Kenya is a coastal zone, and their livelihood depends on the country’s natural resources to support life and meet the needs of its people. The Kenya Lake System presents an exceptional range of geological and biological natural properties of outstanding beauty (Centre, 2023). According to an article titled A Drowning World: Kenyas Quiet Slide Underwater (2022), The Indian Ocean surrounds the region of Eastern Africa, but Kenya’s lakes are essential to the country’s people, economy, and wildlife wrestling in About 1 million people living near Kenya’s freshwater lakes. Among its land, Kenya is rich in mineral resources, including gold, iron ore, talc, soda ash, and gems, including Amethyst, Aquamarine, lolite, ruby, and sapphire. Kenya’s most valuable resource is soda ash, Kenya’s leading mineral export (AZoMining, 2019).
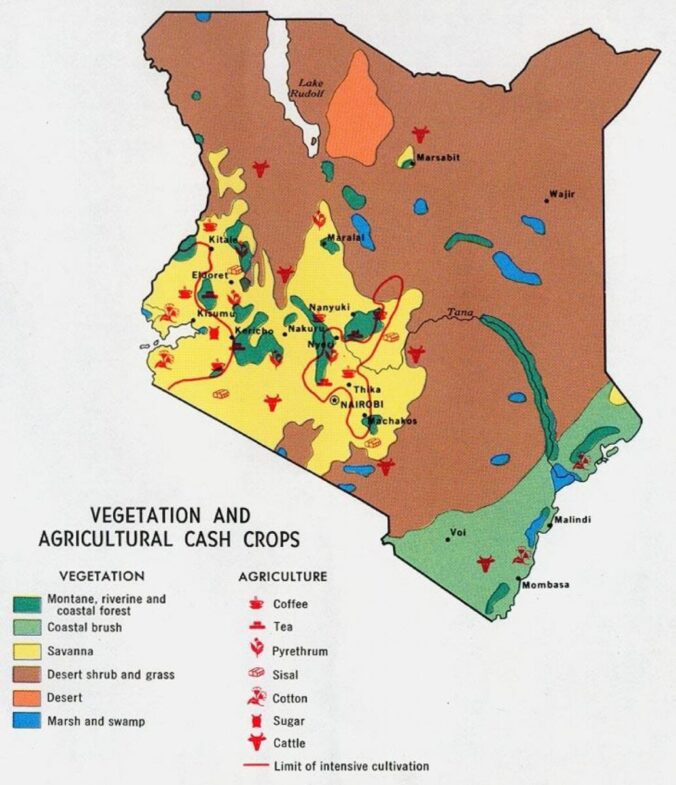
Along with Kenya being known for the outstanding beauty of their landscapes, the country in East Africa is also known for its delectable cuisines. Kenya is home to some of the most popular dishes in the world, like Ugali, which is made from maize flour that turns into a doughy texture. However, if one is looking for something a bit more traditional, Kenya’s specialty meats like Nyama Choma, which translates to Roasted Meat, Goat, and Beef, is a popular dish, and you can also find chicken, fish, and deep-fried snacks like Bhajias (Simborio, 2023). According to Horticulture Kenya (2022), Kenyan Cuisine must include spices and herbs such as Pepper, Parsley, Paprika, Marjoram, Capsicum (chilies and cayenne pepper), Oregano, Pimento, Thyme, Coriander, Bay leaves, Cinnamon, Rosemary, Ginger, Basil, Nutmeg, Mint, Caraway, Savoury, Turmeric, Dill, Cumin, Tarragon, Cloves, Sage, Mace, Cardamom, Anise, Fenugreek, Saffron, Vanilla, Fennel seeds, and Juniper berries. The soils used in agriculture are ferralsols, vertisols, acrisols, lixiosols, luvisols, and nitisols (Infonet-biovision, 2023). Healthy soil is the foundation of productive, sustainable agriculture.
The four factors of production include Kenya’s land which comprises water, Lake Baringo and Lake Naivasha, and salt lakes, including Lake Baringo, Lake Borgio, Lake Nakuru, and Lake Magadi, which are essential to help sustain marine and bird life. Kenya’s lakes and rivers are home to several fish species, which include Large-Toothed Lake Turkana Robber, The Ewaso Nyiro Barb, The Boji Plains Nothobrach, Elongate Nothobranch, and the Dwarf Lake Turkana Robber (Sawe, 2017). However, According to an article titled The Status of Kenya Fisheries (2021), one will say that Lake Victoria contributes to about 80% of the fish production in Kenya, and only 6% of the lake is in Kenya. For their labor, Fisheries production earns between Ksh35,162 and Ksh110,560 monthly (Mywage, 2023). Kenya’s land includes rainforests, Savanna, and semi-arid and arid ecosystems, and their terrain is mainly made up of low plains that rise into central highlands by the Great Rift Valley; most Kenyans live in the highlands (Nationalgeographic, 2023). Considering labor, many profitable crops can be grown in Kenya, varying on factors such as local climate, soil conditions, and market demand; typically, a Farmer working in Kenya can range from the lowest average salary of 277,400 KES to the highest average salary of 885,000 KES and labor is typically dived among the people in the family of all different ages (Worldsalaries, 2023). Building up communities has become one of Kenya’s primary methods of alleviating poverty.
One may say that one of Kenya’s greatest struggles is poverty; the wealthiest people are Kikuyu, the best-represented ethnic group with the highest status, and their job reflects that status with government, business, and education positions—followed by the Luo, who find jobs such as fishermen and boat loaders (Everyculture, 2023). Typically minimum wage varies by job; since 2015, there has been a 12% wage increase. Skilled workers get paid around USD 170/month, while others may receive USD 107/month (Lloydsbanktrade, 2023). Kenya’s capital is based on its monetary unit, Shilling. Kenya has a lower middle-income status, yet it is the most powerful economy in Africa, with many commercial, merchants, and foreign banks (Worldbank, 2023). One may say that Kenya is the leader in digital technology in Africa, witnessing significant growth in Entrepreneurship due to new technology. Kenyans have depended on agriculture for economic growth; however, increased literacy and human labor created more opportunities, resulting in early entrepreneurs working in roles such as pottery, carpentry, and wool making (Mutuku, 2022). These natural resources are essential for the economic life of the people in Kenya.
Page Author: Jailine Collado