Thailand is located in the heart of Southeast Asia (Kids National Geographic, 2021). Cambodia and Laos border the country to the east and northeast, respectively, meanwhile Myanmar borders the country to the northwest. The Andaman Sea and the Gulf of Thailand are to the west, and Burma is to the southeast. The hilly and forested southern area, which connects with Malaysia, is long and narrow. Northern Thailand has the highest mountains.
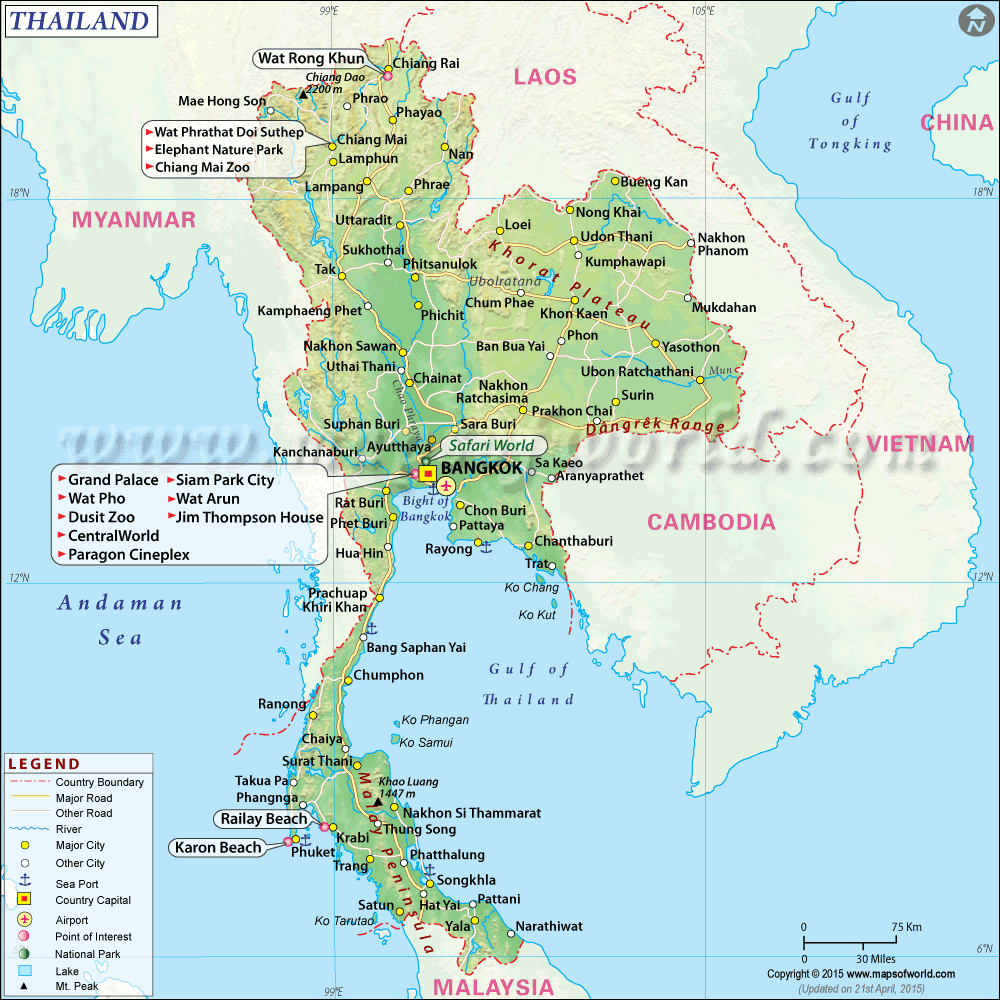
Thailand’s country shape is irregular and that has loosely been compared to the shape of an elephant’s head, with the northern part of the country the animal’s face and ears and the thinner southern part in the Malay Peninsula its trunk (Nam, 2018). Thailand has a total land area of 512,000 square kilometers (198,000 square miles) divided into four geographical regions. The central area, which includes the country’s capital, is located in the southern part of the Chao Phraya River’s river basin. The northernmost area is mountainous and forested, with four main rivers flowing north to south. The northeast area is largely flat plateau lands, and the Malay Peninsula, with coastline on both sides and hundreds of small islands flanking the landmass, is in the south.



