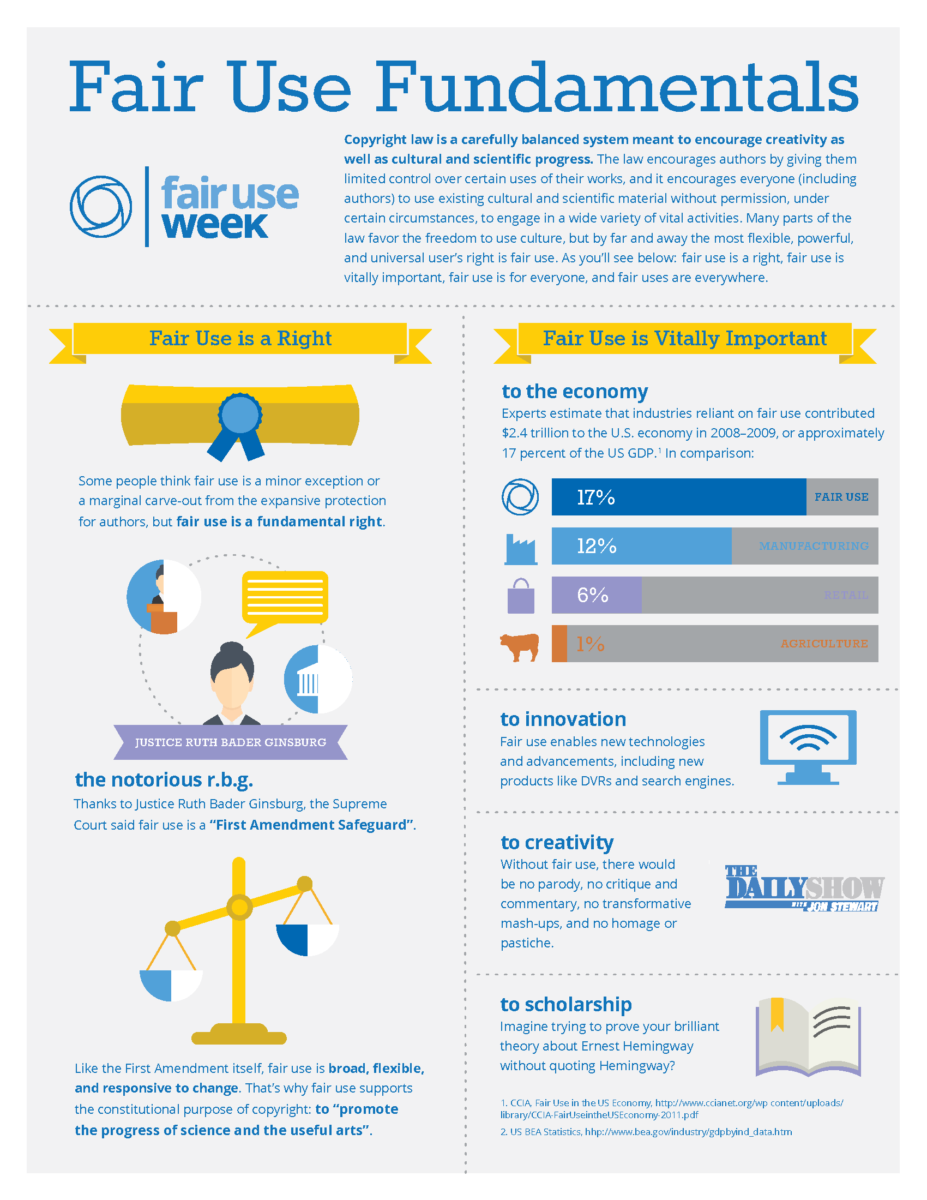
Book authors sometimes incorporate text from their dissertations or previous publications in their book manuscripts. How to handle reuse, with or without modification, is confusing and touches on copyright and authors rights: authors should always review their contract and may need to request permission to reuse their writing. The essay below is a Guest post by Walter Biggins, editor-in-chief, University of Pennsylvania Press, for H-Net’s excellent Feeding the Elephant: A Forum for Scholarly Communications.
In short: Your manuscript probably has a lot of bunches, folds, and lumps. That’s not bad, so long as the presentation is as smooth as possible, in ways that are clean and clear to you and to your press alike.
