Site Grading Techniques
Analyze existing conditions of the site:
· general flow of water
· existing flow lines for surface runoff
· existing structures, trees, etc. to be saved
Set preliminary elevations of structures:
· analyze existing elevations of structures
· check elevations with adjacent elements
· check relationships between buildings, walks, parking lots, etc.
Modify appropriate contours:
· begin from known points and calculate slope to next contour
· work each contour line completely to be sure to meet to existing
· calculate required slopes and modify all other contours as necessary
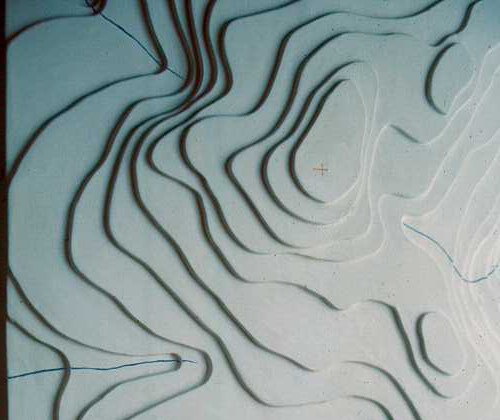
Grading Tips
· Water always flows perpendicular to contours.
· Closely spaced contours = steep slopes / widely spaced contours = a gentle slope.
· A contour which closes on plan indicates a peak or a depression.
· Contours should never cross each other
· Always slope ground away from structures.
· Grading must not extend beyond property lines.
· Start grading slopes at the top of a fill slope and the bottom of a cut slope.
· Contours at curbs point downhill.