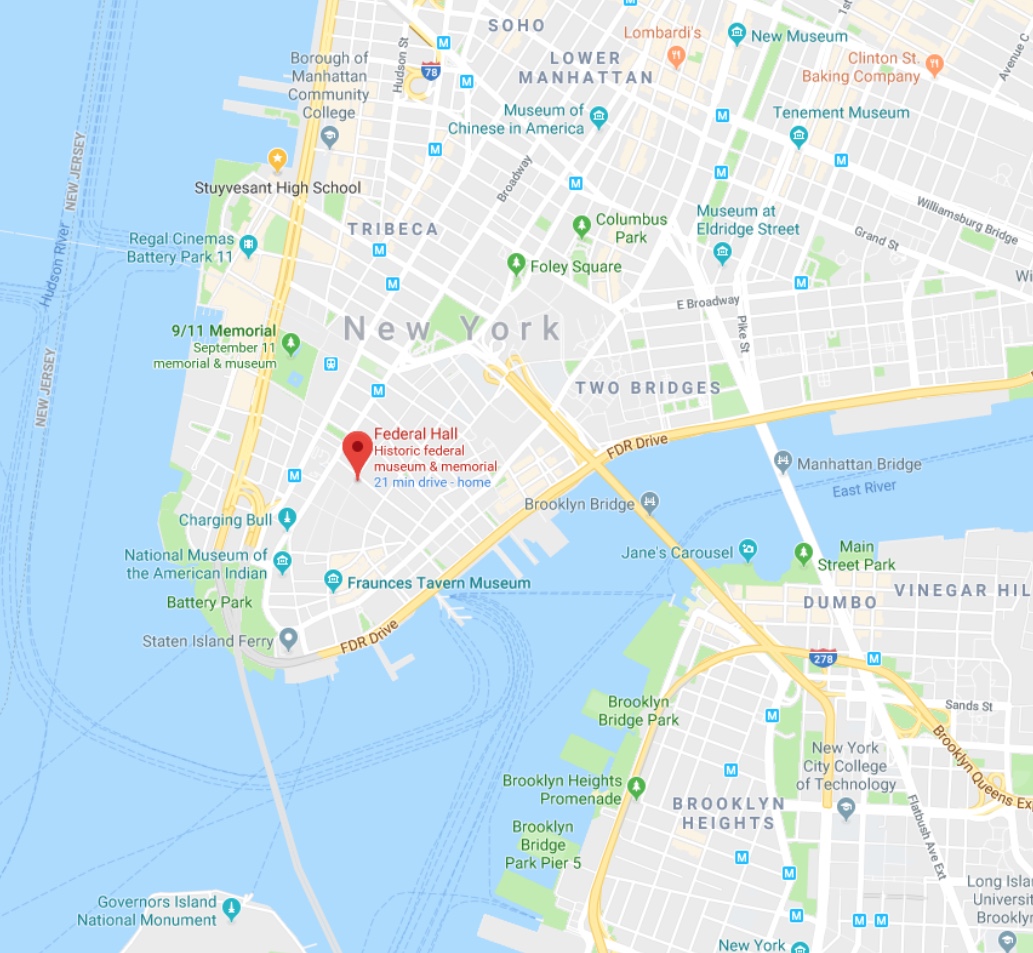
We will be meeting at Federal Hall on Friday February 22 during class time. The address is 26 Wall Street, New York, NY 10005. I will be leaving from Voorhees Hall at 3:00pm. If you want to travel with me, meet me in the lobby of Voorhees by 3:00pm. Please bring a camera and your sketchbook/notebook.
If you want to meet at the site you can use this link to Google Maps: