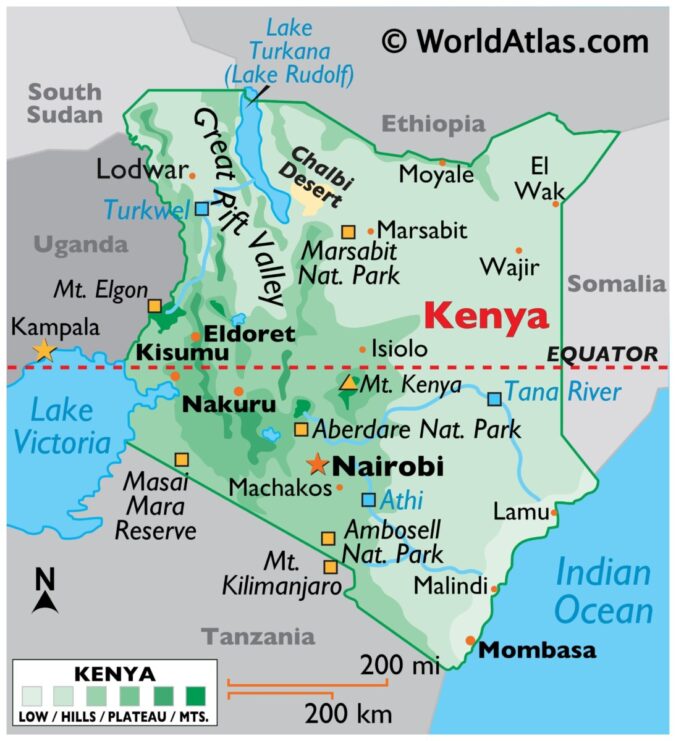
Kenya is among the nineteen countries located in East Africa and it is made up of forty-seven counties. Its longitude and latitude measurements are 0.0236° S, 37.9062° E, and its neighboring countries are Somalia, Uganda, and Ethiopia (Wandibba, 2005).
The Indian Ocean is east of the Kenya coastline, and Lake Victoria is southwest.
Kenya’s major rivers include the Nile, a river that runs through eleven countries, the Tana, the largest and longest river in Kenya; the Ewaso Ng’iro; and the Dawa Mara (Sobania, 2003).
Amongst Kenya’s vast plains and towering mountains is the world’s largest alkaline desert lake, lake Turkana, and the second-highest mountain in Africa, Mount Kenya (Yu, 2019). Mount Kenya is an extinct volcano that last erupted 2.6 million years ago. Kenya’s low plains consist of central highlands that are bisected by the Great Rift Valley. The Great Rift Valley is geologically active, with hot springs, geysers, and frequent earthquakes (National Geographic Society, 2023).
With Lake Victoria being the most productive surface water resource in Kenya, other than the precipitation runoff from the five water towers, most of Kenya’s fertile plateau is in the western part of the country (Wandibba, 2005).
Page Author: Ritchy Isaac