Table of Contents
Fundamentals of Heat Transfer: Types and Mechanism
Heat transfer is a process by which energy is transported in the form of heat between two places with a gradient in temperature. The heat transfer process is an intricate part of a thermodynamic system which deals with several mechanisms of energy transportation. Heat is transferred between the states with thermal gradients through one of three modes, which are as follows-
- Conductive Heat Transfer
- Convective Heat Transfer
- Radiative Heat Transfer
Heat Transfer Through Conduction
Conductive heat transfer is a mechanism of heat transfer in the solid medium followed by a temperature gradient. In principle, this mechanism is activated by the energy transport through the elastic atomic or molecular vibrations. Quantitatively, the heat transfer rate Qk is proportional to the temperature gradient dT/dx times the projected area A through which heat is transferred
Or
The proportionality constant is K is the slope of Qk over which depends on the type of solid medium.
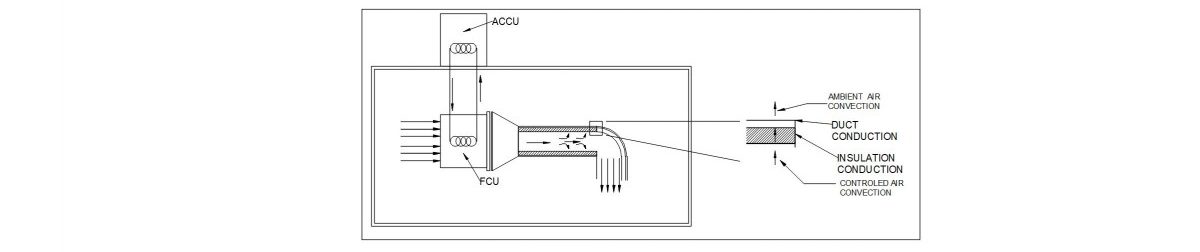
Lets assume heat is being transferred through a glass window of thickness L, from a indoor state T1 to outdoor state T2, as shown in Fig.1.
Fig 1. Heat Transfer conduction through a solid medium
Heat transfer rate at this particular case can be determined using Equation (1) as follows-
Where, dT=(T2-T1) and dx=L. Notice that dT is negative as heat is flowing opposite to the temperature gradient or along the negative slope of temperature profile.
In SI system, the unit of Qk is Watt and in the US customary system Qk is BTU/hr.
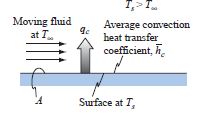
Heat Transfer Through Convection
Convection Heat transfer
Where,
Heat Transfer Through Radiation
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity is a property that determines the ability of a material to conduct or transfer heat from one place to other. The higher the thermal conductivity, higher is the ability to conduct heat.
Referring to Fig. 1, thermal conductivity of the window glass can be determined as follows-
In SI system, the unit of Qk is W/m. K and in the US customary system Qk is BTU/hr.ft.F.