- Wet wall: a wall located in bathrooms, that encloses a water supply or drain lines.

2. Curtain wall: A thin wall usually located on the facade of a building made of ‘light’ materials such as aluminum, in-fills of glass, metal panels ot thin stone. It does not support the roof of the building.

3. Expansion joints: Mid-structure separation designed to relieve stress on building materials. Expansion joint systems are used to bridge the gap and restore the building’s assembly functions while accommodating expected movements.

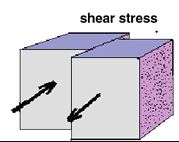
4. Shear stress: If an applied load consists of two equal and opposite parallel forces which do not share the same line of action, then there will be a tendency for one part of the body to slide over, or shear from the other part.
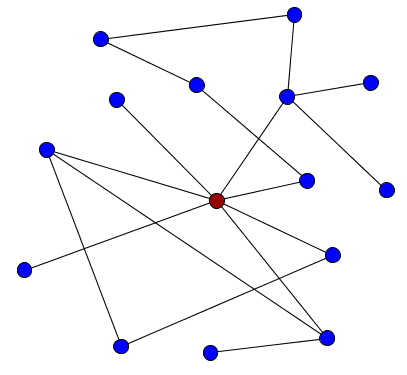
5. Node: A point at which lines or pathways intersect or branch; a central or connecting point.
6. Grandfathered: Something that was once permitted building codes can continue to be, although the code or law has changed.
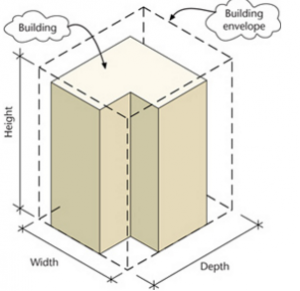
7. Building envelope : The maximum three-dimensional space on a zoning lot within which a structure can be built, as permitted by applicable height, setback and yard controls.
8. Easement: A curve formed at the juncture of two members; forms a smooth transition between surfaces that would otherwise intersect at an angle.
9. Caulked Joints: Joint used for cast iron.

10: Shim: A thin piece of material used to fill between things for a fit adjstment.
11. Galvanic action: is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially to another.
12. Threaded rod: Used in plumbing to stabilize materials; wood, concrete, metal.

13. Pile cap: is a thick concrete mat that rests on concrete or timber pile that have been driven into soft or unstable ground to provide a suitable stable foundation.
14: Still plate: in construction and architecture is the bottom horizontal member of a wall or building to which vertical members are attached.

15. Weephole: is a small opening that allows water to drain from within an assembly.

16. Gasket: Bracing between windows.
17. Metal lath: type of backing material for plaster including a metal wire mesh.

18. Trombe wall: a passive solar building design where a wall is built on the winter sun side of a building with a glass external layer and a high heat capacity internal layer separated by a layer of air.

19. Specific Heat: the heat required to raise the temperature of the unit mass of a given substance by a given amount (usually one degree).
20: Cap Flashing: (roofing) usually composed of metal, used to cover or shield the upper edges of the membrane base flashing.

21. Backer rod: is a round, flexible, closed cell polyethylene foam with an exterior “skin” used as a backing and thickness control device cold-applied sealants.

22.