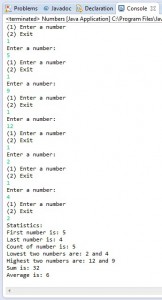
Lab Description:
This program will start with a simple menu of two choices, either to enter a number, or to exit to see the statistics of the entered numbers.
The statistics will have to cover these key points of the entered numbers:
- First number entered
- Last number entered
- Count of number entered
- Lowest two numbers
- Highest two numbers
- Total Sum
- Average
Code:
package Lab1;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Numbers {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int fNumber = 0;
int lNumber = 0;
int min1 = 0;
int min2 = 0;
int high1 = 0;
int high2 = 0;
int count = 0;
int choice;
int number;
int sum = 0;
int average;
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
do{
System.out.println("(1) Enter a number");
System.out.println("(2) Exit");
choice = input.nextInt();
if(choice == 1){
System.out.println("Enter a number:");
number = input.nextInt();
if(count == 0){
fNumber = number;
high1 = number;
high2 = number;
min1 = number;
min2 = number;
}
else if(count == 1){
if(number < high1)
high2 = number;
if(number > min1)
min2 = number;
}
if(number > high1){
high2 = high1;
high1 = number;
}
else if(number > high2)
high2 = number;
if(number < min1){
min2 = min1;
min1 = number;
}
else if(number < min2)
min2 = number;
sum = number + sum;
lNumber = number;
++count;
}
else if(choice == 2)
choice = 'x';
else
System.out.println("Invalid entry.");
}while(choice != 'x');
average = sum / count;
System.out.println("Statistics:");
System.out.printf("First number is: %d\n", fNumber);
System.out.printf("Last number is: %d\n", lNumber);
System.out.printf("Count of number is: %d\n", count);
System.out.printf("Lowest two numbers are: %d and %d\n", min1, min2);
System.out.printf("Highest two numbers are: %d and %d\n", high1, high2);
System.out.printf("Sum is: %d\n", sum);
System.out.printf("Average is: %d\n", average);
}
}