Objective:
- Create a new page in your portfolio and name it “Lab 4” with “EMT 2390L” as its parent.
- For each of the following commands write a description of what it does and provide a screenshot with an example of its usage:
- chmod
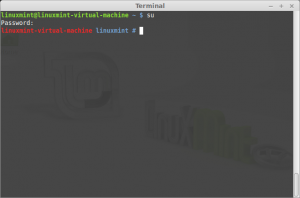
- su
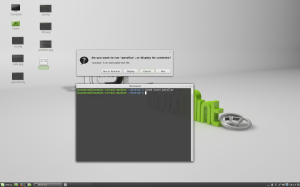
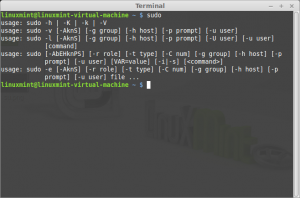
- sudo
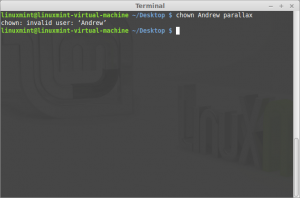
- chown
- passwd
- ps
- kill
- printenv
Command: chmod
Description: Change access permissions, change mode.
If no options are specified, chmod modifies the permissions of the file specified by filename to the permissions specified by permissions.
Permissions defines the permissions for the owner of the file (the “user”), members of the group who owns the file (the “group”), and anyone else (“others”). There are two ways to represent these permissions: with symbols (alphanumeric character), or with octal numbers (the digits 0 through 7).
Let’s say you are the owner of a file named parallax, and you want to set its permissions so that:
- It would read, write, and execute it. Enter: chmod u=rwx NameOfFile (Note: You can also use chmod777 to read, write and execute.)
- It would read and execute it. Enter: chmod g=rx NameOfFile
- It would read it only. Enter: chmod o=r NameOfFile
Command: su
Description: Super / Substitute user identity
Run a command with substitute user and group id, allow one user to temporarily become another user. It runs a command (often an interactive shell) with the real and effective user id, group id, and supplemental groups of a given user.
Command: sudo
Description: Execute a command as another user
Sudo allows a permitted user to execute a command as the superuser or another user, as specified in the sudoers file.
Sudo allows a permitted user to execute a command as another user, according to specifications in the /etc/sudoers file. The real and effective uid and gid of the issuing user are then set to match those of the target user account as specified in the passwdfile.
Command: chown
Description: Change file owner and group
chown changes the user and/or group ownership of each given file. If only an owner (a user name or numeric user ID) is given, that user is made the owner of each given file, and the files’ group is not changed. If the owner is followed by a colon and a group name (or numeric group ID), with no spaces between them, the group ownership of the files is changed as well. If a colon but no group name follows the user name, that user is made the owner of the files and the group of the files is changed to that user’s login group. If the colon and group are given, but the owner is omitted, only the group of the files is changed; in this case, chown performs the same function as chirp. If only a colon is given, or if the entire operand is empty, neither the owner nor the group is changed.
Note: In the picture below you can see chown: invalid user: ‘Andrew’. This is because theres no other user on the system.
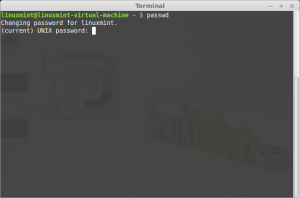
Command: passwd
Description: Modify a user password.
The passwd command changes passwords for user accounts. A normal user may only change the password for his or her own account, while the superuser may change the password for any account. passwd also changes the account or associated password validity period.
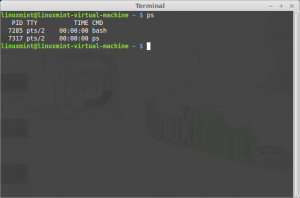
Command: ps
Description: Process status, information about processes running in memory. If you want a repetitive update of this status, use top.
On every Unix-like operating system, the process status command (ps) displays information about active processes. Every operating system’s version of ps is slightly different.
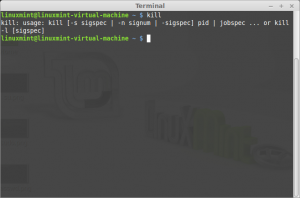
Command: kill
Description: Stop a process from running, either via a signal or forced termination.
Kill is a command used with Linux and Unix variants, as well as various network equipment to stop a process or disconnect a client.
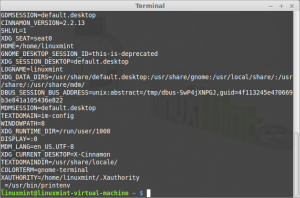
Command: printenv
Description: Print environment variables
printenv prints the values of the specified environment variable. If no variable is specified, print name and value pairs for them all.