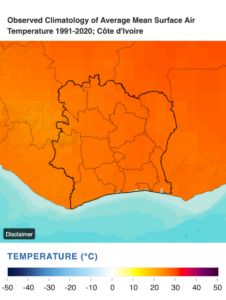
Ivory Coast’s (Côte d’Ivoire) climate is primarily tropical, while regional differences exist. There are two wet and two dry seasons in the humid equatorial climate in the southern portion of the nation. In the south, This climate zone is characterized by high rainfall and temperatures of about 30°C, in a very humid atmosphere (Discover-Ivorycoast, 2021). The southern region of Cote d’Ivoire generally experiences four seasons (World Bank Group, 2024). A shorter rainy season takes place from October to November, while the main one lasts from May to July. All year long, the Average temperatures are between 25°C and 30°C (77–86°F) and range from 10°C to 40°C (50–104°F) (Blue Green Atlas, 2024). The south’s lush soil and steady rainfall make it the perfect place to cultivate products that are important to the nation’s economy, such oil palm, coffee, and cocoa.
On the other hand, the north is characterized by a dry savannah with a single rainfall session and a long dry spell (Zonkouan et al., 2022). This climatic variation is beneficial for the country’s production in sectors such as agriculture and the nature of crops including cotton, cocoa, and coffee (Asseh et al., 2021). Liberia’s northern tracts have favorable climatic conditions for growing cotton, which is an essential input to the textile industry (Sagna et al., 2021). Nevertheless, due to the effects of global climate change, the climate has become unpredictable, which might be dangerous to agriculture, which is necessary for companies depending on a stable raw material supply.