Distance
Astronauts prefer leaving planet Earth on the day of opposition so their commute can be the shortest. The time it takes to get to mars has decreased over centuries, In-space propulsion is a key technology hurdle to shorter a trip to Mars.
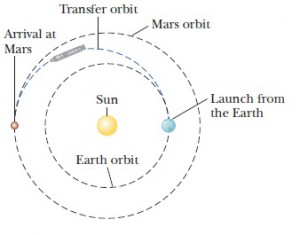
One of the greatest design barriers engineers are facing is dealing with the amount of fuel that will be needed to send a spacecraft on such a round trip distance. More fuel means more weight, and more weight means the need for more fuel to transport that weight. NASA engineers use a method called “Hohnmann Transfer Orbit” – in another words Energy Transfer Orbit, to send a spacecraft from Earth to Mars with the least amount of fuel possible.
In this technique, instead of pointing your rocket directly at Mars, you boost the orbit of your spacecraft so that it’s following a large orbit around the Sun than the Earth. Eventually that orbit will intersect the orbit of Mars – at the exact moment that Mars is there too.
If you need to launch with less fuel, you just take longer to raise your orbit, and increase the journey to Mars.
Radiation
Astronauts must be protected from two sources of radiation sun and cosmic rays. Sun regularly releases a steady stream of solar particles, giant explosions. All these energetic particles are protons. The second source of radiation is cosmic rays, often knows as GCRs. Particles accelerated to the speed of light that are shoot into our solar system from other starts in the Milky Way or other galaxies. Cosmic rays are mostly protons like sun radiation. Some of them are heavier elements ranging from helium op to the heavies elements. They can knock apart atoms in the material they strike, like astronauts, spacecraft, habitat or vehicle causing sub-atomic particles to shower into the structure. It may reach a dangerous level.
There are two things that can be done to shield against radiation. One, you can carry a physical countermeasure like shielding. Originally aluminum was picked because it was light weighted, and is about 25 percent effective at blocking heavy ion radiation particles. Advances are trying to come up with different types of material that is about 33 percent effective. The second action is pharmacological. People are looking into a class of compounds called antioxidants, can soak up certain harmful molecules caused by radiation.