What is Diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes mellitus is a systemic disease characterized by increased blood glucose levels from defects of insulin production.
Objective
Over 30 million Americans have diabetes in the U.S, 7.2 million of those people live undiagnosed.
Diabetes mellitus is something that can be easily screened in a dental office.

Causes of Periodontal disease in patients with Diabetes
- Patients with diabetes have higher number of periodontal bacteria
- Increased glucose levels in cervical fluid promotes growth of microbes
- Poor vascularity
- Blood glucose levels above 6.5%

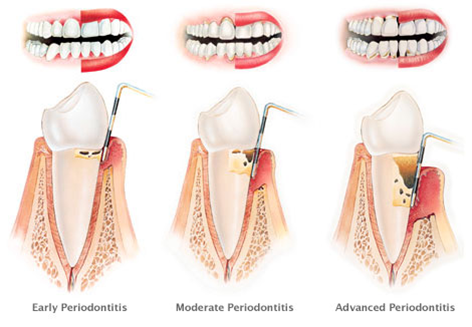
Symptoms of Periodontal disease in patients with Diabetes
- Oral bleeding when brushing or eating
- Persistent bad breath
- Cortical bone loss
- Receding gums
- Slower wound healing
Treatment

- Closely monitor your blood glucose levels within an A1C test of less than 6.5%
- Be proactive on regular 6 month dental check ups, and cleanings
- Brush your teeth twice a day, and use interdental aids such as floss
- Use anti-plaque rinses to prevent plaque build up
- Drink fluoridated water to prevent tooth decay
Conclusion
There is a strong relationship between diabetes and periodontal disease. Oral hygiene services provided by dental hygienist results in reduction of periodontal disease symptoms. The Initial Screening Questionnaire helps to identify patients at moderate and high risk for diabetes and perform (or refer for) diabetes diagnostic A1C testing.
Role of Dental Hygienist
- To evaluate the patient during assessment
- To educate the patient on what diabetes is and how it affects their periodontal health
- To teach proper home care methods to patients who have diabetes and periodontists
- To schedule regular check ups more often
Other research projects:





