Lab 3 Inheritance
Lab 3
Lab 3 procedures:
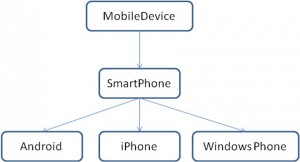
- Create a class called MobileDevice with a private field deviceType that will be initialized to the string “Mobile Device” in the constructor. Include the corresponding setter and getter methods.
- Create another class SmartPhone that will inherit MobileDevice, with a private field deviceType initialized to the string “Smart Phone” in the constructor, and override the getter method by returning the string: “Mobile Device -> Smart Phone”. (Hint: To obtain this result make a call to the super class getter method).
- Create three more classes: Android, iPhone, and WindowsPhone that will inherit SmartPhone, have a private field deviceType initialized to the string “Android”, “iPhone”, or “Windows Phones” correspondingly in the constructor, and override the getter method returning the corresponding string “Mobile Device -> Smart Phone -> iPhone” for iPhone,“Mobile Device -> Smart Phone -> Android” for Android”, or “Mobile Device -> Smart Phone -> Windows Phone” for Windows Phone.
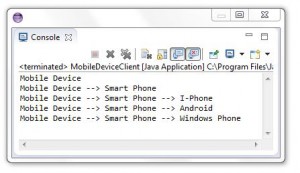
Once you create the classes, run the client code and report your output.
Hierarchy
Overview:
In this lab we where issue a client code, in which we had to create classes to display the corresponding output.
Code:
Mobile device
package Lab3;
public class MobileDevice
{
public String deviceType = "Mobile Device";
public void setDeviceType()
{
return;
}
public String getDeviceType()
{
return deviceType;
}
}
Smart Phone
package Lab3;
public class smartPhone extends MobileDevice {
private String deviceType = "Smart Phone";
public String getDeviceType()
{
deviceType = super.getDeviceType() + " --> " + deviceType;
return deviceType;
}
}
Android
package Lab3;
public class Android extends smartPhone
{
private String deviceType;
public Android()
{
deviceType = "Android";
setDeviceType();
}
public String getDeviceType()
{
deviceType = super.getDeviceType() + " --> " + deviceType;
return deviceType;
}
}
I-Phone
package Lab3;
public class Iphone extends smartPhone
{
private String deviceType;
public Iphone()
{
deviceType = "I-Phone";
setDeviceType();
}
public String getDeviceType()
{
deviceType = super.getDeviceType() + " --> " + deviceType;
return deviceType;
}
}
Windows Phone
package Lab3;
public class WindowsPhone extends smartPhone
{
private String deviceType;
public WindowsPhone()
{
deviceType = "Windows Phone";
setDeviceType();
}
public String getDeviceType()
{
deviceType = super.getDeviceType() + " --> " + deviceType;
return deviceType;
}
}
Client Code
package Lab3;
public class MobileDeviceClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MobileDevice myMobileDevice = new MobileDevice();
smartPhone mySmartPhone = new smartPhone();
Iphone myiPhone = new Iphone();
Android myAndroid = new Android();
WindowsPhone myWindowsPhone = new WindowsPhone();
System.out.println(myMobileDevice.getDeviceType());
System.out.println(mySmartPhone.getDeviceType());
System.out.println(myiPhone.getDeviceType());
System.out.println(myAndroid.getDeviceType());
System.out.println(myWindowsPhone.getDeviceType());
}
}
Screenshots:



Leave a Reply