One of the most common lumps, and sometimes the most time-consuming and process-disorienting to sort out, involves previously published material. Authors often think about material that comes from outside their own work as the problematic wrinkles—i.e., permissions. Do you have permission to reproduce that Warhol painting in your book? Or that map of Mordor? Or those Notorious B.I.G. lyrics? Or that seven-page extract from The Magic Mountain? Can you use this Bob Dylan verse as an epigraph to chapter 3, because you like it and, golly, that seems like fair use to you?
All that is worth considering, and needs to be resolved before you submit a final manuscript. (Spoiler alert: get rid of the Dylan.) But, in concentrating so acutely on the problems that might be caused by others’ work, you often forget to think of your own. In this manuscript, you should ask yourself, what of my own work has appeared elsewhere, and what should I do about that material?
Usually, your own previously published material could fall into five rough categories: scholarly articles published in peer-reviewed journals; essays published in an edited collection; pieces produced for mainstream media, such as magazines, newspapers, and other periodicals; material produced for non-print formats, such as podcasts and audiobooks; and conference papers.
In all of those cases except for the last one, you probably signed an agreement with the publisher of said periodical, book, or platform that granted the press the right to use your work. So, if a version of that material is going to be used in your book, you need to request permission for this—even if the original piece has been altered significantly for publication in book form.
For scholarly monographs and edited collections, there is typically no fee for this use, though the original periodical may request that your book attributes the source of the material properly. Ask if there is a specific credit line to be used, and a specific placement—on the copyright page, for example—where the credit should appear. Many contributor agreements for journals and inclusion in edited collections will include a clause granting permission of this sort; it’s worth requesting said clause if you don’t see it in the original agreement. Furthermore, many journals will spell out the specific granted rights for contributors on their websites, so check there as well.
It’s a good idea to check with a journal before you sign a contract with it about its terms for re-use of your material, and make sure that this is possible. It’s always worth finding out whether the contract stipulates if your work can be reproduced by the journal—in, let’s say, a best-of anthology of the journal—or if the journal can sell the right to have your material reproduced elsewhere, in other languages, and in other formats.
This can become a critical issue if your manuscript’s research was funded and/or sponsored in part by a university, academic affiliation, or institutional grant. An example: Let’s say your manuscript is a revised, greatly overhauled version of your dissertation. The university deposits the defended dissertation into its institutional repository. In doing so, it is possible that the work has been embargoed, which is to say access to it has been restricted in some way, usually for a limited period of time. The University of Oklahoma’s Libraries has a pretty good rundown on the reasons behind embargoes, and why you might choose this process for early versions of your work.
The main issue is that you need to be aware of what this means, and that embargoing parts of the work may mean that it’s problematic for it to appear in your book. You should make your book editor aware of any previously published material within your manuscript, and of the potential restrictions that this may cause, well before you submit everything.
…there’s a tricky balance between creating eager anticipation for the book and over-exposing it…
This is a practical consideration with legal ramifications. Your editor also needs to know how much, and where, your book’s material has appeared for marketing reasons. Your press certainly wants knowledge of your work, and acclaim for it, to be visible prior to the book’s publication. So, access to material related to the book is often a good thing. But there’s a tricky balance between creating eager anticipation for the book and over-exposing it so that its potential buyers think they already know the book—and thus don’t need to buy it. A good editor will be candid with you about how much of the work can be previously published before the exposure adversely affects its reception. My rule of thumb is no more than 25% of it should be accessible freely elsewhere; other editors will have different opinions. The point is: You should check, and plan accordingly.
That, in fact, is the key. At every step of the process, think carefully about what you’re published from the book, in what venues, and if you’ve got permission to do so. Ironing out this wrinkle will save you a lot of time and potential publication delay, and allow your experience to go as smoothly as it can.
Walter Biggins is Editor in Chief at University of Pennsylvania Press where he acquires cultural studies, intellectual and political history of the Americas, as well as Atlantic World and postcolonial studies. Biggins is also a freelance writer and is a coauthor of Bob Mould’s Workbook (Bloomsbury, 2017).
Biggins, Walter. “Working with Your Editor: Previously Published Material in Your Manuscript.” Feeding the Elephant: A Forum for Scholarly Communications., 2 Feb. 2024, https://networks.h-net.org/group/discussions/20022637/working-your-editor-previously-published-material-your-manuscript published under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 United States License ![]()